The correct option is A) Cash book let's understand what is petty cash book: A petty cash book is a cash book maintained to record petty expenses. Petty expenses, mean small or minute expenses for which the payment is made in coins or a few notes or which are smaller denominations like tea or coffeeRead more
The correct option is A) Cash book
let’s understand what is petty cash book:
- A petty cash book is a cash book maintained to record petty expenses.
- Petty expenses, mean small or minute expenses for which the payment is made in coins or a few notes or which are smaller denominations like tea or coffee expenses, postage, bus or taxi fare, stationery expenses, etc.
- The person who maintains the petty cash book is known as the petty cashier.
- It is a simple process that helps organizations by focusing on major transactions as petty cashiers handle all small transactions.
Generally, the petty cashbook is prepared as per the Imprest system. As per the Imprest system, the petty expenses for a period (month or week) are estimated and a fixed amount is given to the petty cashier to spend for that period.
At the end of the period, the petty cashier sends the details to the chief cashier and he is reimbursed the amount spent. In this way, the debit balance of the petty cashbook always remains the same.
The petty cash book has two columns in which
- Cash received is recorded in the Left column i.e, “Receipts” or “Debit” column.
- Cash payments are recorded in the Right column i.e, “Payment” or “Credit” column.
Balance of Petty cash book
The balance of petty cash book is never closed and their balances are carried forward to the next accounting period which is considered one of the most significant qualities of an asset whereas Income doesn’t have any opening balance and their balances get closed at the end of every accounting year.
A petty cash book is placed under the head current asset in the balance sheet. The Closing Balance of the petty cash book is computed by deducting Total expenditure from the Total cash receipt (as received from the head cashier).
Format for petty cash book
Only small denominations are recorded in the petty cash book. It varies with the type, quantity, and need of a business. It involves cash and checks.
- Ordinary Petty cash book:
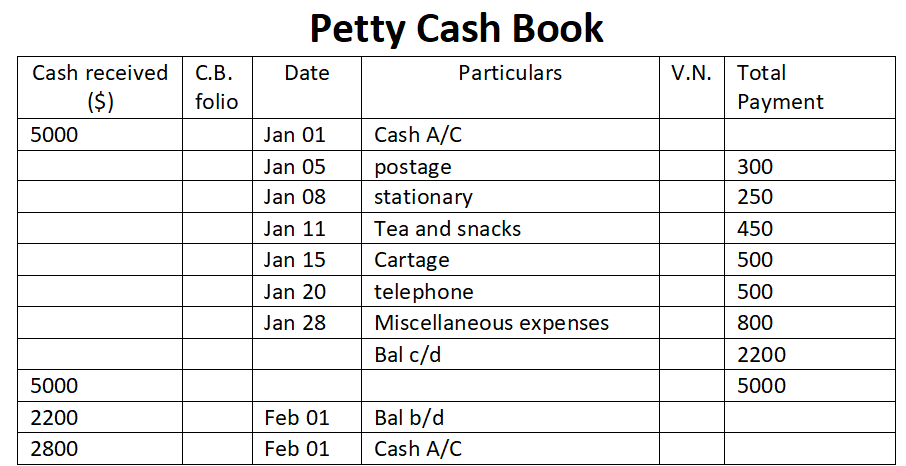
- Analytical Petty cash book:
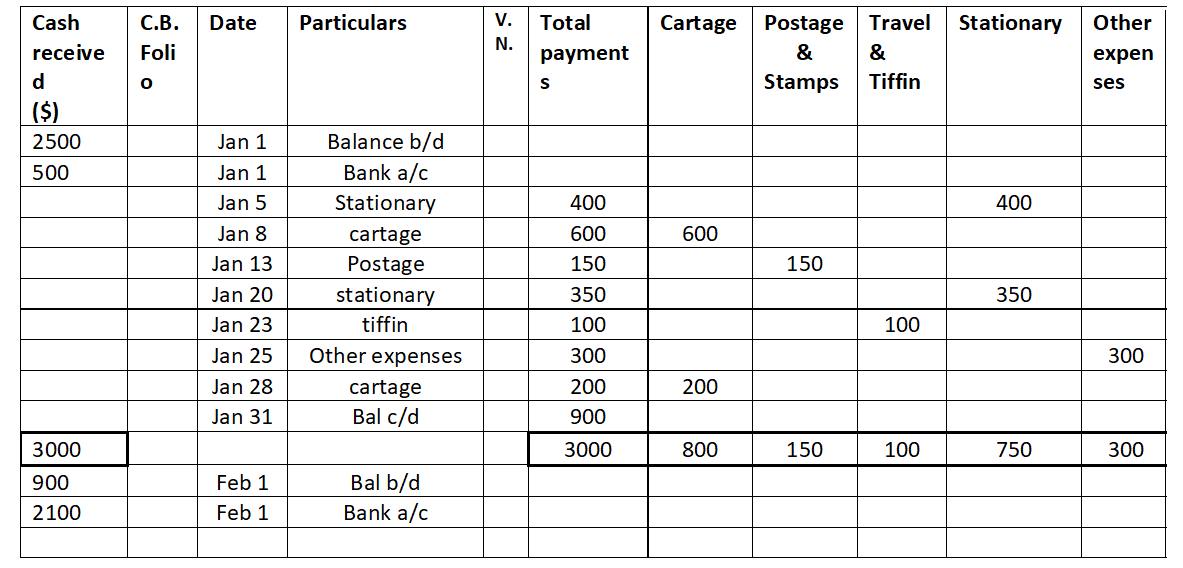
Conclusion
A simple petty cash book is a type of cash book because it records the small expenses which involve small transactions in the ordinary daily business.
A petty cash book is not as important as an income statement, balance sheet, or trail balance it doesn’t measure the accuracy of accounts so it is not treated as a statement.
No journal entries are made in the books of accounts while spending or purchasing using a petty cash book so, it is not treated as a journal.
See less

Bills Payable Book Bills payable book, also known as a B/P book is a subsidiary or secondary book of account in which transactions relating to bills of exchange are recorded. It includes the recording of bills that are payable by a business. In a business where the number of bills exchanging hands iRead more
Bills Payable Book
Bills payable book, also known as a B/P book is a subsidiary or secondary book of account in which transactions relating to bills of exchange are recorded. It includes the recording of bills that are payable by a business.
In a business where the number of bills exchanging hands is large in number, it is very useful, as it is tough to journalize all the bills drawn. A bills payable account generally has a credit balance as it is supposed to be paid at maturity and be a liability.
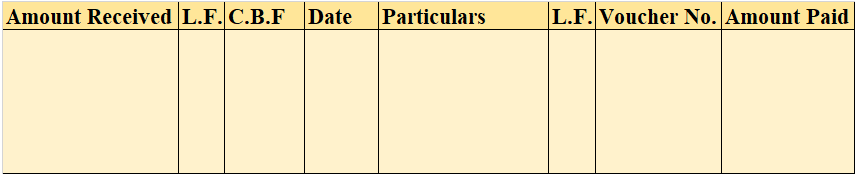
Format for B/P book
Bills Payable A/c

See less