In a partnership firm, the partners may withdraw certain amounts from the firm for their personal use. Such amounts withdrawn by the partners are called drawings. This amount is usually deducted from their capital. The partners are required to pay an amount as interest, based on the time period forRead more
In a partnership firm, the partners may withdraw certain amounts from the firm for their personal use. Such amounts withdrawn by the partners are called drawings. This amount is usually deducted from their capital. The partners are required to pay an amount as interest, based on the time period for which the money was withdrawn. This amount is called Interest on Drawings.
The journal entry for interest on drawings is as follows:
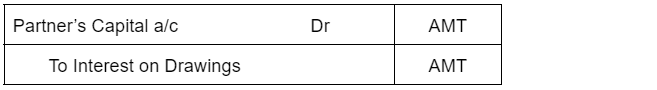
Since interest on drawings is an income to the firm, it is credited based on the rule that “increase in incomes are credited”. Since the partner has to bear the interest amount, his capital account is debited as a “ decrease in capital is debited”.
FORMULAS
The basic formula for interest on drawings is:
Interest on drawings = Amount of Drawings x Rate/100 x No. of months/12
- When equal amounts of drawings are withdrawn at the beginning of every month, then
Interest on Drawings = Total Drawings x Rate/100 x (12+1)/2 - When equal amounts of drawings are withdrawn at the end of every month, then the Interest on Drawings = Total Drawings x Rate/100 x (12-1)/2
- When the date of the drawing is not specified, it is assumed to be withdrawn evenly. Hence Interest on Drawings = Total Drawings x Rate/100 x 6/12
The calculations in 1,2 and 3 are done so that drawings can be calculated for the average period.
EXAMPLE
Jack is a partner who withdrew $20,000 on 1st April 2020. Interest on drawings is charged at 10% per annum. If we have to calculate interest on drawings as of 31st December, then
Interest on Drawings = 20,000 x 10/100 x 9/12 = $1,500
(Here, interest on drawings is outstanding for 9 months, that is from April to December)

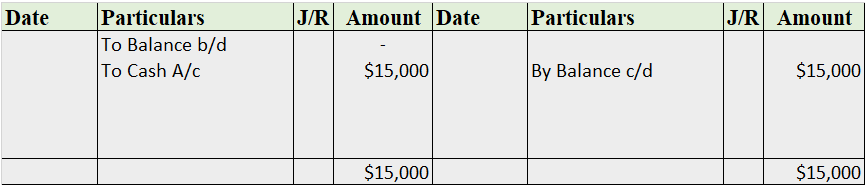
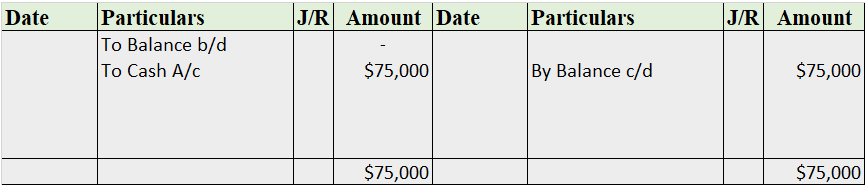
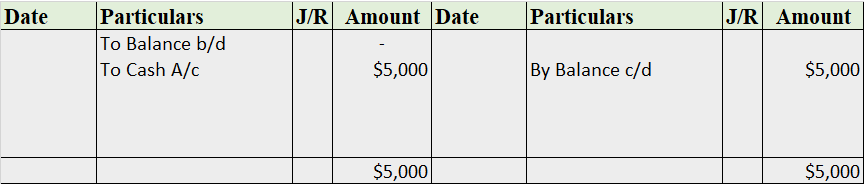
Effective Capital is an amount calculated for purpose of arriving at the maximum limit of managerial remuneration as per the Companies Act, 2013 where profit is inadequate or no profit. Other than that it has no use. Computation of effective capital is given in Explanation I to Schedule II of the CoRead more
Effective Capital is an amount calculated for purpose of arriving at the maximum limit of managerial remuneration as per the Companies Act, 2013 where profit is inadequate or no profit. Other than that it has no use.
Computation of effective capital is given in Explanation I to Schedule II of the Companies Act. Schedule II deals with remuneration payable to managers in case of no profit or inadequate profit in the following manner:
Computation of effective capital is done in the following manner:
Numerical example:
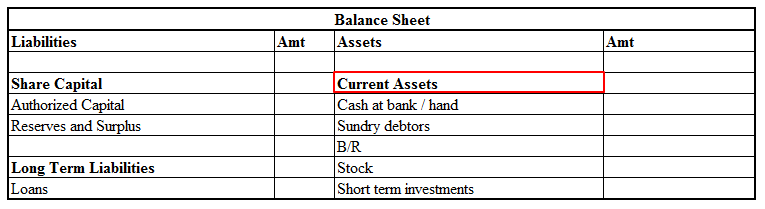
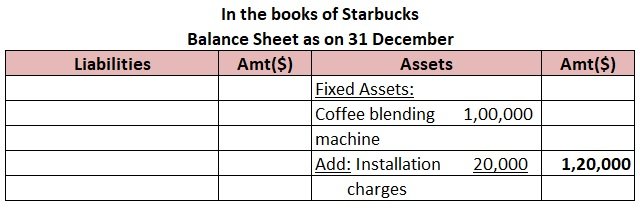
ABC Ltd reports its balance sheet as given below:
We will compute its effective capital for both an investment company and a non-investment company.

See less