A. Cash Book B. Statement C. Journal D. None of These
Net credit sales can be defined as the total sales made by a business on credit over a given period of time less the sales returns and allowances and discounts such as trade discounts. Net Credit Sales = Gross Credit Sales – Returns – Discounts – Allowances. Credit sales can be calculated from the ARead more
Net credit sales can be defined as the total sales made by a business on credit over a given period of time less the sales returns and allowances and discounts such as trade discounts.
Net Credit Sales = Gross Credit Sales – Returns – Discounts – Allowances.
Credit sales can be calculated from the Accounts receivable/ Bills Receivable/ Debtors figure in the Balance Sheet. It will be normally shown under the Current Assets head in the Balance Sheet.
Credit sales = Closing debtors + Receipts – Opening debtors.
Alternatively, you may observe the bills receivable ledger account to locate the figure of credit sales.
Net Credit Sales and related terms
Before we try to understand the concept of net credit sales with an example, let us discuss the term sales return. Sales return means the goods returned by the customer to the seller. It may be due to defects or any other reasons.
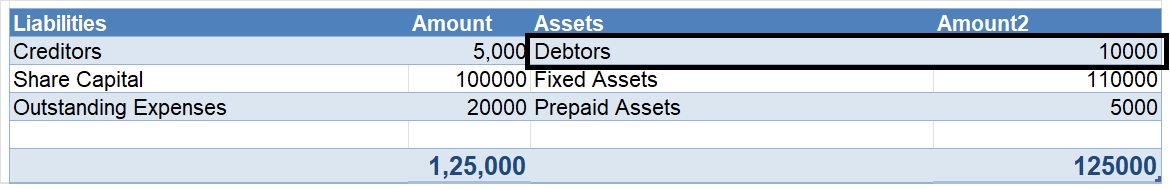
Now let us take an example. John is a retail businessman. He sells smartphones. He buys 100 smartphones from Vivo on credit. The smartphones are worth ₹1.5 lahks. He then returns smartphones worth 20,000 rupees to Vivo. He also gets an allowance of rupees 5,000 from Vivo.
In the above example, the credit sales of Vivo are of rupees 1.5 lakh. The net credit sales is of
1.5 lakh – 20,000 – 5, 000 = 1.25 lakh rupees.
Importance of Net Credit Sales
- Net Credit Sales figure together with the accounts receivable figure acts as an indicator of the credit policy of the company.
- It offers insights into the ability of the company to meet short-term cash obligations.
- The credit policy also affects the total current assets that the company has in the manifestation of Accounts Receivable
Advantages and Disadvantages of Credit Sales.
Advantages
- Increased Sales – The credit Policy facilitates increased sales for the company. The company can attract more customers with a liberal credit policy. For example, Apple got more customers when it started to sell its products on an EMI basis.
- Customer Loyalty / Retention- Regular customers can be retained and made to feel honored by offering them more liberal credit terms.
Disadvantages
- Delay in Cash Collection – Credit Sales imply that the company would get cash on a delayed basis. This money could have otherwise been put to use for some other profitable venture or could have borne interest for the company
- Collection Expenses– The company had to incur additional expenditures for collecting money from debtors.
- Risk of Bad Debts – With credit sales, there is always the risk that the buyer may become bankrupt and may not be able to pay the money due to the seller.

The correct option is A) Cash book let's understand what is petty cash book: A petty cash book is a cash book maintained to record petty expenses. Petty expenses, mean small or minute expenses for which the payment is made in coins or a few notes or which are smaller denominations like tea or coffeeRead more
The correct option is A) Cash book
let’s understand what is petty cash book:
Generally, the petty cashbook is prepared as per the Imprest system. As per the Imprest system, the petty expenses for a period (month or week) are estimated and a fixed amount is given to the petty cashier to spend for that period.
At the end of the period, the petty cashier sends the details to the chief cashier and he is reimbursed the amount spent. In this way, the debit balance of the petty cashbook always remains the same.
The petty cash book has two columns in which
Balance of Petty cash book
The balance of petty cash book is never closed and their balances are carried forward to the next accounting period which is considered one of the most significant qualities of an asset whereas Income doesn’t have any opening balance and their balances get closed at the end of every accounting year.
A petty cash book is placed under the head current asset in the balance sheet. The Closing Balance of the petty cash book is computed by deducting Total expenditure from the Total cash receipt (as received from the head cashier).
Format for petty cash book
Only small denominations are recorded in the petty cash book. It varies with the type, quantity, and need of a business. It involves cash and checks.
Conclusion
A simple petty cash book is a type of cash book because it records the small expenses which involve small transactions in the ordinary daily business.
A petty cash book is not as important as an income statement, balance sheet, or trail balance it doesn’t measure the accuracy of accounts so it is not treated as a statement.
No journal entries are made in the books of accounts while spending or purchasing using a petty cash book so, it is not treated as a journal.
See less