Bad debts mean the money owed by customers who have gone bankrupt or the likelihood of who's ever returning the money is significantly low. Bad debt is a nominal account. A nominal account is an account that records the business transactions belonging to a certain category of income, expense, profitRead more
Bad debts mean the money owed by customers who have gone bankrupt or the likelihood of who’s ever returning the money is significantly low. Bad debt is a nominal account.
A nominal account is an account that records the business transactions belonging to a certain category of income, expense, profit or loss. The balances on nominal accounts are normally written off at the end of each financial year. For example, sales A/c, purchases A/c, interest income, loss from the sale of assets etc.
Why are bad debts A/c classified as a nominal account?
First of all, let us understand the other two types of accounts – personal accounts and real accounts.
Personal accounts deal with the records of the business’ transactions with a particular person or entity. For example Mukesh A/c, Mahesh A/c, Reliance A/c, Suresh and Co. A/c etc.
Real accounts deal with transactions and records related to assets. The balance in these accounts is normally carried forward from one period to another. For example “Furniture A/c “, ” Building A/c ” etc.
Now that we have understood the basic definitions of all three types of accounts, we can discuss the reason behind the classification of bad debts as nominal accounts.
A bad debt is a loss that the company has incurred. It may be due to bankruptcy of customers, customer fraud etc. The company isn’t going to receive that money. The bad debts are written off at the end of the year by transferring them to profit and loss A/c.
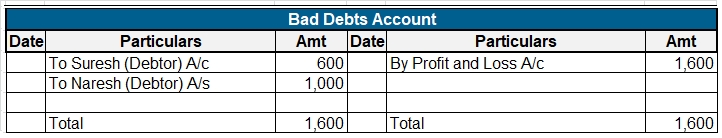
Thus, bad debts relate to loss and are normally not carried forward from one period to another. Hence, they are classified as nominal accounts.
Treatment of Bad Debts
Bad debts are written off at the end of each year by debiting them to the profit and loss A/c. The amount of bad debts is reduced from the amount of debtors that the company has.
A company may also choose to create a provision for bad debts for the balance amount of debtors that the company has after adjusting for bad debts. This provision represents a rough estimate of the amount due to debtors that the business expects to not receive. In other words, it is an estimate of customer bankruptcy that the business expects.
Conclusion
We can conclude that
- There are primarily three types of accounts – real, personal and nominal.
- Bad debts are a nominal account.
- Bad debts is a loss that the business has incurred
- It may be due to bankruptcy of customers, fraud etc
- Bad debts are written off each year by transferring them to the income statement




Ledger Folio A ledger folio, in simple words, is a page number of the ledger account where the relevant account appears. The term 'folio' refers to a book, particularly a book with large sheets of paper. In accounting, it's used to maintain ledger accounts. The use of ledger folio is generally seenRead more
Ledger Folio
A ledger folio, in simple words, is a page number of the ledger account where the relevant account appears. The term ‘folio’ refers to a book, particularly a book with large sheets of paper. In accounting, it’s used to maintain ledger accounts.
The use of ledger folio is generally seen in manual accounting, i.e the traditional book and paper accounting as it is a convenient tool used for tracking the relevant ledger account from its journal entry. Whereas, in computer-oriented accounting (or computerized accounting), it’s not really an issue to track your relevant ledger account.
Ledger folio, abbreviated as ‘L.F.’, is typically seen in journal entries. The ledger folio is written in the journal entries, after the ‘date’ and ‘particulars’ columns. It is really convenient when we’re dealing with and recording a large number of journal entries. As we will be further posting them into ledger accounts, thus, ledger folio comes in as a really useful component of journal entries.
Example
We’ll look at how the ledger folio column is used while recording journal entries.
We can find the relevant ledger accounts on the page numbers of the book as mentioned in the above entries, i.e. the cash and sales account on page – 1 whereas, the purchases and sundry creditors on page – 2 of the relevant ledger book.
See less