Journal entries in the ledger What is a Journal Entry? Journal entry is a form of bookkeeping. All the economic or non-economic transactions in the business are recorded in the journal entries showing a company's debit or credit balances. It is a double-entry accounting method and requires at leastRead more
Journal entries in the ledger
What is a Journal Entry?
Journal entry is a form of bookkeeping. All the economic or non-economic transactions in the business are recorded in the journal entries showing a company’s debit or credit balances. It is a double-entry accounting method and requires at least two accounts or more in a transaction.
The journal entry helps to identify the transactions. We use journals to get a running list of business transactions. Each journal entry provides this specific information about a transaction:
- Date of the transaction.
- Accounts involved in it.
- Payer, payee, receiver, etc.
- Account name.
- Debit and credit of money.
General Ledger
After the transactions are recorded in the journal, they are posted in the principal book called ‘Ledger’. A ledger account contains information about a specific account. It contains the opening balance as well as the closing balances of an account. It summarizes the business transactions.
Transferring the entries from journals to respective ledger accounts is called ledger posting or posting to the ledger accounts. Balancing of ledgers is carried out to find differences at the year’s end, it means finding the difference between the debit and credit amounts of a particular account.
For instance,
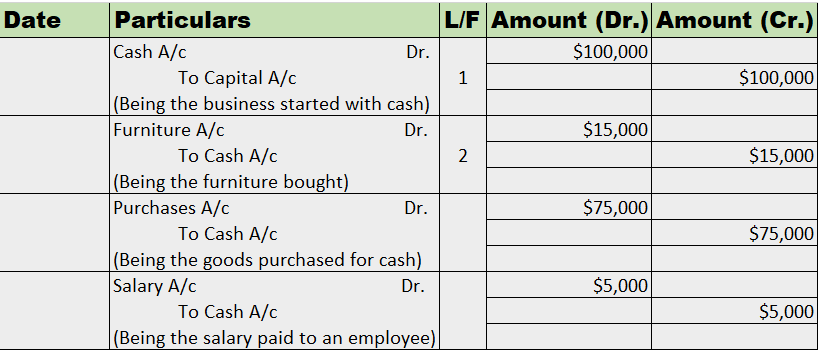
Suppose goods were bought for cash. While passing the journal entry, we’ll be debiting the purchases a/c and crediting the cash a/c by stating it as, ‘To Cash A/c’.
Now, this entry will be affecting both the purchases account and the cash account. In the cash account, we’ll be debiting purchases. Whereas in the purchases account, we’ll be crediting the cash. That’s how it works in the double-entry bookkeeping system of accounting.
Example
Mr. Tony Stark started the business with cash of $100,000. He bought furniture for business for $15,000. He further purchased goods for $75,000. He hired an employee and paid him a salary of $5,000.
Now, we’ll be journalizing the transactions and posting them into the ledger accounts.
Journal Entries
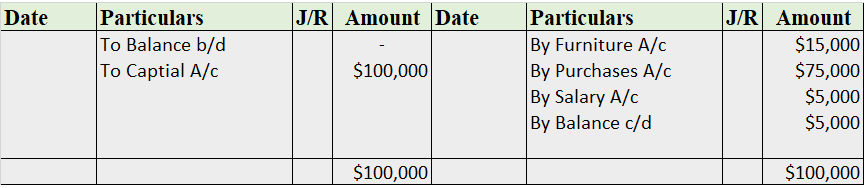
Recording into Ledger Account
Cash A/c
Capital A/c
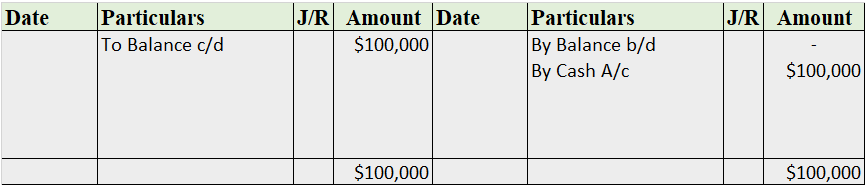
Furniture A/c
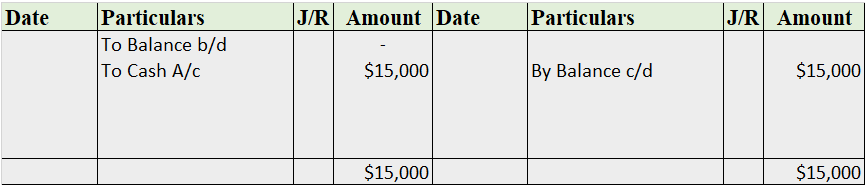
Purchases A/c
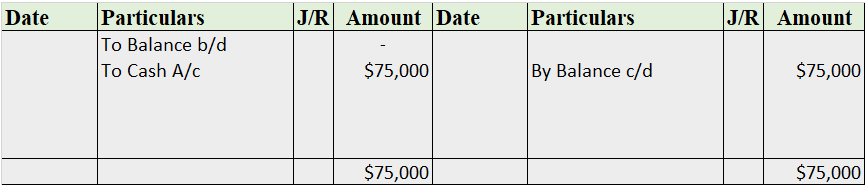
Salary A/c
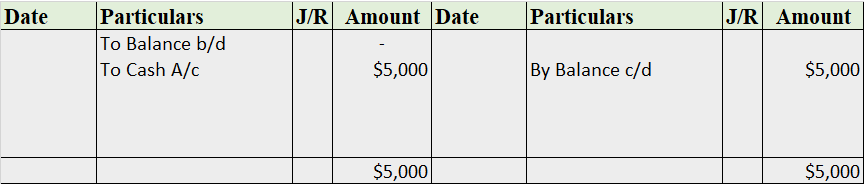
Note: The balance b/d is not applicable as this is the business’ commencement year.
See less

Sales Return is shown on the debit side of the Trial Balance. Sales Return is also called Return Inward. Sales Return refers to those goods which are returned by the customer to the seller of the goods. The goods can be returned due to various reasons. For example, due to defects, quality differenceRead more
Sales Return is shown on the debit side of the Trial Balance.
Sales Return is also called Return Inward.
Sales Return refers to those goods which are returned by the customer to the seller of the goods. The goods can be returned due to various reasons. For example, due to defects, quality differences, damaged products, and so on.
In a business, sales is a form of income as it generates revenue. So, when the customer sends back those goods sold earlier, it reduces the income generated from sales and hence goes on the debit side of the trial balance as per the modern rule of accounting Debit the increases and Credit the decreases.
For Example, Mr. Sam sold goods to Mr. John for Rs 500. Mr. John found the goods damaged and returned those goods to Mr. Sam.
So, here Sam is the seller and John is the customer.
The journal entry for sales return in the books of Mr. Sam will be
Treatment in Trial Balance

See less