When a loan is taken from a person by a business, there is an asset and liability being created. Cash is being brought into the business which increases the asset whereas the financial obligation of the company rises when a loan is taken and hence a liability increases. For example, Mark Ltd. has taRead more
When a loan is taken from a person by a business, there is an asset and liability being created. Cash is being brought into the business which increases the asset whereas the financial obligation of the company rises when a loan is taken and hence a liability increases.
For example, Mark Ltd. has taken a loan from John for $5,000. Therefore the journal entry can be shown as:
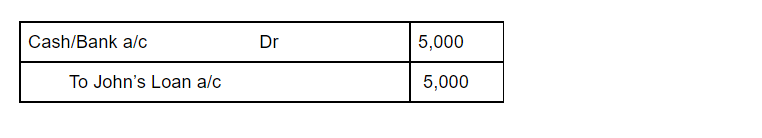
According to the modern rules of accounting, increase in assets is Debit and increase in liability is credit. The company may have taken the loan to finance its business or for some emergency. When it is time for the business to pay off the loan, they can either pay it off completely or in instalments. They must pay off the principal amount along with interest.
Now for our above example, if Mark Ltd paid off the entire loan after one year at 10% interest, then the journal entry would be:
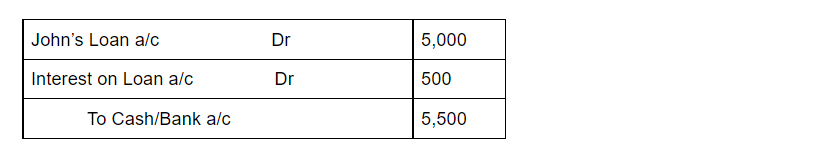
Here, the interest on loan account is debited since an increase in expense is debited. Loan account will be debited because the obligation is now reduced and hence liability decreases. Finally, we credit cash since cash is leaving the business which implies a decrease in assets.
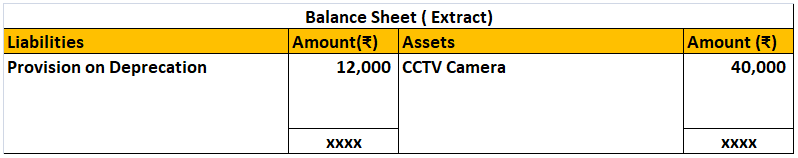
If the entire loan is not paid off in that year, then the balance of the loan amount will be shown in the balance sheet under the head liabilities.
See less

Sometimes a business may earn an income by delivering the goods/services within the stipulated time. But the business may not have issued an invoice to the customer. Such a scenario is what is called unbilled revenue. Note that as per the accrual concept of accounting, sales are recognized on the daRead more
Sometimes a business may earn an income by delivering the goods/services within the stipulated time. But the business may not have issued an invoice to the customer. Such a scenario is what is called unbilled revenue.
Note that as per the accrual concept of accounting, sales are recognized on the day it was made, irrespective of whether the business receives cash or not.
The business records unbilled revenue by passing the following journal entry:
Unbilled Revenue is treated as an asset because it is yet to be fully recognized as an income. Therefore it is debited. Revenue A/c is credited as there is an increase in income.
Once the bill/invoice has been issued to the customer, the following entry is passed to close the Unbilled Revenue A/c.
Let me explain this concept with an example,
Luca Traders, a business dealing in stationery and office supplies receives an order on August 5th for 1,000 pens worth 10 each. On August 8th they deliver the pens but they are yet to issue an invoice to the customer. They issue the invoice only on August 13th.
So the sales revenue of 10,000 (1,000*10) will be treated as an unbilled revenue for the period of August 8th – August 12th. On August 8th the following entry is made to record unbilled revenue.
When the invoice is sent to the customer on August 13th, the following journal entry is posted to close the unbilled revenue A/c.