Working capital is defined as the difference between current assets and current liabilities of a business. Current assets include cash, debtors and stock whereas current liabilities include creditors and short term loans etc. FORMULA Current Assets - Current Liabilities = Working Capital Zero workinRead more
Working capital is defined as the difference between current assets and current liabilities of a business. Current assets include cash, debtors and stock whereas current liabilities include creditors and short term loans etc.
FORMULA
Current Assets – Current Liabilities = Working Capital
Zero working capital is when a company has the exact same amount of current assets and current liabilities. When both are equal, the difference becomes zero and hence the name, Zero working capital. Working Capital may be positive or negative. When current assets exceed current liabilities, it shows positive working capital and when current liabilities exceed current assets, it shows negative working capital.
Zero working capital can be operated by adopting demand-based production. In this method, the business only produces units as and when they are ordered by the customers. Through this method, all stocks of finished goods will be eliminated. Also, raw material is only ordered based on the amount of demand.
This reduces the investment in working capital and thus the investment in long term assets can increase. The company can also use the funds for other purposes like growth or new opportunities.
EXAMPLE
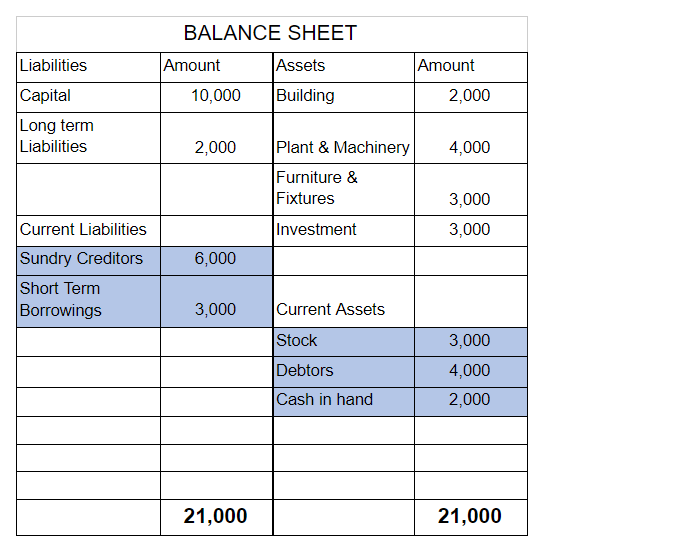
Suppose a company has Inventory worth Rs 3,000, Debtors worth Rs 4,000 and cash worth Rs 2,000. The creditors of the company are Rs 6,000 and short term borrowings are Rs 3,000.
Now, total assets = Rs 9,000 ( 3,000 + 4,000 + 2,000)
And total liabilities = Rs 9,000 ( 6,000 + 3,000)
Therefore, working capital = 9,000 – 9,000 = 0


Introduction Internal reconstruction refers to the process of restructuring a sick company’s balance sheet by certain methods to turn it financially healthy, thus saving it from potential liquidation. Explanation When a company has been making losses for many years, it has a huge amount of accumulatRead more
Introduction
Internal reconstruction refers to the process of restructuring a sick company’s balance sheet by certain methods to turn it financially healthy, thus saving it from potential liquidation.
Explanation
When a company has been making losses for many years, it has a huge amount of accumulated losses due to which the reserve and surplus appear at a very low or negative amount in the balance sheet.
Also, such a company is said to be overcapitalised as it is not able to generate enough returns to its capital.
As the company is overcapitalised, the assets are also overvalued. The balance sheet also contains many fictitious assets and unrepresented intangible assets.
The balance sheet of such a ‘sick’ company looks like the following:
Hence, to save the company from liquidation,
In this way, its balance sheet gets rid of all undesirable elements and the company gets a new life without being liquidated. This process is known as internal reconstruction.
Legal compliance
The internal reconstruction of a company is governed by the provisions of the Companies Act, 2013.
See less