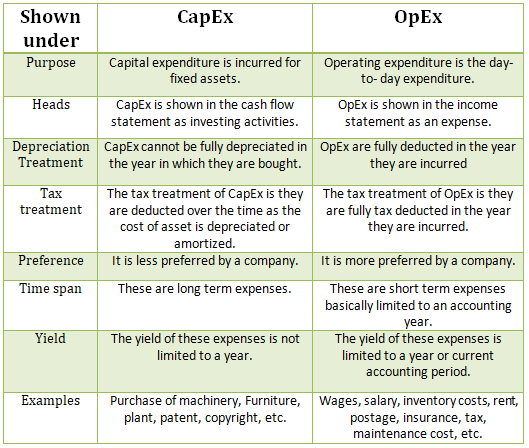
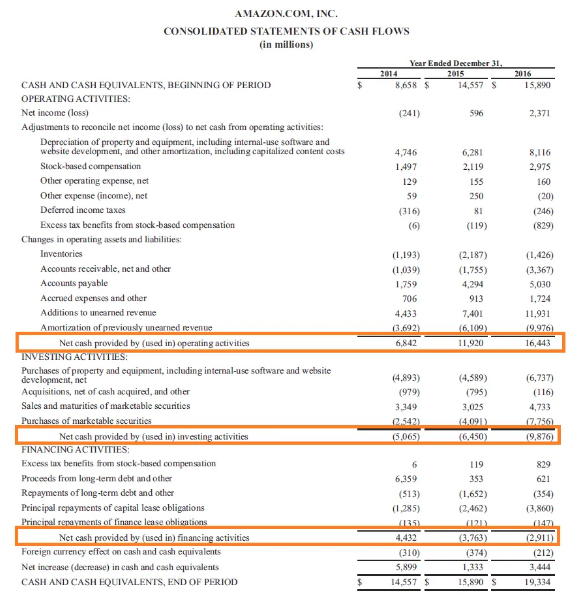
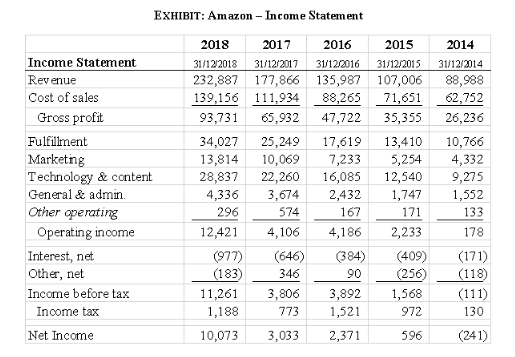
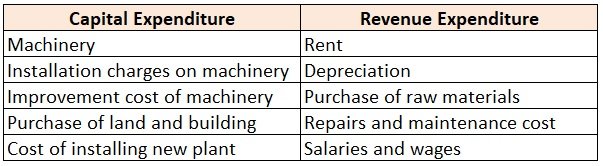
Everyone must have heard about the term “cooking the books”. This term is generally associated with Creative accounting. In simple words, Creative accounting is a method of accounting in which the management tries to show a better picture of the business than the reality. Let us now understand thisRead more
Everyone must have heard about the term “cooking the books”. This term is generally associated with Creative accounting. In simple words, Creative accounting is a method of accounting in which the management tries to show a better picture of the business than the reality. Let us now understand this concept in detail.
What is Creative accounting?
Creative accounting is a method of accounting in which the management manipulates the books of accounts by finding loopholes to showcase a better image of the business.
It is a practice of using accounting loopholes to make a company’s financial position look better than it really is. It is not exactly illegal but it is more of a gray area.
For example, a business may delay reporting expenses to increase the profits to present a better short-term position.
The goal of creative accounting is to impress the shareholders, investors, get loans or boost stock prices.
However, this can also be very risky and have serious consequences. It can reduce the trust of the investors and customers. In some cases, like Enron and WorldCom the world has seen how creative accounting lead to legal consequences.
Common Techniques of Creative Accounting
Some of the common techniques used by the business to manipulate the financial position are as follows:
- Revenue Recognition: Techniques such as recognizing revenue before it is actually earned is a method of creative accounting.
- Expense manipulation: Delaying the recognition of expenses to show a better position of the business in a short-term.
- Undervaluing liabilities: Undervaluing the liabilities of the business by not recognizing any future costs such as insurance or warranty etc.
- Asset Valuation: Overstating the value of asses or high amount of depreciation can be some ways of manipulating the value of assets.
- Tax avoidance: This is a way of reducing the tax liability by manipulating the financial statements to lower the profits.
- Cookie jar accounting: This is a method in which profits in the good years are saved in excess to use in the years of difficulty.
Ethical implications of Creative Accounting
There are several ethical implications with respect to creative accounting. Some of these are discussed below:
- Misleading Stakeholders: Creative accounting is a method to mislead the stakeholders including the investors, creditors, government, etc. This can lead to loss of trust.
- Loss of trust: The shareholders will lose trust over the company if the manipulation is discovered. Creative accounting breaches the fundamental of honesty.
- Non – compliance: Creative accounting leads to the non-compliance of the rules and regulations of the country which requires the businesses to follow certain accounting and reporting standards.
- Unfair competition: Creative accounting can make a company look more profitable and stable than it actually is, misleading investors and customers. This can leave honest businesses, who follow the rules, at a disadvantage.
- Moral responsibility: Management and business has the moral responsibility of working in the best interest of the society and the stakeholders.
Conclusion
The key takeaways from the above discussion are as follows:
- Creative accounting is the practice of using accounting loopholes to make a company’s financial position look better than it really is.
- The goal of creative accounting is to impress the shareholders, and investors, get loans, or boost stock prices.
- Revenue recognition, expense manipulation, and asset valuation are some of the common techniques of Creative accounting.
- The ethical implications of creative accounting include misleading stakeholders, eroding trust, compromising regulatory compliance, promoting unfair competition, neglecting moral responsibility, etc.
See less

Definition Section 43 of the companies act 2013 prescribes that the share capital of a company broadly can be of two types or classes : Preference shares Equity shares Preference shares Preference shares are the shares that carry the following two preferential rights : Preferential rights to receivRead more
Definition
Section 43 of the companies act 2013 prescribes that the share capital of a company broadly can be of two types or classes :
Preference shares
Preference shares are the shares that carry the following two preferential rights :
Classes of preference shares
Preference shares are broadly classified as follows :
With reference to the dividend
Cumulative preference shares are those preference shares that carry the right to receive arrears of dividends before the dividend is paid to the equity shareholders.
Non-cumulative preference shares are those that do not carry the right to receive arrears of dividends.
Participation in surplus profit
Participating preference shares of the company may provide that after the dividend has been paid to the equity shareholders, the holders of preference shares will also have a right to participate in the remaining profits.
Non-participating preference shares are those preference shares that do not carry the right to participate in the remaining profits after the equity shareholders have paid the dividend.
Convertibility
Convertible preference shares are those preference shares that carry the right to be converted into equity shares.
Non-convertible preference shares are those that do not carry the right to be converted into equity shares.
Redemption
Redeemable preference shares are those preference shares that are redeemed by the company at the time specified for the repayment or earlier.
Irredeemable preference shares are preference shares the amount of which can be returned by the company to the holders of such shares when the company is wound up.
Equity shares
Equity shares are those shares that are not preference shares.
Equity shares are the most commonly issued class of shares that carry the maximum ‘risk and reward ‘ of the business the risks of losing part or all the value of the shares if the business incurs losses.
The rewards are the payment of higher dividends and appreciation in the market value.
See less