Goodwill Patents Preliminary Expense A/c Claims Receivable
Definition Current assets are defined as cash and other assets that are expected to be converted into cash or consumed in the production of goods or rendering of services in the normal course of business. Or in other words, we can say that the expected realization period is less than the operating cRead more
Definition
Current assets are defined as cash and other assets that are expected to be converted into cash or consumed in the production of goods or rendering of services in the normal course of business.
Or in other words, we can say that the expected realization period is less than the operating cycle period although it is more than the period of 12 months from the date of the balance sheet.
For example, goods are purchased with the purpose to resell and earn a profit, debtors exist to convert them into cash i.e., receive the amount from them, bills receivable exist again for receiving cash against it, etc.
List of current assets
The list of current assets is as follows:-
- Cash in hand
- Cash equivalents
- Bills receivables
- Sundry debtors
- Prepaid expenses
- Accrued income
- Closing stock
- Short-term investments ( marketable securities )
- Other liquid assets
Now here are a few definitions for the above list of current assets which are as follows:-
-
Cash in hand
Cash comprises cash on hand and demand deposits with banks.
-
Cash equivalents
Cash equivalents are short-term, highly liquid investments that are readily convertible into known amounts of cash and which are subject to an insignificant risk of changes in value.
-
Bills receivables
It means a bill of exchange accepted by the debtor, the amount of which will be received on the specific date.
-
Sundry debtors
A debtor is a person or entity who owes an amount to an enterprise against credit sales of goods and/or services rendered.
-
Prepaid expenses
Expense that has been paid in advance and benefit of which will be available in the following years or year.
-
Accrued income
Income that has been earned in the accounting period but in respect of which no enforceable claim has become due in that period by the enterprise.
-
Closing stock
Stock or inventory at the end of the accounting period which is shown in the balance sheet and which is valued on the basis of the “ cost or net realizable value, whichever is lower “ principle is called closing stock.
-
Short term investment
Investments that are also known as marketable securities and are held for a temporary period of time i.e, for less than 12 months, and can be easily converted into cash are called short-term investments.
Criteria for classification
Now let us see the classification of assets in the case of companies as per Schedule III of the Companies act 2013.
An asset is a current asset if it satisfies any one of the following criteria which are as follows:-
- It is held primarily for the purpose of being traded.
- It is expected to be realized in or is intended for sale or consumption in the company’s normal operating cycle.
- It is expected to be realized within 12 months from the reporting date.
- It is cash and cash equivalent unless it is restricted from being exchanged or used to settle a liability for at least 12 months after the reporting date.
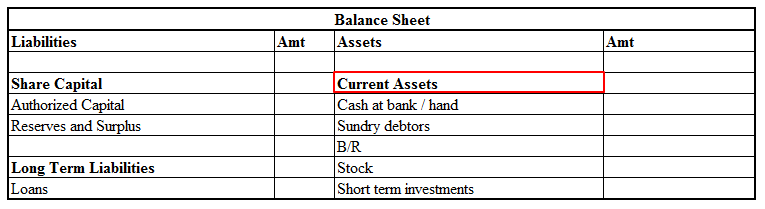
Here is an extract of the balance sheet showing current assets

Fictitious assets are expenses or losses not written off entirely in the profit and loss account during the accounting year in which they occur. Fictitious assets have no realizable value or physical existence. In the above, (C) preliminary expense is a fictitious asset. Preliminary expenses are theRead more
Fictitious assets are expenses or losses not written off entirely in the profit and loss account during the accounting year in which they occur. Fictitious assets have no realizable value or physical existence.
In the above, (C) preliminary expense is a fictitious asset. Preliminary expenses are the expenses incurred before the incorporation of a business. The word ‘fictitious’ means fake, these are not actually the assets of a company even though they are represented in the assets of the balance sheet.
Since the benefit of a fictitious asset is received over a period of time, the whole amount is not charged to the profit and loss account. The amount is amortized over several years. These expenses are non-recurring in nature. These expenses are shown as assets under the head miscellaneous expenditure. Also known as deferred revenue expenditure.
For example: A company incurred $50,000 as promotion costs before the formation of the business. This promotion cost will be deferred over 5 years. In the first year, $10,000 will be charged to the profit and loss account and the remaining $40,000 will be shown as an asset under the heading miscellaneous expenditure. Subsequently, $10000 will be charged to profit and loss for the next 4 years. The amount of $50,000 will be deferred over a span of 5 years.
Some other examples of fictitious assets :
Goodwill
Goodwill is not a fictitious asset because goodwill has a realizable value and can be sold in the market. Goodwill is an intangible asset which does not have a physical existence but can be traded for monetary value. Goodwill has an indefinite life and is sold when the business is sold. Goodwill can be self-generated or purchased. Goodwill is shown as an intangible asset under the heading fixed asset in the financial statements.
Patents
Patents are intangible assets which do not have a physical existence but have realizable value and can be sold in the market. So, patents do not come under the category of fictitious assets. Patents are basically intellectual property. The purchase price of the patent is the initial purchase cost which is amortized over the useful life of the asset. Patents are shown as intangible assets under the heading fixed asset in the balance sheet of the company.
Claim receivable
Claim receivable is an asset if the claim has been authorized by the insurance company. Claim receivable has a monetary value, so does not come under the category of a fictitious asset. If the claim is not yet authorized by an insurance company, it will be shown as a footnote in the financial statements. Authorized claim receivable is shown as a current asset in the financial statement.
See less