The correct option is 3.) The term current assets do not include furniture. Explanation A current asset is any asset that can reasonably be expected to be sold, consumed, or exhausted through the normal operations of a business within one accounting year. Thus, current assets don't have life for morRead more
The correct option is 3.)
The term current assets do not include furniture.
Explanation
A current asset is any asset that can reasonably be expected to be sold, consumed, or exhausted through the normal operations of a business within one accounting year. Thus, current assets don’t have life for more than a year.
Example: Cash and cash equivalent, stock, liquid assets, etc.
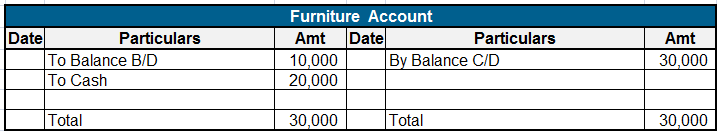
Furniture is expected to have a useful life for more than a year and they are bought for a long term by a company.
Cash is a more liquid asset of a company making it a more “current” asset. It requires no conversion and is spendable as it is. Thus, making it a vital current asset.
Stock in trade is a current asset because it can be converted into cash within one year and all the stock in trade of a company is expected to be sold within one accounting period and should not stick for a longer period.
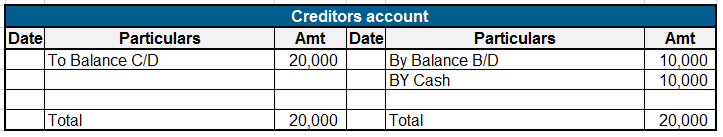
Advance payment, on the other hand, is an amount paid to an employee, essentially a short-term loan by the employer. It’s recorded on the asset side of the balance sheet and as these assets are used, they are expended and recorded on the income statement for the period in which they are incurred, making it a short-term asset ending within an accounting year.
Thus, on the asset side of the balance sheet, we can clearly see which current assets are and which are not included in the current asset
Balance Sheet (As at…..)
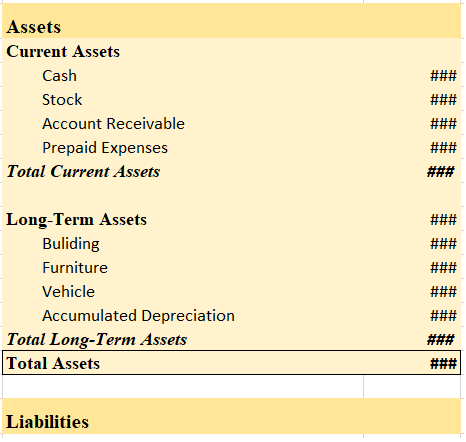
Therefore, (3) Furniture, won’t be included in current assets.
See less
A cheque that has been issued but yet not presented to the bank for payment is known as an unpresented cheque Generally what happens is when a cheque is issued to a party or say, creditor, the business immediately records them in the bank column of the cash book but the creditor might not present thRead more
A cheque that has been issued but yet not presented to the bank for payment is known as an unpresented cheque
Generally what happens is when a cheque is issued to a party or say, creditor, the business immediately records them in the bank column of the cash book but the creditor might not present them immediately to the bank for payment on the same date. The bank will only debit the account when it will be presented to it, therefore as long as the cheque remains unpresented there will be a difference in both the books i.e cash book and passbook.
Let me give you a short example of the above treatment
Suppose on 27th January, in the books of Mr. Shyam, the balance of the bank column as per the cash book is Rs 10,000. He received a cheque of Rs 5,000 from Mr. Hari, one of his debtors, which was sent to the bank for collection. The amount of the cheque was not collected by the bank until 31st January. Due to this, there arises a difference of Rs 5,000 in the cash book and pass book of Mr. Shyam.
Following will be the entry in Mr. Shyam cash book and passbook
In the books of Mr. Shaym
Cash book (bank column only)
Mr. Shyam
Bank Statement
How it is treated in the bank reconciliation statement?
There lies a temporary difference in both the books as the represented cheques will eventually be presented. Therefore we will not alter the cash book. The bank statement shows the greater amount of Rs 5,000 as compared to the cashbook, therefore we will debit the amount of unpresented cheque which will eventually make it balance to the level of bank statement.
See less