Similarly, someone asked Are loose tools current assets
Similarly, someone asked Are loose tools current assets
See lessPlease briefly explain why you feel this question should be reported.
Please briefly explain why you feel this answer should be reported.
Please briefly explain why you feel this user should be reported.
Similarly, someone asked Are loose tools current assets
Similarly, someone asked Are loose tools current assets
See lessDefinition Prepaid expenses are those expenses whose payments are done in advance which can be for the goods or services whose benefit will accrue in the subsequent accounting period. A prepaid expense is a current asset. prepaid expenses are classified under the head current assets in the balance sRead more
Prepaid expenses are those expenses whose payments are done in advance which can be for the goods or services whose benefit will accrue in the subsequent accounting period.
A prepaid expense is a current asset. prepaid expenses are classified under the head current assets in the balance sheet.
This is because they provide future economic benefits to the company. As such, they are assets that can be used to generate revenue in the future.
For example prepaid rent, prepaid insurance, etc.
Current assets are defined as cash and other assets that are expected to be converted into cash or consumed in the production of goods or rendering of services in the normal course of business.
Or in other words, we can say that the expected realization period is less than the operating cycle period although it is more than the period of 12 months from the date of the balance sheet.
For example, goods are purchased with the purpose to resell and earn a profit, debtors exist to convert them into cash i.e., receive the amount from them, bills receivable exist again for receiving cash against it, etc.
Current liabilities are liabilities that are payable generally within 12 months from the end of the accounting period or in other words which fall due for payment in a relatively short period.
For example bills payable, short-term loans, etc.
Now let me try to explain to you that prepaid expenses are classified as current assets and not as a current liability which is as follows :
Now let us take an example for explaining prepaid expenses which are mentioned below.
An insurance premium of Rs 50000 has been paid for one year beginning (previous year). The financial year ends on 31st march YYYY.
It means the premium for 6 months i.e., 1st April, YYYY(current year) to 30th September, YYYY(current year) amounting to Rs 25000 is paid in advance.
Thus, of premium paid in advance (Rs 25000) is a Prepaid Expense. It will be accounted as an expense in the financial year ending 31st march next year. In the balance sheet as of 31st march YYYY ( current year ) it will be shown as Current Asset.
Here is an extract of the profit /loss account and balance sheet of the above example:
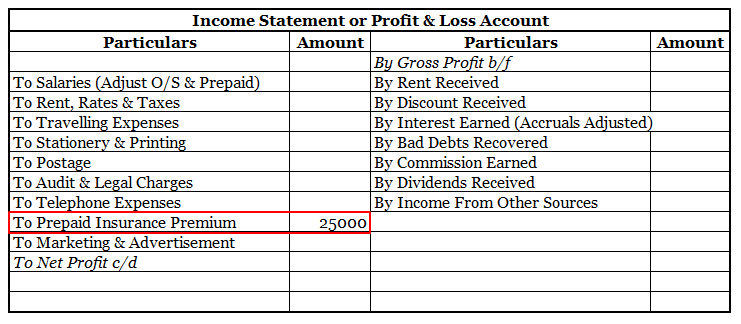
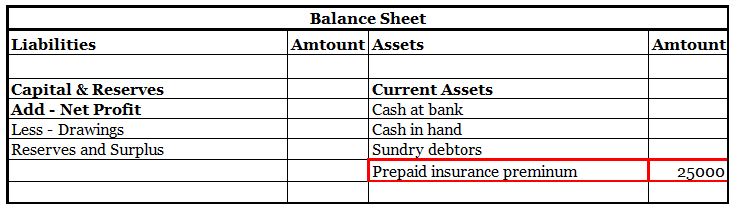
There are a few things to keep in mind when dealing with prepaid expenses.
See less
Accruals are not the same as provisions both are totally different from each other. Accruals and provision both are vital parts of accounts but work differently Accrual Accrual expense means the transaction that takes place in a particular period must be accounted for in that period only irreRead more
Accruals are not the same as provisions both are totally different from each other. Accruals and provision both are vital parts of accounts but work differently
Accrual
Accrual expense means the transaction that takes place in a particular period must be accounted for in that period only irrespective of the fact when such an amount has been paid.
