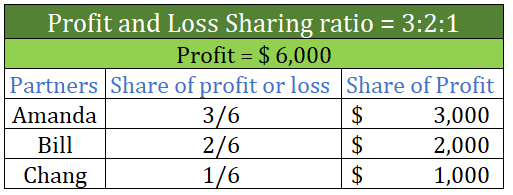
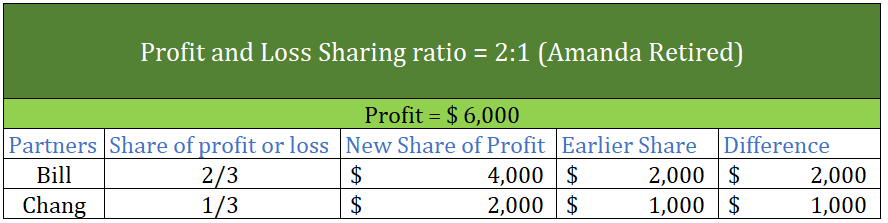
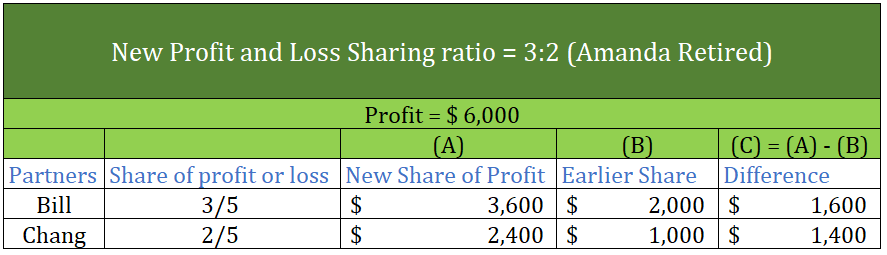
Realisation account A realisation account is a nominal account prepared at the time of dissolution of a business. All the assets and liabilities except cash and bank balance are transferred to the realisation account. A realisation account is prepared to calculate the profit or loss on the dissoluRead more
Realisation account
A realisation account is a nominal account prepared at the time of dissolution of a business. All the assets and liabilities except cash and bank balance are transferred to the realisation account. A realisation account is prepared to calculate the profit or loss on the dissolution or closing of the firm.
All the assets are transferred to the debit of the realisation account and all the liabilities are transferred to the credit of the realisation account. When assets are sold, Cash A/c is debited and Reliastion A/c is credited and when liabilities are paid off, Cash A/c is credited and Realisation A/c is credited.
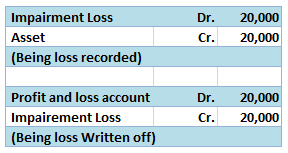
If the credit side exceeds the debit side of the realisation account, it results in profit. In contrast, if the debit side exceeds the credit side of the realisation account, it results in a loss. in case of profit, the Capital account is credited and in case of loss, the Capital account is debited.
The debit side of the realisation account
All the assets including Land and building, Plant and machinery, furniture, stock, debtor and investment are transferred to the debit of the realisation account and payment of outside liabilities is also recorded on the debit side of the realisation account. Payment made for dissolution expenses is also recorded on the debit side of the realisation account.
- Assets: All the assets including Land and building, Plant and machinery, Furniture, Stock, sundry debtors, and investments are transferred to the debit side of the realisation account. The debit balance of profit and loss balance is not transferred.
- Accounting entry for this is as follows:
Realisation A/c Dr…..
To Assets A/c …..
(All the assets transferred to the realisation account)
- Cash and bank A/c: Payment for the liabilities including sundry creditors, outstanding expenses, bills payable, loans and advances, bank overdrafts and cash credit is transferred to the debit side of the realisation account.
-
- Accounting entry for this is as follows:
Realisation A/c Dr…..
To Cash A/c …..
(Payment made for liabilities)
- Profit on realisation: If the credit side of the realisation account exceeds the debit side, it results in a profit then the capital account is credited.
-
- Accounting entry for this is as follows:
Realisation A/c Dr…..
To Capital A/c …..
(Being profit transferred to the capital account)
Credit side of realisation account:
All the liabilities and provisions are transferred to the credit side of the realisation account. Capital account of partners, profit and loss balance and loans from partners are not transferred. Sale proceeds of all the assets including Land and building, Plant and machinery, furniture, stock, debtor and investment are transferred to the credit side of the Realisation account.
