Let us first understand what working capital is. Working capital means the funds available for the day-to-day operations of an enterprise. It is a measure of a company’s liquidity and short term financial health. They are cash or mere cash resources of a business concern. It also represents the exceRead more
Let us first understand what working capital is.
Working capital means the funds available for the day-to-day operations of an enterprise. It is a measure of a company’s liquidity and short term financial health. They are cash or mere cash resources of a business concern.
It also represents the excess of current assets, such as cash, accounts receivable and inventories, over current liabilities, such as accounts payable and bank overdraft.

Sources of Working Capital
Any transaction that increases the amount of working capital for a company is a source of working capital.
Suppose, Amazon sells its goods for $1,000 when the cost is only $700. Then, the difference of $300 is the source of working capital as the increase in cash is greater than the decrease in inventory.
Sources of working capital can be classified as follows:
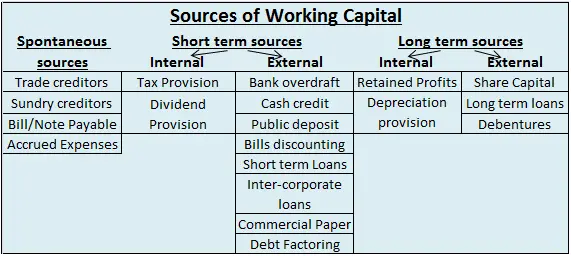
Short Term Sources
- Trade credit: Credit given by one business firm to the other arising from credit sales. It is a spontaneous source of finance representing credit extended by the supplier of goods and services.
- Bills/Note payable: The purchaser gives a written promise to pay the amount of bill or invoice either on-demand or at a fixed future date to the seller or the bearer of the note.
- Accrued expenses: It refers to the services availed by the firm, but the payment for which is yet to be done. It represents an interest-free source of finance.
- Tax/Dividend provisions: It is a provision made out of current profits to meet the tax/dividend obligation. The time gap between provision made and payment of actual payment serves as a source of short-term finance during the intermediate period.
- Cash Credit/Overdraft: Under this arrangement, the bank specifies a pre-determined limit for borrowings. The borrower can withdraw as required up to the specified limits.
- Public deposit: These are unsecured deposits invited by the company from the public for a period of six months to 3 years.
- Bills discounting: It refers to an activity wherein a discounted amount is released by the bank to the seller on purchase of the bill drawn by the borrower on their customers.
- Short term loans: These loans are granted for a period of less than a year to fulfil a short term liquidity crunch.
- Inter-corporate loans/deposits: Organizations having surplus funds invest with other organizations for up to six months at rates higher than that of banks.
- Commercial paper: These are short term unsecured promissory notes sold at discount and redeemed at face value. These are issued for periods ranging from 7 to 360 days.
- Debt factoring: It is an arrangement between the firm (the client) and a financial institution (the factor) whereby the factor collects dues of his client for a certain fee. In other words, the factor purchases its client’s trade debts at a discount.
Long Term Sources
- Retained profits: These are profits earned by a business in a financial year and set aside for further usage and investments.
- Share Capital: It is the money invested by the shareholders in the company via purchase of shares floated by the company in the market.
- Long term loans: These loans are disbursed for a period greater than 1 year to the borrower in his account in cash. Interest is charged on the full amount irrespective of the amount in use. These shareholders receive annual dividends against the money invested.
- Debentures: These are issued by companies to obtain funds from the public in form of debt. They are not backed by any collateral but carry a fixed rate of interest to be paid by the company to the debenture holders.
Another point I would like to add is that, although depreciation is recorded in expense and fixed assets accounts and does not affect working capital, it still needs to be accounted for when calculating working capital.
See less
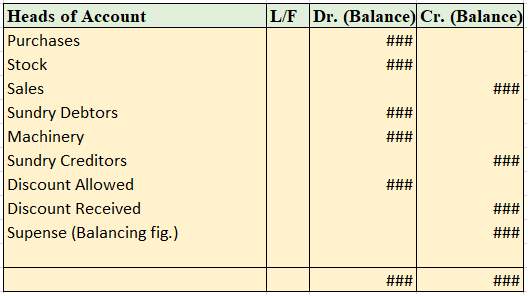
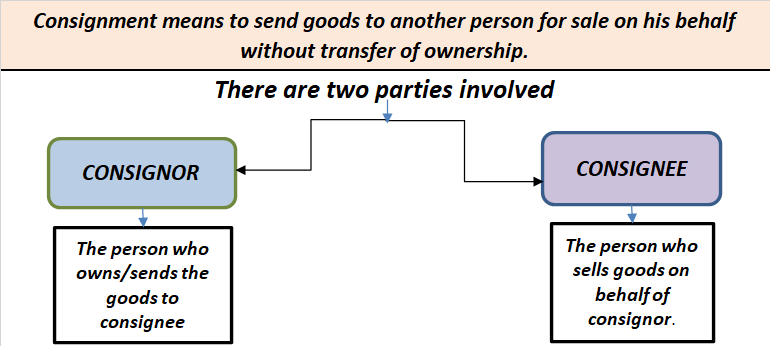
There are two types of ledger accounts in the accounting system – temporary and permanent. Temporary accounts are those whose balances zero out and we do not carry forward balances to the next year. Examples are revenue and expenses accounts or nominal accounts. The balances of such accounts are traRead more
There are two types of ledger accounts in the accounting system – temporary and permanent.
Temporary accounts are those whose balances zero out and we do not carry forward balances to the next year. Examples are revenue and expenses accounts or nominal accounts. The balances of such accounts are transferred to the profit and loss account and therefore are not balanced.
Permanent accounts are those whose balances are carried forward to the next accounting year in form of opening balances. These accounts are balanced and such balances are transferred to the balance sheet. Examples are assets, liability and capital accounts or personal and real accounts.
Balancing an account means equaling both the debit and the credit side of the account. Generally, there is a difference between the accounts recorded as a carry down balance in the case of permanent accounts and as a transfer balance in the case of temporary accounts.
Balancing serves as a check to the double-entry rule of accounting.
Balanced accounts
As discussed above, the balanced accounts are shown in the balance sheet and the balancing figure for such accounts are carried forward to the next accounting period.
Unbalanced accounts
As per the above discussion, the balancing figures of unbalanced accounts are transferred to the profit and loss account and no balances are carried forward to the next accounting period.
Suppose a company Shine Ltd. has machinery costing 5,00,000 at the beginning of the accounting period and charges depreciation of 10% on the asset. The company also has creditors amounting to 50,000 at the beginning of the period and purchases goods amounting to 30,000 on credit. It has a cash balance of 95,000 at the beginning of the period and earns interest amounting to 10,000.
Following ledgers would be prepared to record the above entries:
The above ledgers can be shown as follows:
The balance of the machinery account will be shown in the balance sheet and therefore it is a balanced account.
The balance is transferred to the profit and loss account and therefore depreciation account is an unbalanced account.
The balance of creditors account will be shown in the balance sheet and therefore it is a balanced account.
The balance is transferred to the profit and loss account and therefore purchases account is an unbalanced account.
The balance of the cash account will be shown in the balance sheet and therefore it is a balanced account.
The balance is transferred to the profit and loss account and therefore interest account is an unbalanced account.
See less