Expenses are of two types, are Direct Expenses Indirect Expenses Direct Expenses Direct expenses are those expenses are which are directly related to the manufacturing or production of the final goods. These expenses are also known as Manufacturing expenses. Manufacturing or production of gooRead more
Expenses are of two types, are
- Direct Expenses
- Indirect Expenses
Direct Expenses
Direct expenses are those expenses are which are directly related to the manufacturing or production of the final goods. These expenses are also known as Manufacturing expenses.
Manufacturing or production of goods indicates the conversion of Raw material into finished goods. the expenses incurred in the stage of conversion are treated as Direct expenses or Manufacturing expenses.
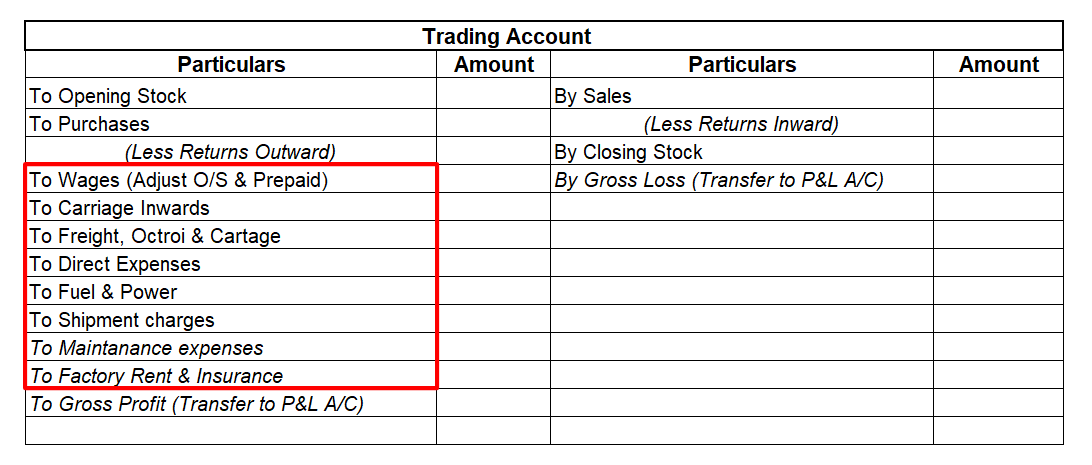
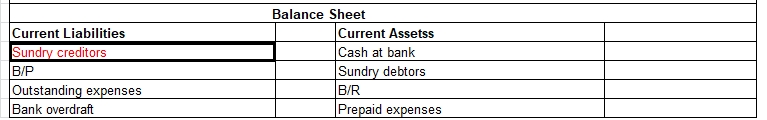
Direct expenses are shown on the Debit side of the Trading Account.
Indirect Expenses
Indirect expenses are those expenses that are incurred to run a business day-to-day and maintenance of the company. In other words, they are not directly related to making a product or service or buying a wholesale product to resell.
Indirect expenses are classified into three types, which are
- Factory Expenses
- Administrative Expenses
- Selling & Distribution Expenses
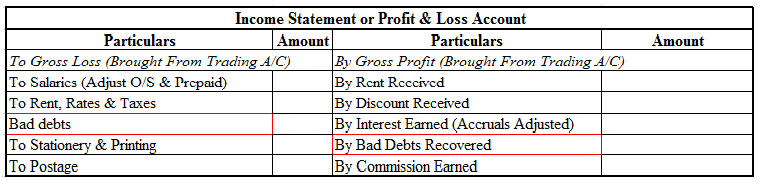
Indirect Expenses are shown on the Debit side of the Profit and Loss Account.
Presentation of Direct Expenses in Trading Account
Examples of Direct Expenses
- Gas, water, and Fuel: Gas, water, and fuel are the essentials to run a factory and are used in machinery to manufacture its final goods.
- Wages: Wages are the daily payments to the workers or Labours working in the factory premises on a daily or weekly payment basis.
- Freight and Carriage: Freight and Carriage are the expenses related to the importing of raw materials from the godown or from the outsiders to the Factory.
- Factory Rent: Rent paid for the factory area or any payment related to the place of the factory is known as factory rent.
- Factory Lighting: The expenses related to the uniform distribution of light over the working plane are obtained in the factory premises.
- Factory Insurance: The payment of insurance related to the factory will come under direct expenses.
- Manufacturing Expenses: Any other expenses related to the manufacturing process of finished goods are manufacturing expenses.
