A Capital Account is an account that shows the owner's equity in the firm and a Partner's Capital Account is an account that shows the partner's equity in a partnership firm. Partner’s Capital Account includes transactions between the partners and the firm. Examples of such transactions are: CapitalRead more
A Capital Account is an account that shows the owner’s equity in the firm and a Partner’s Capital Account is an account that shows the partner’s equity in a partnership firm.
Partner’s Capital Account includes transactions between the partners and the firm. Examples of such transactions are:
- Capital introduced in the firm
- Capital withdrawn
- Interest on Capital
- Interest on Drawings
- Profit or loss in the financial year, etc.
When partners are given interest on their capital contribution in the firm, it is called on Interest on Capital.
In case the partnership firm does not have a Partnership Deed, the Partnership Act does not include a provision for Interest on Capital. However, if the partners want they can mutually decide the rate of Interest on Capital.
Interest on Capital is calculated on the opening capital of the partners and is only allowed when the firm makes a profit, that is, in case a firm incurs losses, it cannot allow Interest on Capital to its partners.
Example:
In a partnership firm, there are two partners A and B, and their capital contribution is Rs 10,000 and 20,000 respectively. Interest on capital is @ 10% p.a. The Interest on Capital for both the partners is:
Partner A- 10,000 * 10/100 = 1,000
Partner B- 20,000 * 10/100 = 2,000
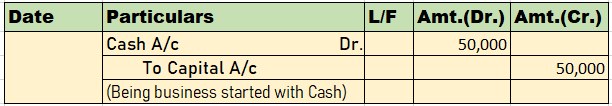
The journal entry for Interest on Capital is an adjusting entry and is shown as:
| Interest on Capital A/c Dr. | 3,000 | |
| To A’s Capital a/c | 1,000 | |
| To B’s Capital A/c | 2,000 |
- Partner’s Capital Account is credited because it is credit in nature and interest on capital is an addition to the account.
- Interest on Capital Account is debited because it is an expense account.
See less

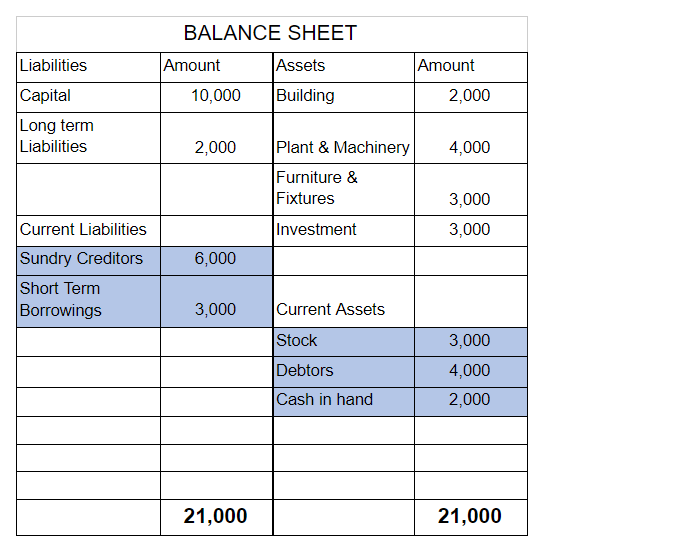
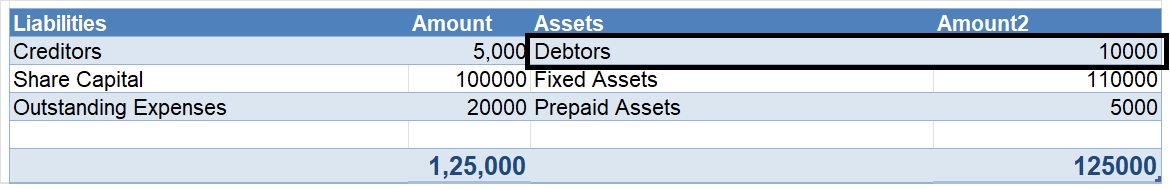
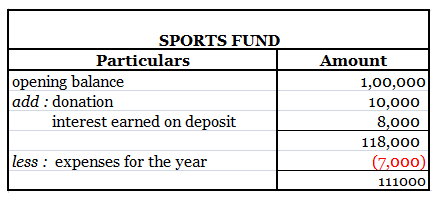

Working Capital is the capital used in the daily operations of the business. It is calculated as the difference between current assets and current liabilities. Gross working capital means current assets and net working capital means the difference between current assets and current liabilities. WorkRead more
Working Capital is the capital used in the daily operations of the business. It is calculated as the difference between current assets and current liabilities. Gross working capital means current assets and net working capital means the difference between current assets and current liabilities.
Working Capital indicates the short-term liquidity of its business. It means the ability of a company to meet its daily requirements through short-term financing.
Working Capital can be;
Positive or negative working capital follows a simple rule of math. If current assets are more than current liabilities, working capital is positive and if current assets are less than current liabilities, working capital is negative. When current assets are equal to current liabilities, working capital is zero.
Negative working capital for a short period means that the company has made a big payment to its vendors, or a significant increase in the creditor’s account because of credit purchases.
However, if working capital is negative for a longer period it indicates that the company is struggling with its operating requirements or that it has to finance its daily operations through long-term borrowings.
The current ratio for a company is calculated as:
Current Assets divided by Current Liabilities.
Working Capital and Current Ratio are interrelated. If the Current Ratio is more than 1, it means current assets exceed current liabilities and Working Capital is positive. However, if the Current Ratio is less than 1, it means current liabilities exceed current assets and Working Capital is negative.
For example-
If Current Assets are Rs 50,000 and Current Liabilities are Rs 70,000 then
Working Capital= Current Assets – Current Liabilities
WC = Rs 70,000 – Rs 50,000
WC = Rs. 20,000
Current Ratio = Current Assets / Current Liabilities
CR = Rs.50,000/ Rs. 70,000
CR = 0.71< 1
See less