The reserves created for specific purposes in business are called specific reserves. According to the Companies Act, 2013, these reserves cannot be used for any other purposes. However, if the Article of Association of a company allows, these reserves can be used for other purposes as well. Amount tRead more
The reserves created for specific purposes in business are called specific reserves. According to the Companies Act, 2013, these reserves cannot be used for any other purposes. However, if the Article of Association of a company allows, these reserves can be used for other purposes as well.
Amount to any specific reserve is generally transferred from the Profit and Loss Appropriation Account.
Various specific reserves are:
- Debenture Redemption Reserve
Debentures are debt instruments of a company and they have to be redeemed, that is, paid back after the expiry of the specified period. According to Accounting Standards, companies are required to set aside a specific amount in Debenture Redemption Reserve, when they are due for redemption.
- Securities Premium Reserve
When shares or debentures are issued at a price higher than its book value/face value, the difference between the market value and book value is called Securities Premium. The amount of Securities Premium is transferred to Securities Premium Account. This amount is utilized to issue fully paid bonus shares, write off preliminary expenses, write off commission discounts, etc., to provide a premium on redemption of debentures.
- Investment Fluctuation Reserve
The investments made by a company are subject to fluctuations in its market value. Company Law and Accounting Standards require companies to provide for such fluctuations by creating a reserve called Investment Fluctuation Reserve.
- Dividend Equalisation Reserve
Companies are required to pay a dividend to their shareholders. It is often difficult for a company to maintain a consistent rate of dividend as the dividend paid is equivalent to the profit made by a company during the financial year which is not consistent. So, Dividend Equalisation Reserve is created to maintain a consistent rate of dividend on shares over time, in the event of both high and low profits.
See less




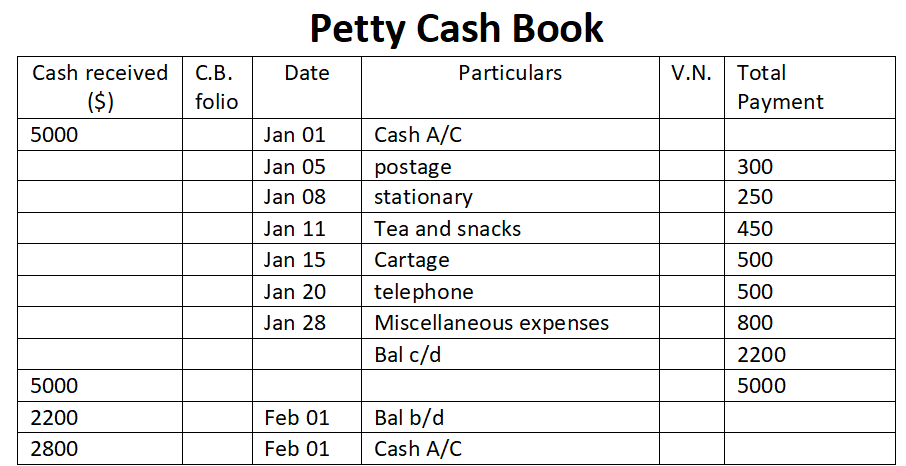
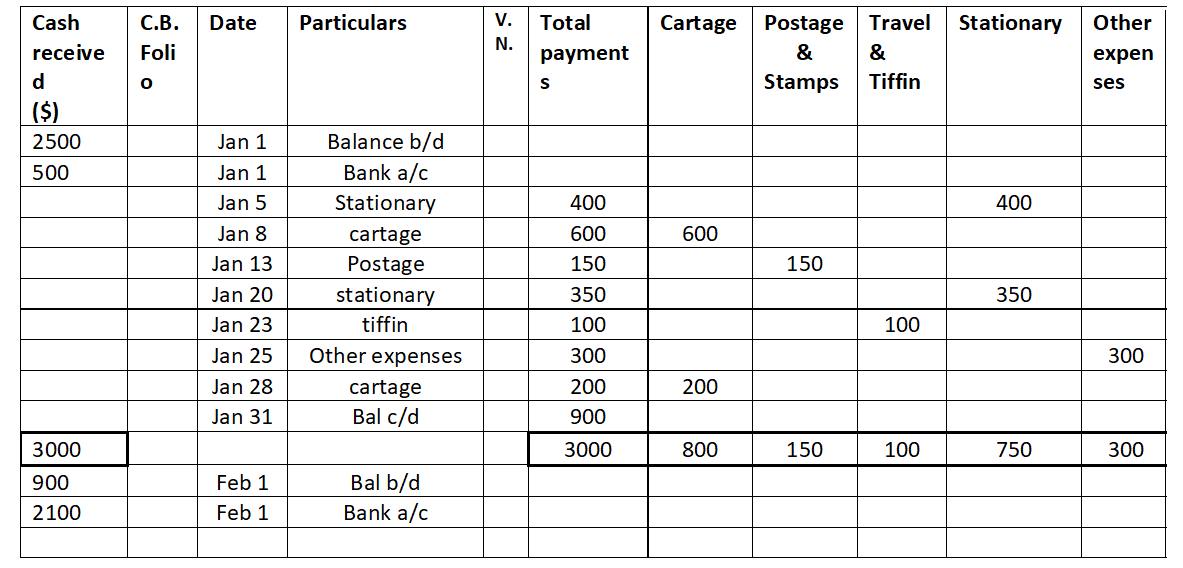
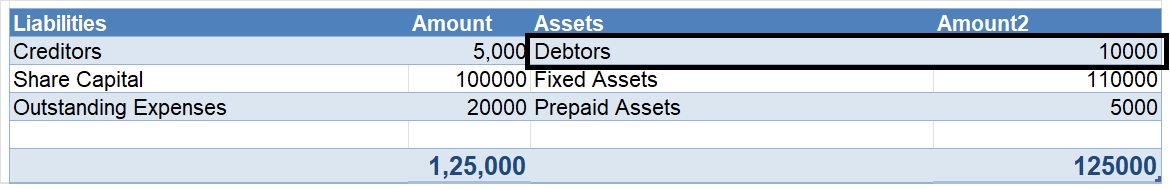
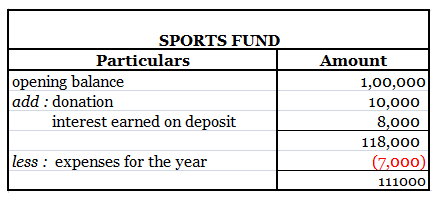
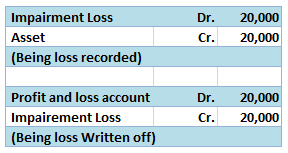
The term "principal book of accounts'' refers to the set of ledgers that an entity prepares to group the similar transactions recorded as journal entries under an account. So to put it simply, the principal book of accounts mean ledgers. Ledgers are prepared by posting the debits and credits of a joRead more
The term “principal book of accounts” refers to the set of ledgers that an entity prepares to group the similar transactions recorded as journal entries under an account.
So to put it simply, the principal book of accounts mean ledgers.
Ledgers are prepared by posting the debits and credits of a journal entry to the respective accounts.
A ledger groups the transactions concerning the same account. For example, Mr B is a debtor of X Ltd. Hence all the transactions entered into with Mr. will be grouped into the ledger Mr B A/c in the books of X Ltd.
Ledgers are of utmost importance because all the information to any account can be known by its ledger.
Preparation of ledger is very important because all the information to any account can be known by its ledger. Ledgers also display the balance of each and every account which may be debit or credit. This helps in the preparation of the trial balance and subsequently the financial statements of an entity.
Hence, it is the most important book of accounts and calling it the ‘books of final entry’ is also justified.
See less