No, capital account is not a real account. Capital account represents the amount of money invested by the owner/owners of the business along with the retained earnings net of drawings or dividends. Capital account has a natural credit balance because it is an internal liability of the business. CapiRead more
No, capital account is not a real account.
Capital account represents the amount of money invested by the owner/owners of the business along with the retained earnings net of drawings or dividends. Capital account has a natural credit balance because it is an internal liability of the business.
Capital account is a personal account because, as discussed above, it represents the investment of the owner or owners. Personal account represents person or persons.
Whereas a real account represents the material assets of a business. Example:- Cash A/c, Fixed assets A/c etc. That’s why the capital account is not a real account.
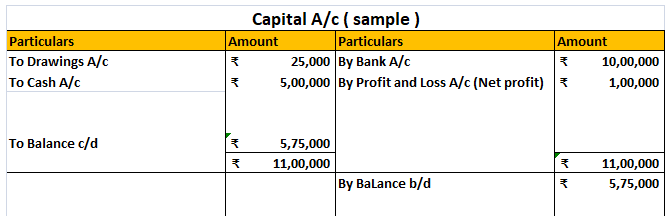
Being a personal account, the following golden rule of accounting applies to capital account:-
“Debit the receiver and credit the giver”
Here, as the owner gives an amount as an investment into the business (owner and the business are separate entities), the capital account has a credit balance.

Bad Debt is the amount that is irrecoverable from the debtors. It is the portion of the receivables. It includes two accounts “Bad Debts A/c” and “Debtors A/c or Accounts Receivable A/c”. The amount cannot be recovered by the debtor for reasons like the debtor is no longer in the position to pay offRead more
Bad Debt is the amount that is irrecoverable from the debtors. It is the portion of the receivables. It includes two accounts “Bad Debts A/c” and “Debtors A/c or Accounts Receivable A/c”.
The amount cannot be recovered by the debtor for reasons like the debtor is no longer in the position to pay off the debt or has become insolvent.
There are two methods to write off bad debts:
1. Direct Method: In this method, the amount of bad debts is directly deducted from the total receivables and the second effect is transferred to the debit side of Profit and Loss A/c as an expense.
The journal entry for bad debts as per modern rules of accounting is as follows:
Journal entry for transferring bad debts to profit and loss account:
For example, A Ltd had a total receivable of Rs.2,50,000 and bad debts for the period amounted to Rs.10,000.
Here, the journal entries will be:
2. Allowance for Doubtful Debts: In this method allowance is the estimation of the debts which is doubtful to be paid. The company creates a reserve for such debts which are uncollectible.
Firstly, the company will create a reserve which will be based on the accounts receivable. The journal entry will be:
When a specific receivable is uncollectible it will be charged as an expense, and Allowance for Doubtful Debts will be “Debited” and Accounts Receivable will be “Credited”.
For example, Mr.B sold goods worth Rs.15,000 to Mr.D. He creates an allowance of Rs.15,000 in case Mr.D fails to pay the amount. At the end of the period, Mr.D defaults and does not pay the debt.
In this case, Mr.B will first record the journal entry for allowance and then will write off Mr.D’s account.