An accrual of the expenditure which is not paid will be listed in the books of accounts. These accruals can be further divided into two parts
Accrual Expense
Accrual Expense means any transaction that takes place in a particular period but the amount for it will be paid on a later period.
For example- 10,000 for the month of March was paid in April month then this rent will be accounted for in the books in March
These are the following accrued expense
Accrual Revenue
Accrual Revenue means any transaction that takes place in a particular period but the amount for it will be received on later period. For example- If interest of 10,000 on bonds for the period of March is received in April months then this amount will be accounted for in March. These are the following accrued revenue
PROVISIONS
Provision refers to making a provision/allowance against any probable future expense that the company might incur in the near future. This amount is uncertain and difficult to predict its surety.
However, as per the prudence concept of accounting a company needs to anticipate the losses that will incur in the near future due to which provision is made.
For example- A company has debtors of 10,000 but as per the company’s previous records company anticipates that 1% of debtors will become bad debts. So in this case company will make a provision of 1% that is 100 on it.
There are various types of provisions which are-
Financial analysis of a company means analyzing the previous data of the company and giving recommendations based on that whether the company will improve in the future on not. It is the process of evaluating the financial performance and stability of the company. There are various types of financiaRead more
Financial analysis of a company means analyzing the previous data of the company and giving recommendations based on that whether the company will improve in the future on not.
It is the process of evaluating the financial performance and stability of the company.
There are various types of financial analysis. They are leverage, growth, cash flow, liquidity, profitability, etc.
The main objectives of Financial analysis are
1.Reviewing the current position: In order to know if the company is doing well, past analysis of data is required to be carried out. Regular recording of the transactions helps to understand the financial position of the company.
For example, A company wants to generate a revenue of 2000 crores in the next 5 years. The last four years’ data shows revenue as 1100, 1300,1600, 1800 crores respectively.
So from the above, we can say that the company is performing well and looks like it will reach the desired target in the fifth year or may perform better than the target desired.
However, if the revenue declines, it will cause concern for the team but the team will get time to gear up and work efficiently to achieve the desired target.
2. Ease in decision making: For Future decision-making, quarterly financials play an important role. Subsidiary books and accounts like the sales book, purchase orders, manufacturing a/c, etc. help in giving more reliable information.
For example, If sales are increasing inconsistently in a quarter, and in the next quarter the level of sales decrease due to any reason then the management can analyze and change the strategy.
3. Performance Comparison: It helps in comparing the performance of the business every month, quarterly, half-yearly, and yearly. Analyzing the data can help the management to compare if the company is proceeding in the right direction.
4. Assessing the profitability: Financial statements are used to assess the profitability of the firm. The analysis is made through the accounting ratios, trend line, etc. Accounting ratios calculated for a number of years shows the trend of change of position i.e. positive, negative or static. The assessing of the trend helps the management to analyze if the company is making profits or not.
5. Measure the solvency of the firm: Financial analysis helps to measure the short-term and long-term efficiency of the firm for the benefit of the Stakeholders.
6. Helps the end-users: The owners are the end-users for whom the financial statements are prepared. Financial statements are the summaries that are prepared for providing various disclosures to the owners which helps them understand the statements in a better way. If the end-users arrive at the right decision with the help of financial statements that means the objective is achieved.
7. Other objectives:
General reserve is the part of profits or money kept aside to meet future uncertainties and obligations of the entity. General reserve is created out of revenue profits for unspecified purposes and therefore is also a part of free reserves. General reserve forms a part of the Profit & Loss ApprRead more
General reserve is the part of profits or money kept aside to meet future uncertainties and obligations of the entity. General reserve is created out of revenue profits for unspecified purposes and therefore is also a part of free reserves.
General reserve forms a part of the Profit & Loss Appropriation account and is created to strengthen the financial position of the entity and serves as a sources of internal financing. It is upon the discretion of the management as to how much of a reserve is to be created. No reserve is created when the entity incurs losses.
