Interest on capital Interest on capital is interest payable to the owner/partners for providing a firm with the required capital to commence the business. It's a fixed return that a business owner is eligible to receive. When the business firm faces a loss, the interest on capital will not be providRead more
Interest on capital
Interest on capital is interest payable to the owner/partners for providing a firm with the required capital to commence the business. It’s a fixed return that a business owner is eligible to receive.
When the business firm faces a loss, the interest on capital will not be provided. It is permitted only when the business earns a profit. Such payment of interest is generally observed in partnership firms. It is provided before the division of profits among the partners in a partnership firm.
If an owner or partner introduces additional capital to the business, it is also taken into account for providing interest on capital.
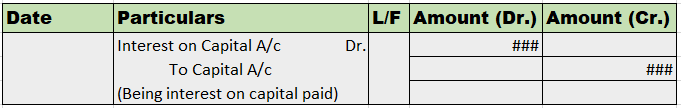
Sample journal entry
Interest on capital is an expense for business, thus, debited as per the golden rules of accounting, debit the increase in expense, and the owner/partner’s capital a/c is credited as per the rule, credit all incomes and gain.
As per the modern rules of accounting, we debit the increase in expenditure and credit the increase in capital.
As we know, as per the business entity concept, business and owner are two different entities and a business is a separate living entity. Therefore, the capital introduced by the owner/partners is the amount on which they’re eligible to receive a return.
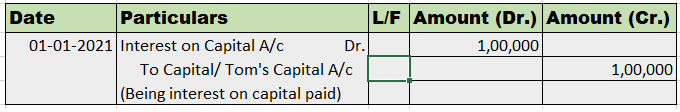
Example:
Tom is the business owner of the firm XYZ Ltd. He has contributed ₹ 10,00,000 to the business with 10% interest provided to Tom at the end of the year.
Solution:
Here interest on capital will be calculated as,
Interest on capital = Amount invested × Rate of interest × Number of Months/12
= 10,00,000 × 10% × 12/12
= ₹ 1,00,000

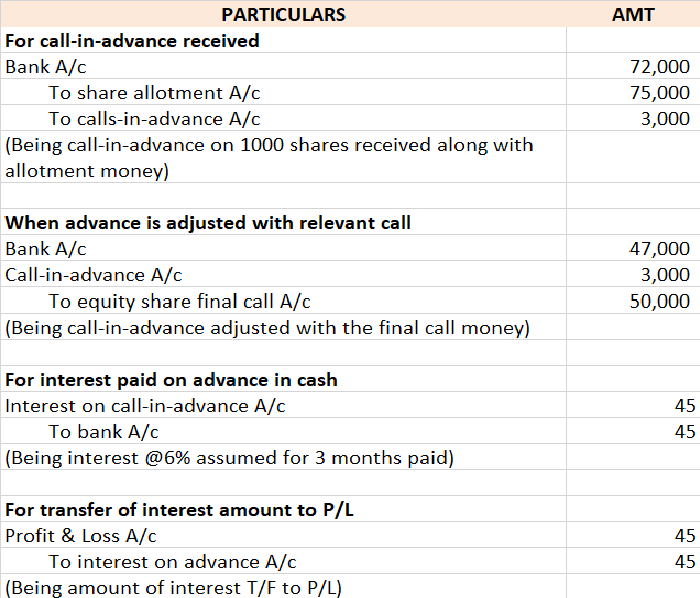
General reserve is the part of profits or money kept aside to meet future uncertainties and obligations of the entity. General reserve is created out of revenue profits for unspecified purposes and therefore is also a part of free reserves. General reserve forms a part of the Profit & Loss ApprRead more
General reserve is the part of profits or money kept aside to meet future uncertainties and obligations of the entity. General reserve is created out of revenue profits for unspecified purposes and therefore is also a part of free reserves.
General reserve forms a part of the Profit & Loss Appropriation account and is created to strengthen the financial position of the entity and serves as a sources of internal financing. It is upon the discretion of the management as to how much of a reserve is to be created. No reserve is created when the entity incurs losses.
General reserve is shown in the Reserves & Surplus head on the liability side of the balance sheet of the entity and carries a credit balance.
Suppose, an entity, ABC Ltd engaged in the business of electronics earns a profit of 85000 in the current financial year and has an existing general reserve amounting to 100000. The management decides to keep aside 20% of its profits as general reserve.
Then the amount to be transferred to general reserve will be = 85000*20% = 17000.
In the financial statements it will be shown as follows-
Now, in the next financial year, the entity incurs losses amounting to 45000. In this case, no amount shall be transferred to the general reserve of the entity and will be shown in the financial statement as follows-
The creation of general reserve can sometimes be deceiving since it does not show the clear picture of the entity and absorbs losses incurred.
See less