Format for realisation Account is as under:
| Realisation A/c | |||
| Particulars | Amount | Particulars | Amount |
| To Land & Building | By Provision for Doubtful Debts A/c | ||
| To Plant & Machinery | By Sundry Creditors A/c | ||
| To Furniture | By Bills Payable A/c | ||
| To Debtors | By Outstanding Expenses A/c | ||
| To Goodwill A/c | By Bank Loan, Overdraft, Cash Credit A/c | ||
| To Investment A/c | By Bank/ Cash A/c (Assets realized): | ||
| To Bank/ Cash A/c (Liabilities Paid): | Land and Building | ||
| Sundry Creditors | Plant and Machinery | ||
| Bill Payable | Furniture | ||
| Outstanding Expenses | Stock | ||
| Bank Loan, | Debtors | ||
| Overdraft, | Bad Debts recovered | ||
| Cash Credit | Investment | ||
| To Bank/ Cash A/c | By Capital A/cs | ||
| (Realisation Expenses) | (assets taken over) | ||
| To Capital A/c | By Capital A/cs | ||
| (Realisation Expenses) | (Loss on Realisation) | ||
| To Capital A/cs | |||
| (Profit on Realisation) | |||
| Total | Total |

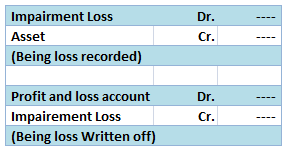
The Realisation account is prepared at the time of dissolution of the Partnership firm to ascertain profit or loss from the sale of assets and payment of liabilities of the firm. All assets that can be converted into cash (i.e. from which any value can be realised) and all external liabilities thatRead more
The Realisation account is prepared at the time of dissolution of the Partnership firm to ascertain profit or loss from the sale of assets and payment of liabilities of the firm. All assets that can be converted into cash (i.e. from which any value can be realised) and all external liabilities that are to be paid are recorded in the Realisation A/c.
DISSOLUTION OF PARTNERSHIP FIRM
It means the firm closes down its business and comes to an end. Simply, it means the firm will cease to exist in the future. As the firm is closing down, it will sell all its assets to realise all the value blocked in the assets, it is liable to pay off all of its liabilities whether due now or on some future date, and the remaining amount (if any) is distributed among the partners.
REALISATION ACCOUNT
This account is prepared only once, at the time of dissolution of the Partnership firm. It is opened to dispose of all the assets of the firm and make payments to all the external creditors of the firm.
It ascertains the profit earned or loss incurred on the realisation of assets and payment of liabilities.
The Realisation account is a NOMINAL ACCOUNT (Debit all expenses and losses, Credit all incomes and gains)
ITEMS RECORDED IN THE REALISATION ACCOUNT
DEBIT SIDE OF REALISATION ACCOUNT
1. TRANSFER OF ASSETS
Assets are any property or the possession of the business enterprise that allows it to get cash or any other benefit in the future.
Since all assets are sold at the time of the dissolution, all assets that can be converted into cash are transferred to the Debit side of the Realisation A/c at their book values.
Such as Plant & Machinery, Building, Debtors, etc.
EXCEPTIONS
NOTE – If there is any provision against any asset, such as ‘Provisions for Bad debts’ or ‘Provision for Depreciation, then such assets are transferred to the Debit side of the Realisation A/c at its gross value and the Provision is transferred to the Credit side of the Realisation A/c.
For example – Suppose there are Debtors of $50,000 and the Provision for Doubtful Debts is $2,000.
Then, Debtors will be recorded on the Debit side with a value of $50,000 and the Provision for Doubtful Debt on the Credit side with the amount of $2,000.
2. PAYMENT OF LIABILITIES
All liabilities are either paid in cash or the Partner agrees to pay for some liabilities. Since they are expenses, they are recorded on the debit side of the Realisation A/c as “Debit all expenses and Losses”
3. PROFIT ON REALISATION
There is profit when Cr. side > Dr. side, as it means incomes are more than the payments made. This profit is distributed among the partners.
CREDIT SIDE OF THE REALISATION ACCOUNT
1. TRANSFER OF LIABILITIES
Liabilities refer to the amount owed by the firm to outsiders. All liabilities must be paid off before accounts are closed. So, all external liabilities are transferred to the Credit side of the Realisation account, to make their payment.
Such as creditors, bills payable, loans, outstanding expenses, partner’s wife’s loan, etc.
EXCEPTION (not included)
2. SALE OF ASSETS
Assets can be sold for cash or taken by the Partner. The amount received from the sale of assets is recorded on the credit side of the Realisation account as “Credit all incomes and gains”.
Also, if any asset is given to the creditors in part or full payment of his dues, then the agreed amount is deducted from the creditor’s claim and no other entry is passed.
3. LOSS ON REALISATION:
There is a loss, if the Dr. side> Cr. side, which means Expenses > Incomes. This loss is also distributed among the Partners.
See less