General reserve is shown in the Reserves & Surplus head on the liability side of the balance sheet of the entity and carries a credit balance.
Suppose, an entity, ABC Ltd engaged in the business of electronics earns a profit of 85000 in the current financial year and has an existing general reserve amounting to 100000. The management decides to keep aside 20% of its profits as general reserve.
Then the amount to be transferred to general reserve will be = 85000*20% = 17000.
In the financial statements it will be shown as follows-
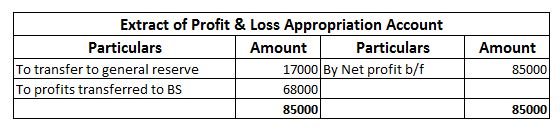
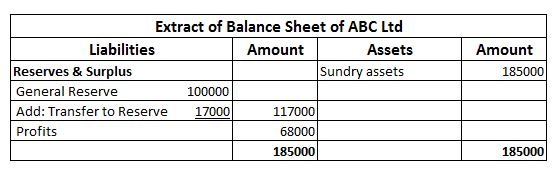
Now, in the next financial year, the entity incurs losses amounting to 45000. In this case, no amount shall be transferred to the general reserve of the entity and will be shown in the financial statement as follows-
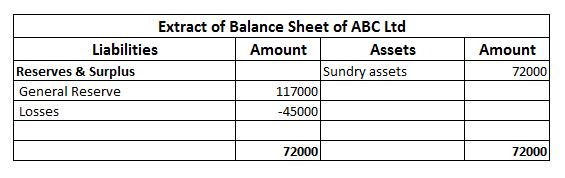
The creation of general reserve can sometimes be deceiving since it does not show the clear picture of the entity and absorbs losses incurred.
See lessGoodwill Patents Preliminary Expense A/c Claims Receivable
Fictitious assets are expenses or losses not written off entirely in the profit and loss account during the accounting year in which they occur. Fictitious assets have no realizable value or physical existence. In the above, (C) preliminary expense is a fictitious asset. Preliminary expenses are theRead more
Fictitious assets are expenses or losses not written off entirely in the profit and loss account during the accounting year in which they occur. Fictitious assets have no realizable value or physical existence.
In the above, (C) preliminary expense is a fictitious asset. Preliminary expenses are the expenses incurred before the incorporation of a business. The word ‘fictitious’ means fake, these are not actually the assets of a company even though they are represented in the assets of the balance sheet.
Since the benefit of a fictitious asset is received over a period of time, the whole amount is not charged to the profit and loss account. The amount is amortized over several years. These expenses are non-recurring in nature. These expenses are shown as assets under the head miscellaneous expenditure. Also known as deferred revenue expenditure.
For example: A company incurred $50,000 as promotion costs before the formation of the business. This promotion cost will be deferred over 5 years. In the first year, $10,000 will be charged to the profit and loss account and the remaining $40,000 will be shown as an asset under the heading miscellaneous expenditure. Subsequently, $10000 will be charged to profit and loss for the next 4 years. The amount of $50,000 will be deferred over a span of 5 years.
Some other examples of fictitious assets :
Goodwill is not a fictitious asset because goodwill has a realizable value and can be sold in the market. Goodwill is an intangible asset which does not have a physical existence but can be traded for monetary value. Goodwill has an indefinite life and is sold when the business is sold. Goodwill can be self-generated or purchased. Goodwill is shown as an intangible asset under the heading fixed asset in the financial statements.
Patents are intangible assets which do not have a physical existence but have realizable value and can be sold in the market. So, patents do not come under the category of fictitious assets. Patents are basically intellectual property. The purchase price of the patent is the initial purchase cost which is amortized over the useful life of the asset. Patents are shown as intangible assets under the heading fixed asset in the balance sheet of the company.
Claim receivable is an asset if the claim has been authorized by the insurance company. Claim receivable has a monetary value, so does not come under the category of a fictitious asset. If the claim is not yet authorized by an insurance company, it will be shown as a footnote in the financial statements. Authorized claim receivable is shown as a current asset in the financial statement.
