As you know all transactions occurring in a business are recorded in the journal (book of original entry) in chronological order. After recording them in the journal, they are posted to their respective ledger accounts. Here I've explained the steps involved in posting a journal entry to the ledger.Read more
As you know all transactions occurring in a business are recorded in the journal (book of original entry) in chronological order. After recording them in the journal, they are posted to their respective ledger accounts.
Here I’ve explained the steps involved in posting a journal entry to the ledger.
Posting of an account debited in the journal entry:
Step 1: Identify the account which has to be debited in the ledger.
Step 2: Write the date of the transaction under the ‘Date Column’ of the debit side of the ledger account.
Step 3: Write the name of the account which has been credited in the journal entry in the ‘Particulars Column’ on the debit side of the account as “To (name of the account)”.
Step 4: Write the page number of the journal where the entry exists in the ‘Journal Folio (JF) Column’.
Step 5: Enter the amount in the ‘Amount Column’ on the debit side of the ledger account.
Posting of an account credited in the journal entry:
Step 1: Identify the account which has to be credited in the ledger.
Step 2: Write the date of the transaction under the ‘Date Column’ of the credit side of the ledger account.
Step 3: Write the name of the account which has been debited in the journal entry in the ‘Particulars Column’ on the credit side of the account as “By (name of the account)”.
Step 4: Write the page number of the journal where the entry exists in the ‘Journal Folio (JF) Column’.
Step 5: Enter the amount in the ‘Amount Column’ on the credit side of the ledger account.
I’ll explain the process of preparing a ledger A/c with a simple transaction.
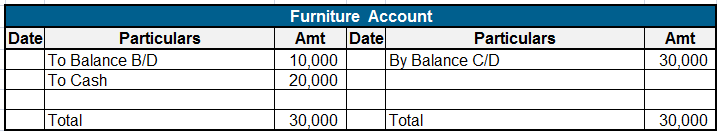
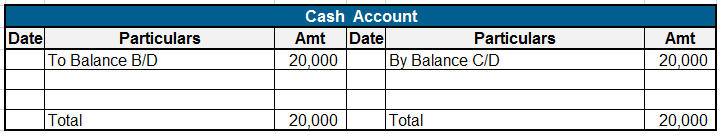
On 1st May ABC Ltd. purchased machinery for 5,00,000. In the Journal the following entry will be made.
| Machinery A/c | 5,00,000 |
| To Bank A/c | 5,00,000 |
| (Being machinery purchased for 5,00,000) |
Let’s assume that this entry appears on page no. 32 of the journal. Now we will open Machinery A/c and Bank A/c in the Ledger.
On the debit side of the Machinery A/c “To Bank A/c” will be written. In the Bank A/c “By Machinery A/c” will be written on the credit side.
An extract of both the accounts are as follows:
Machinery A/c
| Date | Particulars | J.F. | Amt. | Date | Particulars | J.F. | Amt. |
| May-01 | To Bank A/c | 32 | 5,00,000 |
Bank A/c
| Date | Particulars | J.F. | Amt. | Date | Particulars | J.F. | Amt. |
| May-01 | By Machinery A/c | 32 | 5,00,000 |

Return inwards are the goods returned by the customer to the seller. The goods are returned for reasons like defects, excess delivery, and low quality. Return inwards are also known as Sales Returns. Sales returns are a contra account to sales revenue. The amount of sales returns is deducted from thRead more
Return inwards are the goods returned by the customer to the seller. The goods are returned for reasons like defects, excess delivery, and low quality. Return inwards are also known as Sales Returns.
Sales returns are a contra account to sales revenue. The amount of sales returns is deducted from the total sales in the Trading section of the Trading and Profit & Loss Account.
In subsidiary books, return inwards are recorded only for those goods which are sold on credit to the customer.
For example, On 1 August E Electronics sold 50 units of television to Hill Hotels on credit for Rs.25,000 each. Out of which 5 units were found to be defective and were returned back to E Electronics. In that accounting period, E Electronics made a total sales of Rs.20,00,000 (including the item sold to Hill Hotels).
E Electronics in its Trading section of Trading and P&L A/c will account for a sales return of Rs.1,25,000 (Rs.25,000*5) and this amount will be deducted from the total sales. The same will be recorded in the subsidiary books as it accounts for sales made on credit.
Extract of Profit & Loss Account:
For a business, sales returns will either have a decrease in the sales revenue or it will increase the sales returns and allowances which is a contra account to sales revenue. An increase in sales returns will decrease gross profit.
See less