An asset is a resource in the name of the company or controlled by the company that holds economic value and will provide it future benefits. A company invests in various kinds of assets for manufacturing purposes and investment purposes as well. Some examples of assets are: Plant and Machinery InveRead more
An asset is a resource in the name of the company or controlled by the company that holds economic value and will provide it future benefits.
A company invests in various kinds of assets for manufacturing purposes and investment purposes as well. Some examples of assets are:
- Plant and Machinery
- Investments
- Inventory
- Cash and Cash Equivalents, etc.
Assets can be broadly divided into two categories based on their physical existence:
- Tangible Assets
- Intangible Assets
Tangible Assets can be further divided into two categories based on their life and role in the operating cycle:
- Non-Current Assets
- Current Assets
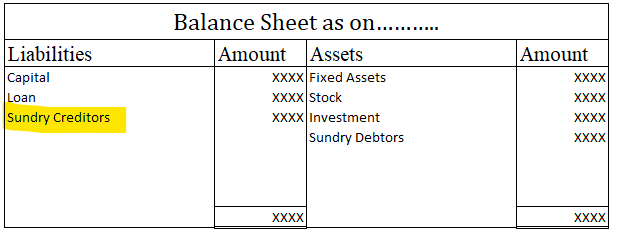
Since the company derives benefit from the asset, an asset account is debit in nature. If an asset account has a credit balance, it would fundamentally make it a liability. However, there are certain exceptions to it.
In the case of Bank Overdraft, which means a company withdraws more from the bank than it has deposited in its account, Bank Account can also be shown having a credit balance.
Contra Assets Accounts are the accounts that are contrary to the basic nature of an assets account, that is it is contrary to the debit nature of the assets account and hence are credit in nature.
Examples of Contra Assets Account are:
Accumulated Depreciation Account which is essentially Plant Assets Account also has a credit balance as it is used to depreciate the asset, or in other words, reduce the value of the assets, hence it also has a credit balance.
When there are balances in the Account Receivables Account that are not paid to the company or have a very low probability of being paid, they are recorded in a separate account called Bad Debts Account, which is also credit in nature.
See less


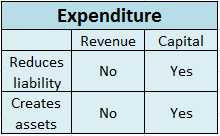
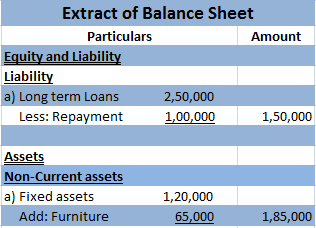
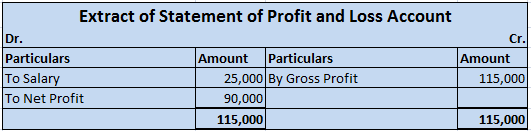
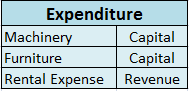
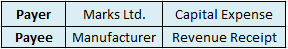
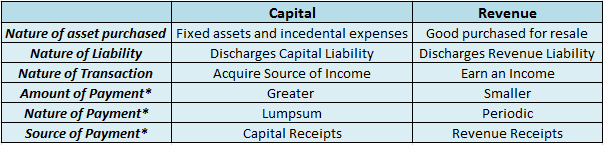
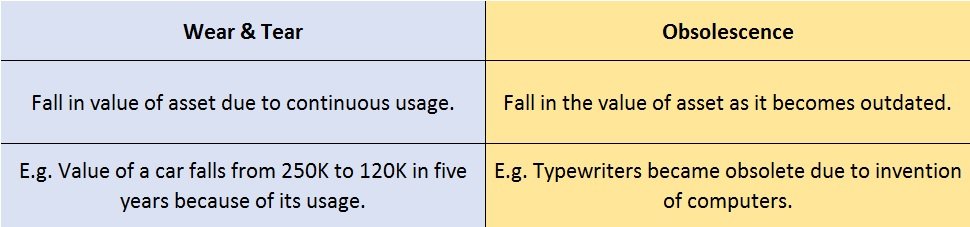
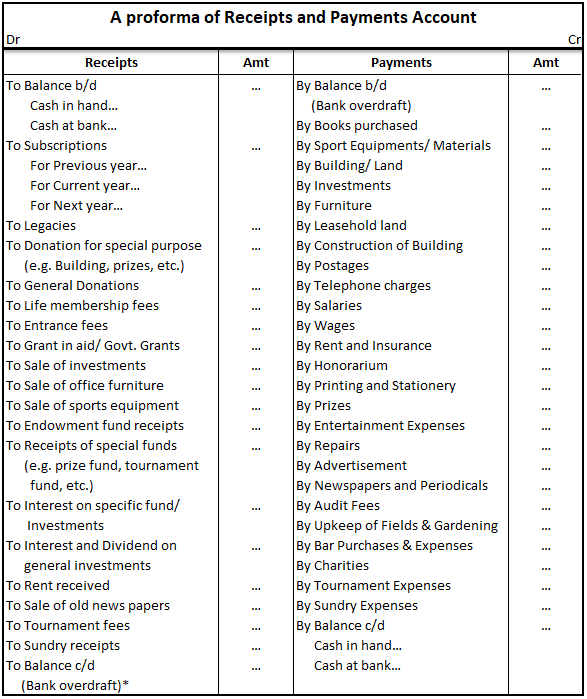
Capital maintenance is a principle that states profit should not be recorded until its cost or capital has been maintained. In other words, profit should not be recognized unless net assets have been maintained. Capital maintenance states that profit recognized is the increase in the value of net asRead more
Capital maintenance is a principle that states profit should not be recorded until its cost or capital has been maintained. In other words, profit should not be recognized unless net assets have been maintained.
Capital maintenance states that profit recognized is the increase in the value of net assets. However, there are two exceptions to it:
It is important because:
Capital maintenance is of two types:
It is measured by the value of assets at the beginning and end of the financial year.
It is measured by the production capacity at the beginning and end of the financial year.
Capital maintenance is concerned with keeping proper account balances of assets and not the physical assets.
Inflation is the increase in the economic value of goods due to the lower purchasing power and not an actual increase in the value of assets. So, if the value of an asset is increased due to inflation it does not depict the right picture for the company.
Hence, if the value of assets increases due to inflation, companies need to adjust the value of assets to assess if capital maintenance has occurred.
See less