A. Trading Account B. Trial Balance C. Profit and Loss Statements D. Balance Sheet
The profits earned by a company are mainly divided into two parts: Dividend, and Retained Earnings The part of profit distributed to its shareholders is called a dividend. The part of the profit that the company holds for future expansion or diversification plans is called retained earnings. As theRead more
The profits earned by a company are mainly divided into two parts:
- Dividend, and
- Retained Earnings
The part of profit distributed to its shareholders is called a dividend. The part of the profit that the company holds for future expansion or diversification plans is called retained earnings.
As the name suggests, retained earnings are the profit that is retained in the company. Retained earnings can be used for various purposes:
- To distribute as dividends to shareholders
- Expansion of business
- Diversification
- For an expected merger or acquisition
As the profits of the company belong to shareholders, retained earnings are considered as profits re-invested in the company by the shareholders.
The formula to calculate the cost of retained earnings is:
(Expected dividend per share / Net proceeds) + growth rate
- Expected dividend is the dividend an investor expects for his investment in the company’s shares based on the last year’s dividend, trends in the markets, and financial statements presented by the company.
- Net proceeds is the market value of a share, that is, how much an investor would get if he sells his shares today.
- Growth rate represents growth of company’s revenue, dividend from previous years in the form of a percentage.
The expected dividend per share is divided by net proceeds or the current selling price of the share, to find out the market value of retained earnings.
The growth rate is then added to the formula. It’s the rate at which the dividend grows in the company.
For example:
The net proceeds from share is Rs 100, expected dividend growth rate is 2% and expected dividend is 5.
Cost of retained earnings
= (Expected dividend per share / Net proceeds) + Growth rate
= (5 / 100) + 0.02
= 0.07 or 7%
See less



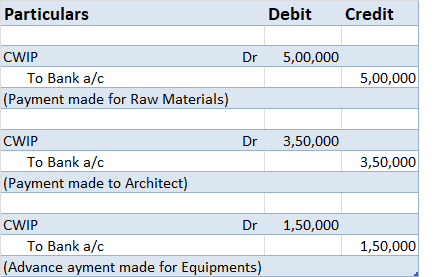
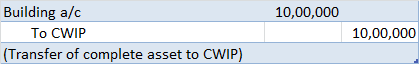
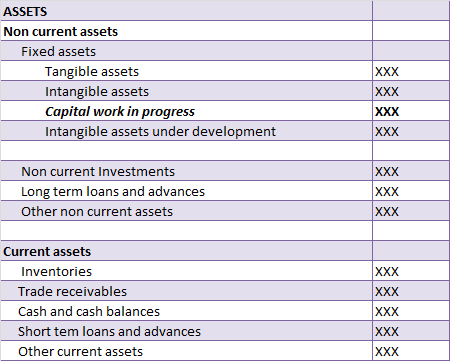
The correct answer is Option C. The Profit and loss statement is also referred to as the statement of revenues and expenses. It is because the Profit and Loss statement reports all types of revenue that have been earned and all types of expenses that have been incurred during a particular period ofRead more
The correct answer is Option C.
The Profit and loss statement is also referred to as the statement of revenues and expenses. It is because the Profit and Loss statement reports all types of revenue that have been earned and all types of expenses that have been incurred during a particular period of time.
Option A Trading Account reports only the operating revenues and operating expenses.
Option B Trial Balance shows the balances of all the ledgers of a business and is prepared to check the arithmetical accuracy of the books of accounts.
Option D Balance sheet reports the balances of assets and liabilities of a business as at a particular date.
People often confuse the trading and the profit and loss statement to be the same. But they are different.
Trading Account is prepared with aim of arriving at operating profit or gross profit whereas the profit and loss statement is prepared to arrive at the net profit of a business and reports every revenue and expense whether operating or non operating in nature.
Operating revenue and operating expense are earned or incurred respectively are related to the chief business activities of a business.
Features of profit and loss statement:
- It is prepared to measure the net profit of a business hence its profitability.
- It is usually prepared for a period of one year but many companies do prepare quarterly statements to better judge their performance.
- It helps the management in decision making and the other stakeholders like shareholders, creditors to make informed decisions.
See less