Financial analysis of a company means analyzing the previous data of the company and giving recommendations based on that whether the company will improve in the future on not. It is the process of evaluating the financial performance and stability of the company. There are various types of financiaRead more
Financial analysis of a company means analyzing the previous data of the company and giving recommendations based on that whether the company will improve in the future on not.
It is the process of evaluating the financial performance and stability of the company.
There are various types of financial analysis. They are leverage, growth, cash flow, liquidity, profitability, etc.
The main objectives of Financial analysis are
1.Reviewing the current position: In order to know if the company is doing well, past analysis of data is required to be carried out. Regular recording of the transactions helps to understand the financial position of the company.
For example, A company wants to generate a revenue of 2000 crores in the next 5 years. The last four years’ data shows revenue as 1100, 1300,1600, 1800 crores respectively.
So from the above, we can say that the company is performing well and looks like it will reach the desired target in the fifth year or may perform better than the target desired.
However, if the revenue declines, it will cause concern for the team but the team will get time to gear up and work efficiently to achieve the desired target.
2. Ease in decision making: For Future decision-making, quarterly financials play an important role. Subsidiary books and accounts like the sales book, purchase orders, manufacturing a/c, etc. help in giving more reliable information.
For example, If sales are increasing inconsistently in a quarter, and in the next quarter the level of sales decrease due to any reason then the management can analyze and change the strategy.
3. Performance Comparison: It helps in comparing the performance of the business every month, quarterly, half-yearly, and yearly. Analyzing the data can help the management to compare if the company is proceeding in the right direction.
4. Assessing the profitability: Financial statements are used to assess the profitability of the firm. The analysis is made through the accounting ratios, trend line, etc. Accounting ratios calculated for a number of years shows the trend of change of position i.e. positive, negative or static. The assessing of the trend helps the management to analyze if the company is making profits or not.
5. Measure the solvency of the firm: Financial analysis helps to measure the short-term and long-term efficiency of the firm for the benefit of the Stakeholders.
6. Helps the end-users: The owners are the end-users for whom the financial statements are prepared. Financial statements are the summaries that are prepared for providing various disclosures to the owners which helps them understand the statements in a better way. If the end-users arrive at the right decision with the help of financial statements that means the objective is achieved.
7. Other objectives:
- It helps to settle disputes among the parties.
- It helps in the expansion decision of the firm.
- It helps in analyzing the amount of tax to be paid.
- It reduces the chances of fraud.
- It provides information about resources.
- It provides a true and fair view of financial position.


Whenever the proprietor/owner of a business withdraws cash or goods from the business for his/her personal use, we call it drawings. For example, Alex, proprietor of a soap manufacturing company, takes 50 pack of soaps costing 30 each for his personal use. So, 1,500 (50*30) will be considered as draRead more
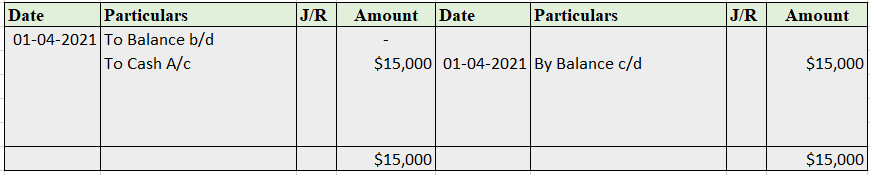
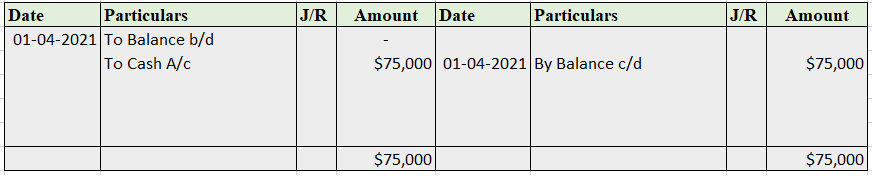
Whenever the proprietor/owner of a business withdraws cash or goods from the business for his/her personal use, we call it drawings. For example, Alex, proprietor of a soap manufacturing company, takes 50 pack of soaps costing 30 each for his personal use. So, 1,500 (50*30) will be considered as drawings of Alex. One important thing to note here is whenever goods are withdrawn for personal use they are valued at cost.
Drawings are not an asset/liability/expense/income to the business. The drawings account is a contra-equity account. A contra-equity account is a capital account with a negative balance i.e. debit balance. It reduces the owner’s equity/capital.
Drawings being a contra-equity account has a debit balance, reducing the owner’s capital in the business. This is because withdrawals for personal use represent a reduction of the owner’s equity in the business.
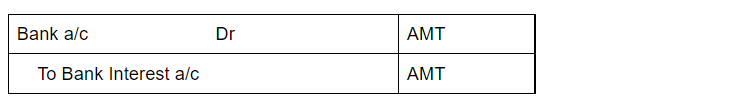
Drawings are not shown in the Income Statement as they are neither an expense nor an income for the business. However, the following journal entries are passed to record drawings for the year:
Drawings A/c is debited because it reduces the owner’s capital. Cash/Purchases A/c is debited as a withdrawal reduces the assets of the business.
At the end of the year, drawings A/c are closed by transferring it to the owner’s capital A/c. We post the following entry to close the drawings A/c at the end of the year:
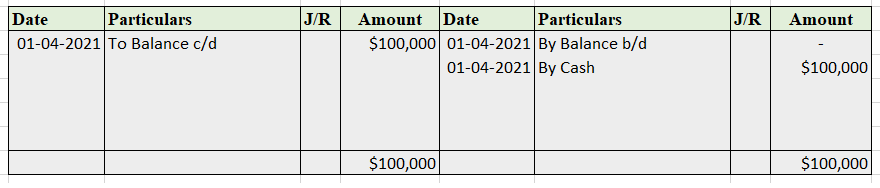
In the balance sheet, drawings are shown by deducting it from the owner’s capital A/c.
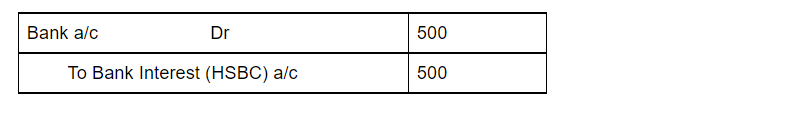
Let us take our earlier example of Alex. He withdrew soaps worth 1,500. At the end of the year, his capital was worth 5,500. The journal entry for recording the drawings is as follows:
In the balance sheet, drawings worth 1,500 are shown as follows:

See less