Introduction Internal reconstruction refers to the process of restructuring a sick company’s balance sheet by certain methods to turn it financially healthy, thus saving it from potential liquidation. Explanation When a company has been making losses for many years, it has a huge amount of accumulatRead more
Introduction
Internal reconstruction refers to the process of restructuring a sick company’s balance sheet by certain methods to turn it financially healthy, thus saving it from potential liquidation.
Explanation
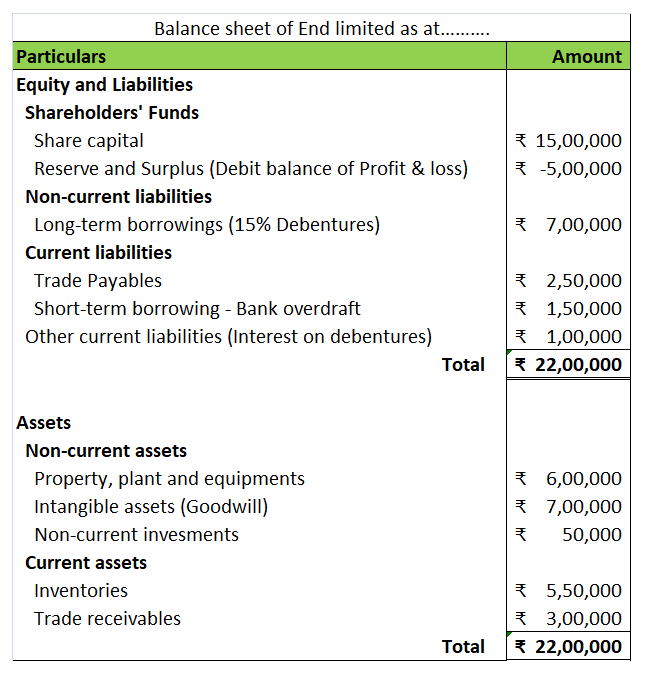
When a company has been making losses for many years, it has a huge amount of accumulated losses due to which the reserve and surplus appear at a very low or negative amount in the balance sheet.
Also, such a company is said to be overcapitalised as it is not able to generate enough returns to its capital.
As the company is overcapitalised, the assets are also overvalued. The balance sheet also contains many fictitious assets and unrepresented intangible assets.
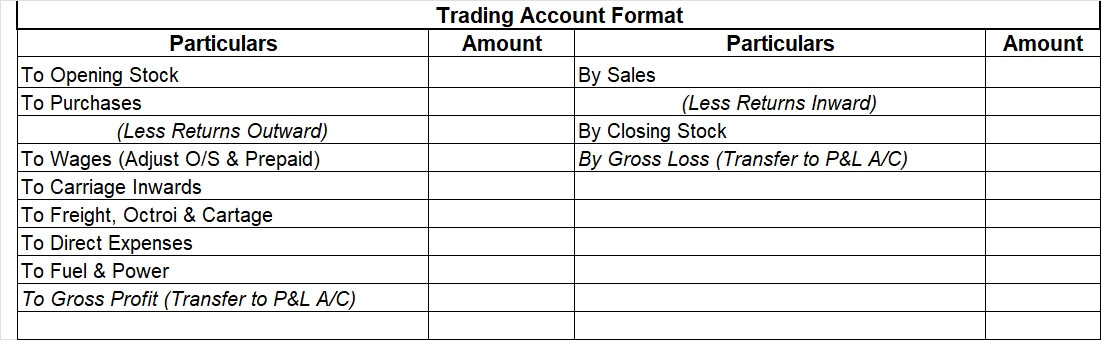
The balance sheet of such a ‘sick’ company looks like the following:
Hence, to save the company from liquidation,
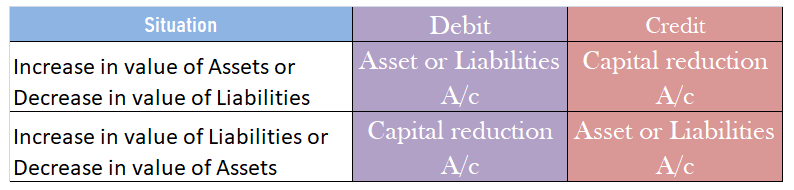
- its assets and liabilities are revalued and reassessed,
- its capital is reduced by paying off part of paid-up capital to shareholders or cancelling the paid-up capital.
- the right of shareholders related to preference dividends is altered,
- agreements are made with creditors to reduce their claims and
- fictitious assets and accumulated losses are written off.
In this way, its balance sheet gets rid of all undesirable elements and the company gets a new life without being liquidated. This process is known as internal reconstruction.
Legal compliance
The internal reconstruction of a company is governed by the provisions of the Companies Act, 2013.
See less

Outstanding Income is the income that is due and is being earned but not yet received. The person/ firm has the legal rights to receive that part of the income which it has earned. Outstanding Income is an Asset Account for the business/ the person. According to the modern approach, for Asset AccounRead more
Outstanding Income is the income that is due and is being earned but not yet received. The person/ firm has the legal rights to receive that part of the income which it has earned.
Outstanding Income is an Asset Account for the business/ the person.
According to the modern approach, for Asset Account:
So the journal entry will be-
For Example, Mr. Rashid works as a laborer in a factory and he earns wages @Rs 500/day.
So by the end of the week, he receives a payment of Rs 3000 of Rs 3500 i.e. he receives payment of 6 days instead of 7 days. So here Rs 500 would be an outstanding income of Mr. Rashid as he has earned that income but has not received it yet.
Journal Entry –
Another example, Yes Bank gave a loan of Rs 10,00,000 to company Ford @ 10% as interest payable monthly. The interest for one month i.e. Rs 1,00,000 has not been received by Yes Bank which is being due. So it will be outstanding income for Yes Bank since it is due but not yet received.
Journal entry-
Accounting Treatment for Outstanding Income-
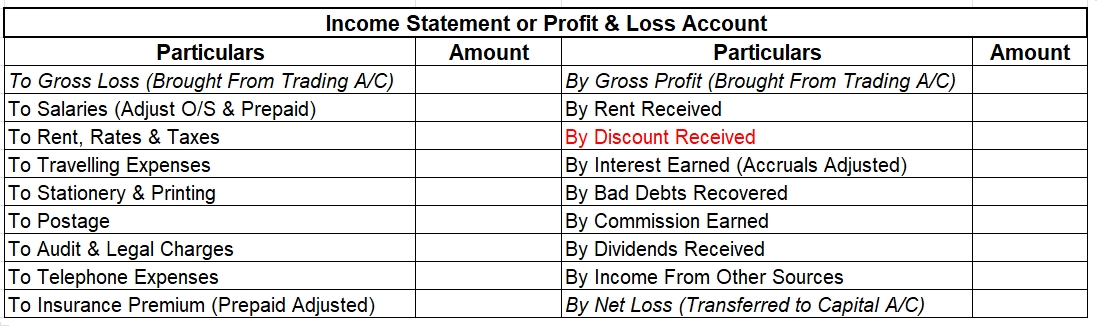
The Outstanding Income is shown on the credit side of the income statement as the income is earned for the current year but not yet received.
Outstanding Income is an Asset for the business and hence shown on the Assets side of the balance sheet.
See less