Return inwards are the goods returned by the customer to the seller. The goods are returned for reasons like defects, excess delivery, and low quality. Return inwards are also known as Sales Returns. Sales returns are a contra account to sales revenue. The amount of sales returns is deducted from thRead more
Return inwards are the goods returned by the customer to the seller. The goods are returned for reasons like defects, excess delivery, and low quality. Return inwards are also known as Sales Returns.
Sales returns are a contra account to sales revenue. The amount of sales returns is deducted from the total sales in the Trading section of the Trading and Profit & Loss Account.
In subsidiary books, return inwards are recorded only for those goods which are sold on credit to the customer.
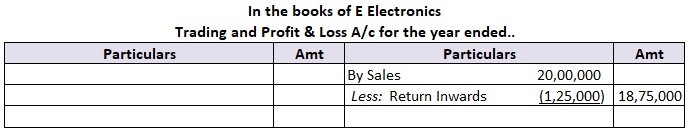
For example, On 1 August E Electronics sold 50 units of television to Hill Hotels on credit for Rs.25,000 each. Out of which 5 units were found to be defective and were returned back to E Electronics. In that accounting period, E Electronics made a total sales of Rs.20,00,000 (including the item sold to Hill Hotels).
E Electronics in its Trading section of Trading and P&L A/c will account for a sales return of Rs.1,25,000 (Rs.25,000*5) and this amount will be deducted from the total sales. The same will be recorded in the subsidiary books as it accounts for sales made on credit.
Extract of Profit & Loss Account:
For a business, sales returns will either have a decrease in the sales revenue or it will increase the sales returns and allowances which is a contra account to sales revenue. An increase in sales returns will decrease gross profit.
See less
Bad debts mean the money owed by customers who have gone bankrupt or the likelihood of who's ever returning the money is significantly low. Bad debt is a nominal account. A nominal account is an account that records the business transactions belonging to a certain category of income, expense, profitRead more
Bad debts mean the money owed by customers who have gone bankrupt or the likelihood of who’s ever returning the money is significantly low. Bad debt is a nominal account.
A nominal account is an account that records the business transactions belonging to a certain category of income, expense, profit or loss. The balances on nominal accounts are normally written off at the end of each financial year. For example, sales A/c, purchases A/c, interest income, loss from the sale of assets etc.
Why are bad debts A/c classified as a nominal account?
First of all, let us understand the other two types of accounts – personal accounts and real accounts.
Personal accounts deal with the records of the business’ transactions with a particular person or entity. For example Mukesh A/c, Mahesh A/c, Reliance A/c, Suresh and Co. A/c etc.
Real accounts deal with transactions and records related to assets. The balance in these accounts is normally carried forward from one period to another. For example “Furniture A/c “, ” Building A/c ” etc.
Now that we have understood the basic definitions of all three types of accounts, we can discuss the reason behind the classification of bad debts as nominal accounts.
A bad debt is a loss that the company has incurred. It may be due to bankruptcy of customers, customer fraud etc. The company isn’t going to receive that money. The bad debts are written off at the end of the year by transferring them to profit and loss A/c.
Thus, bad debts relate to loss and are normally not carried forward from one period to another. Hence, they are classified as nominal accounts.
Treatment of Bad Debts
Bad debts are written off at the end of each year by debiting them to the profit and loss A/c. The amount of bad debts is reduced from the amount of debtors that the company has.
A company may also choose to create a provision for bad debts for the balance amount of debtors that the company has after adjusting for bad debts. This provision represents a rough estimate of the amount due to debtors that the business expects to not receive. In other words, it is an estimate of customer bankruptcy that the business expects.
Conclusion
We can conclude that
- There are primarily three types of accounts – real, personal and nominal.
- Bad debts are a nominal account.
- Bad debts is a loss that the business has incurred
- It may be due to bankruptcy of customers, fraud etc
- Bad debts are written off each year by transferring them to the income statement
See less