- Cargo Expenses: These are the expenses related to goods or freight being shipped or carried by the ocean, air, or land from one place to another.
- Upkeep and Maintenance: These are the expenses related to the maintenance of the factory for smooth running.
- Repairs on Machinery: The expenses related to any repair on machinery which is used in the production.
- Coal, Oil, and Grease: Coal, oil, and grease are the essentials to run machinery which results in the conversion of raw material to finished goods.
- Custom Charges: The expenses related to the payment of any Customs duty for the material imported.
- Clearing Charges: A clearing charge is a charge assessed on securities transactions by a clearing house for completing transactions using its own facilities.
- Depreciation on Machinery: Generally it is a nonmonetary expense but recorded in the trading account as a direct expense as per the accrual accounting.
- Import duty: any payment related to the importing of any machinery or any material from other countries is known as import duty.
- Octroi: this is the tax levied by a local political unit, normally the commune or municipal authority, on certain categories of goods as they enter the area.
- Shipping expenses: any expense related to the shipment charges of the raw material is known as shipping expenses.
- Motive power: Motive Power basically means any power, such as electricity or steam energy, etc, used to impart motion to any source of mechanical energy.
- Dock dues: a payment that a shipping company must pay for the use of a port.

Revenue also called income is nothing but the income generated by individuals or businesses from the sale of goods or investing capital or assets. Some examples of revenue are as follows:- Sales revenue Dividend received Interest earned Rent received Commission 1. SALES REVENUE Sales revenueRead more
Revenue also called income is nothing but the income generated by individuals or businesses from the sale of goods or investing capital or assets. Some examples of revenue are as follows:-
1. SALES REVENUE
Sales revenue is the income received by the individual or business by selling its product or provision of services. the words “sale” and “revenue” are used interchangeably to mean the same thing. It is to be noted that revenue does not necessarily mean it has been received in cash, it can be partly in cash or partly on credit also.
How to calculate sales revenue?
SALES REVENUE = NO. OF UNITS SOLD * AVERAGE PRICE PER UNIT
For example:- Amazon sold 4000 units of shirts @ 500 each. Therefore sales revenue for amazon is
Sales revenue = 4000 * 500
= 20,00,000
Treatment of sales revenue in the financial statement, since sales are part of a trading account and appear on the credit side of the trading account.
2. DIVIDEND RECEIVED
Naina, this can be explained in simple terms. Suppose you own shares of a company which declares dividend so the dividend received is income for you. Since it does not reduce the assets of a company nor creates a liability it is shown as income and posted on the credit side of profit & loss A/c.
Let me give you a short example of a dividend received, suppose you own 1000 shares of ABC.ltd. the company at the quarter-end calculate its earnings and decides to declare a dividend of Rs 5 per share. Therefore you would receive 1000* 5 i.e Rs 5000 as dividend income.
3. INTEREST INCOME EARNED
Interest income is the earnings the entity receives on any investments made. To be more precise it is money earned by an individual or business for lending their fund either by putting them as deposit in the bank. It is shown on the credit side of the profit & loss A/c.
A very simple example for interest earned is when a business or an individual deposits money in the bank as savings and decided not to touch it for the coming years then such a depositor will gain interest on such savings by the bank. such type of income so received is treated as interest received and shown as income in the profit & loss A/c.
3. RENT RECEIVED
When money is received by the business for exchange of use of assets of the business by the other person, then it will be called rent received. Rent can be received by the business firm in respect of land, building, machinery, etc. As rent received is income for the business firm, it is shown on the credit side of profit & loss A/c.
For example, X. ltd received Rs 20,000 via cash on one of its properties to Mr. Z. Then rent so received shall be treated as income in the books of ABC. ltd and same shall be treated as income and shown in the profit & loss statement.
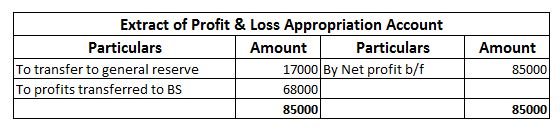
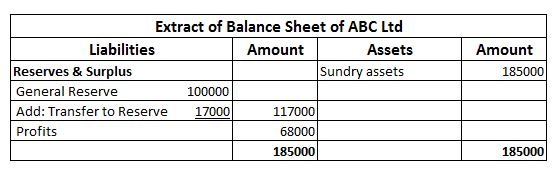
Summarised extract of profit & loss account is shown below for dividend received, Rent received and interest earned.

See less