See lessFirstly, let’s understand the meaning of both terms. Revenue receipts: The term 'revenue' suggests these are the amounts received by a business due to its operating activities. These receipts arise in a recurring manner in a business. Such receipts don’t affect the balance sheet. They are shown inRead more
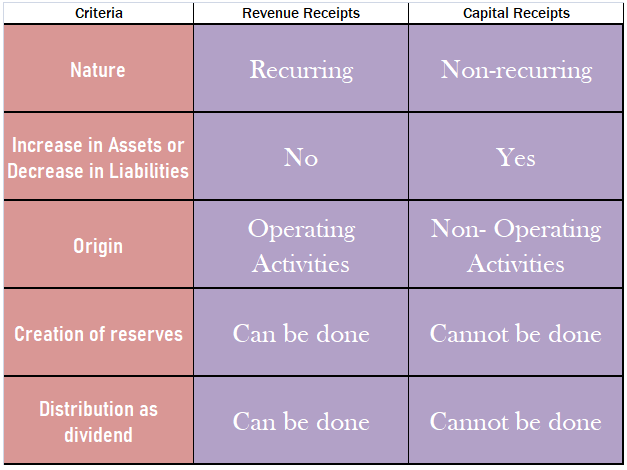
Firstly, let’s understand the meaning of both terms.
Revenue receipts: The term ‘revenue‘ suggests these are the amounts received by a business due to its operating activities. These receipts arise in a recurring manner in a business. Such receipts don’t affect the balance sheet. They are shown in the statement of profit or loss. Such receipts are essential for the survival of the business.
Examples of revenue receipts are as follows:
Capital receipts: The term ‘capital’ that such receipts are do not arise due to operating activities, hence not shown in the Profit and loss statement. These are the money received by a business when they sell any asset or undertake any liability. These receipts do not arise in a recurring manner in a business. They don’t affect the profit or loss of the business. They are not essential for the survival of the business.
Examples of capital receipts are as follows:
I have given a table below for more understanding:
No, the building is not a current asset. Explanation Current assets are those in a business that is reasonably expected to be sold, consumed, cashed, or exhausted within one year of accounting through normal day-to-day business operations. Examples: Cash and cash equivalent, stock, liquid assets, etRead more
No, the building is not a current asset.
Current assets are those in a business that is reasonably expected to be sold, consumed, cashed, or exhausted within one year of accounting through normal day-to-day business operations.
Examples: Cash and cash equivalent, stock, liquid assets, etc.
The building is expected to have a valuable life for more than a year and is bought for a longer term by a company. The building is a fixed asset/non-current asset, those assets which are bought by the company for a long term and aren’t supposed to be consumed within just one accounting year.
In order to understand it more clearly, let’s see the two types of assets in the classification of the assets on the basis of convertibility:
In the classification of the assets on the basis of their convertibility, they are classified either as current assets or fixed assets. Also referred to as current assets/ non-current assets or short-term/ long-term assets.
Let us take a look at the balance sheet’s asset side and see where building and current assets are shown
Balance Sheet (for the year ending…)
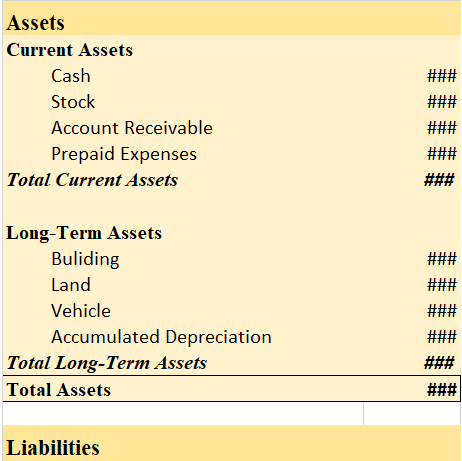
As we can see, the building is shown on the long-term assets side and not in the current assets.
Therefore, the building is not a current asset.
