Fictitious assets On seeing or hearing ‘fictitious’, the words which come to our mind are ‘not true, ‘fake’ or ‘fantasy’. So, fictitious assets are those items that appear on the assets side of the balance sheet but are actually not assets. In substance, fictitious assets are the expenses and lossesRead more
Fictitious assets
On seeing or hearing ‘fictitious’, the words which come to our mind are ‘not true, ‘fake’ or ‘fantasy’. So, fictitious assets are those items that appear on the assets side of the balance sheet but are actually not assets.
In substance, fictitious assets are the expenses and losses that are not completely written off in a financial year and are required to be carried forward to the next financial year.
The examples of fictitious assets are as follows:
- Deferred Advertisement expense
- Loss on the issue of debentures.
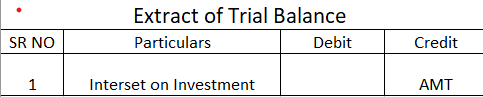
- Debit balance of Profit and Loss account ( Net loss )*
- Preliminary expenses.
Fictitious assets appear on the asset side of the balance sheet as expenses and losses have a debit balance.
*when the balance sheet is prepared as per Schedule III of Companies Act, the Net loss is shown as a negative figure under the head Reserve and Surplus.
Intangible Assets
Intangible assets mean the assets which don’t have any physical existence. They cannot be seen or touched but are assets because they do provide future economic benefits to the business. Like tangible assets (like machinery and building), they can be also created, purchased or sold.
Like tangible assets are depreciated, intangible assets are gradually written over by amortization over their useful lifespan to account for the economic benefits provided by them.
Following are the examples of intangible assets:
- Goodwill
- Brand name
- Trademark
- Patents
- Copyrights
Intangible assets which are created by the business-like goodwill or brand recognition do not appear in the balance sheet.
Only acquired intangible assets can be shown in the balance sheet. Like purchased goodwill, patents, trademarks etc.
Intangible assets also face impairment if their fair value is less than their carrying value after deducting amortization expense. The difference between carrying value and fair value is shown in the Profit and loss A/c as impairment charge and the asset is valued at fair value in the balance sheet.
See less



Receipts and payment account is a summary of cash transactions prepared at the end of the accounting period from the cash book where the transactions are recorded in chronological order. It is an Asset/ Real Account that records both revenue and capital receipts and payments. It is mainly prepared fRead more
Receipts and payment account is a summary of cash transactions prepared at the end of the accounting period from the cash book where the transactions are recorded in chronological order. It is an Asset/ Real Account that records both revenue and capital receipts and payments. It is mainly prepared for non-profit organizations and helps in the preparation of final accounts.
Proforma
Income and Expenditure Account is an account prepared by not-for-profit organizations to see whether the income of a particular period is sufficient to cover the expenses of that period. If the revenue is more than the expenses, it is known as “Surplus” or “Excess of Income over Expenditure” and if the expenses are more than Income, it is known as “Deficit” or “Excess of Expenditure over Income”. The account is prepared on the accrual basis of accounting i.e. all revenue incomes whether received or not and all revenue expenditures of the period whether paid or not are taken into account. However, in case of surplus, the money is not distributed among the members. Similarly, if there is a deficit it is not borne by the members.
Proforma

See less