The current ratio is a liquidity ratio that measures a firm’s ability to pay off its short-term liabilities with its current assets. The current ratio is important because short-term liabilities are due within a period of twelve months. The current ratio is calculated using two standard figures thatRead more
The current ratio is a liquidity ratio that measures a firm’s ability to pay off its short-term liabilities with its current assets. The current ratio is important because short-term liabilities are due within a period of twelve months.
The current ratio is calculated using two standard figures that are shown in the company’s balance sheet: current assets and current liabilities. The formula for the same goes as:
Current ratio = Current Assets / Current Liabilities
A current ratio of 2:1 is considered ideal. Generally, a ratio between 1.5 to 2 is considered beneficial for the business, which means that the company has more financial resources (Current Assets) to cover its short-term debt (Current Liabilities).
A high current ratio may indicate that the business is having difficulties managing its capital efficiently to generate profits.
On the other hand, a lower current ratio (especially lower than 1) would signify that the company’s current liabilities exceed its current assets and the business may have difficulty covering its short-term debt. Although the definition of a good current ratio may vary in the different industry groups.
Example- Where,
1) CR is 2:1, the company is in a good situation as it has double the Current Assets in order to cover the short-term debt.
2) CR is 0.5:1, the company is not in a good situation as it has only half the Current Assets in order to cover the short-term debt.
See less
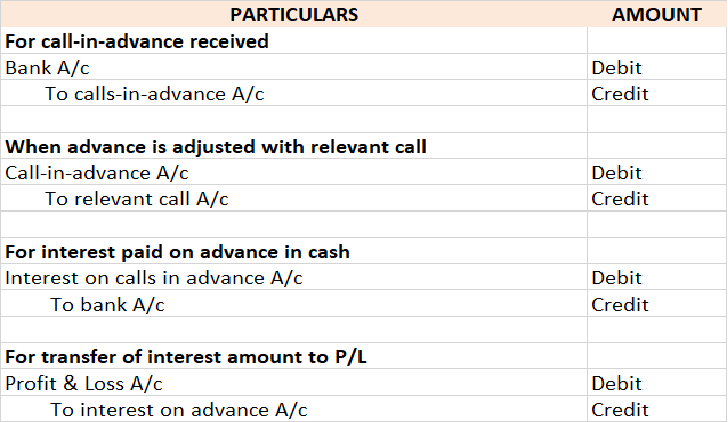
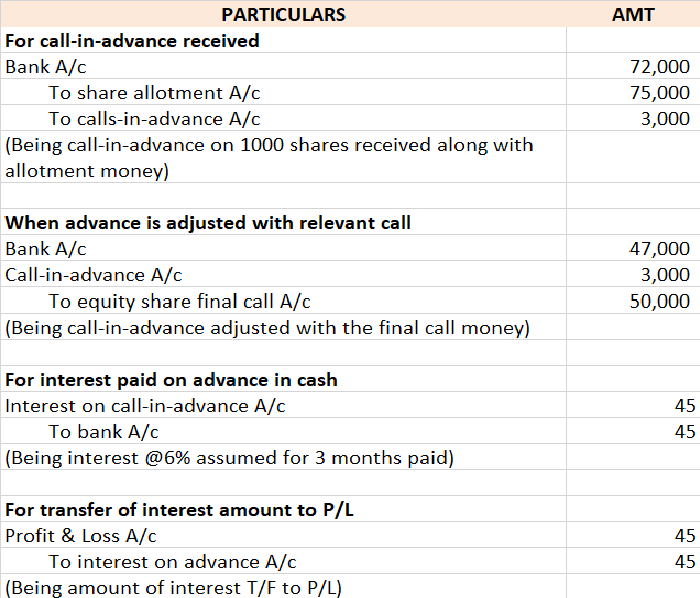
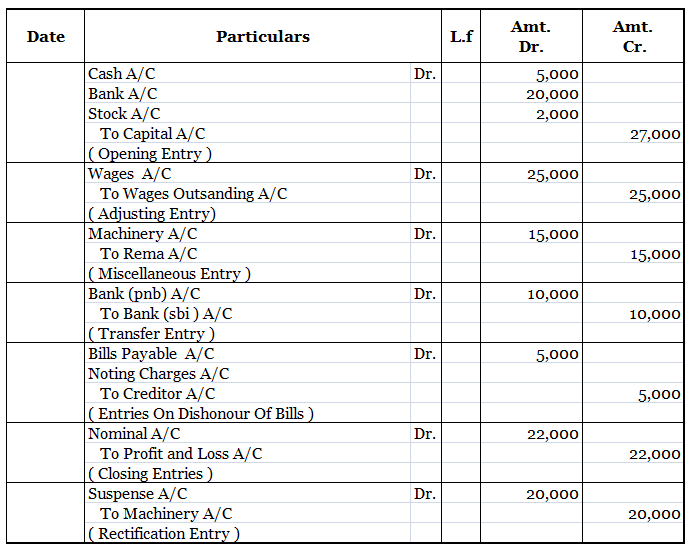
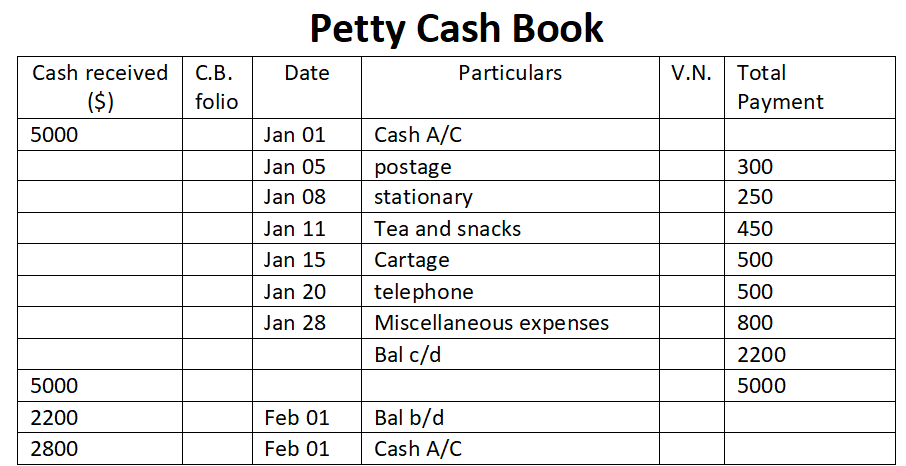
There are three types of businesses that can be commenced, they are sole proprietorship, partnership, and joint-stock company. As we all know, to start any business a certain sum of money has to be invested by the owner which is known as the capital of the business in terms of accounting. In companiRead more
There are three types of businesses that can be commenced, they are sole proprietorship, partnership, and joint-stock company. As we all know, to start any business a certain sum of money has to be invested by the owner which is known as the capital of the business in terms of accounting.
In companies, commencement is a declaration issued by the company’s directors with the registrar stating that the subscribers of the company have paid the amount agreed. In a sole proprietorship, the business can be commenced with the introduction of any asset such as cash, stock, furniture, etc.
Journal entry
In the journal entry, “Started business with Cash”
As per the golden rules of accounting, the cash a/c is debited because we bring in cash to the business, and as the rule says “debit what comes in, credit what goes out.” Whereas the capital a/c is credited because “debit all expenses and losses, credit all incomes and gains”
As per modern rules of accounting, cash a/c is debited as cash is a current asset, and assets are debited when they increase. Whereas, on the increment on liabilities, they are credited, therefore, capital a/c is credited.
Therefore, the entry we’ll be passing is-
See less