See less
The reserves created for specific purposes in business are called specific reserves. According to the Companies Act, 2013, these reserves cannot be used for any other purposes. However, if the Article of Association of a company allows, these reserves can be used for other purposes as well. Amount tRead more
The reserves created for specific purposes in business are called specific reserves. According to the Companies Act, 2013, these reserves cannot be used for any other purposes. However, if the Article of Association of a company allows, these reserves can be used for other purposes as well.
Amount to any specific reserve is generally transferred from the Profit and Loss Appropriation Account.
Various specific reserves are:
Debentures are debt instruments of a company and they have to be redeemed, that is, paid back after the expiry of the specified period. According to Accounting Standards, companies are required to set aside a specific amount in Debenture Redemption Reserve, when they are due for redemption.
When shares or debentures are issued at a price higher than its book value/face value, the difference between the market value and book value is called Securities Premium. The amount of Securities Premium is transferred to Securities Premium Account. This amount is utilized to issue fully paid bonus shares, write off preliminary expenses, write off commission discounts, etc., to provide a premium on redemption of debentures.
The investments made by a company are subject to fluctuations in its market value. Company Law and Accounting Standards require companies to provide for such fluctuations by creating a reserve called Investment Fluctuation Reserve.
Companies are required to pay a dividend to their shareholders. It is often difficult for a company to maintain a consistent rate of dividend as the dividend paid is equivalent to the profit made by a company during the financial year which is not consistent. So, Dividend Equalisation Reserve is created to maintain a consistent rate of dividend on shares over time, in the event of both high and low profits.
See less
All expenses whose benefits are received over the years or the expenses or losses that are to be written off over the years are classified as Deferred revenue expenses. It includes fictitious expenses like preliminary expenses, loss on issue of debentures, advertising expenses, loss due to unusual oRead more
All expenses whose benefits are received over the years or the expenses or losses that are to be written off over the years are classified as Deferred revenue expenses. It includes fictitious expenses like preliminary expenses, loss on issue of debentures, advertising expenses, loss due to unusual occurrences like loss due to fire, theft, and research and development expenses, etc.
DEFERRED REVENUE EXPENSES
There are certain expenses which are revenue in nature (i.e. expenses incurred to maintain the earning capacity of the firm and generate revenue) but whose benefits are received over a period of years generally between 3 to 7 years. It means its benefit is received not only in the current accounting period but over a few consecutive accounting periods.
CHARACTERISTICS
EXAMPLES
ADVERTISING EXPENSES refers to the expenses incurred for promoting the goods or services of the firm through various channels like TV, Social media, Hoardings, etc.
As the benefit of advertising is not received not only in the period when such expenses were incurred but also in the coming few years, it is classified as Deferred revenue expense.
For example – Suppose the company incurred $10 lakh on advertising to introduce a new product in the market and estimated that its benefit will last for 4 years. In this case, $250,000 will be written off every year, for 4 consecutive years.
EXCEPTIONAL LOSSES are losses that are incurred because of some unusual event and don’t happen regularly like loss from fire, theft, earthquake, flood or any other natural disaster, confiscation of property, etc.
Since these losses can’t be written off in the year they occurred they are also treated as Deferred revenue expenditure and are written off over the years.
RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT EXPENSES are expenses incurred on researching and developing new products or improving the existing ones. Its benefits are received for many years and thus are classified as Deferred revenue expenses.
For example – Expenses incurred on the creation of intangible assets like patents, copyrights, etc.
PRELIMINARY EXPENSES are those expenses which are incurred before the incorporation and commencement of the business. It includes legal fees, registration fees, stamp duty, printing expenses, etc.
These expenses are fictitious assets and are written off over the years.
TREATMENT
It is debited to the P&L amount (amount written off that year) and the remaining amount on the Aeest side of the Balance Sheet.
In the above example of advertising expenses, in Year 1, $250,000 will be debited in the P&L A/c and the remaining amount of $750,000 is shown on the Asset side of the Balance Sheet.
In Year 2, $250,00 in P&L A/c and the remaining $500,000 in Balance Sheet.
In Year 3, $250,000 in P&L A/c and the remaining $250,000 in the Balance Sheet and in the last Year 4, only the remaining amount of $250,000 in P&L A/c and nothing in the Balance Sheet.
See less