The receipt of cash is recorded by debiting the cash account to the account from which the cash is received. This source account may be the sales account, account receivable account or any other account from which cash is received. The journal entry is: An entity may receive cash in the following evRead more
The receipt of cash is recorded by debiting the cash account to the account from which the cash is received. This source account may be the sales account, account receivable account or any other account from which cash is received.
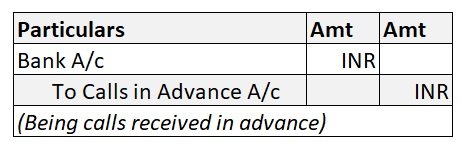
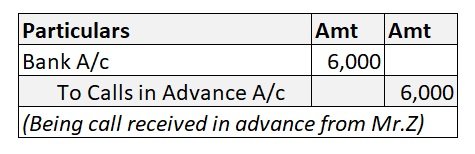
The journal entry is:

An entity may receive cash in the following events:
- Sales of goods or provision of services
- Payment from account receivables
- Sale of assets.
- Withdrawal of cash from the bank
- Introduction of additional capital in the business
- Subscription or donation received in case of non-profit oriented concerns.
- Other income in cash
This list is not exhaustive. There may be many such events. However, the cash account will be always debited.
Rules of accounting applicable on the cash account
As per the golden rules of accounting, the cash account is a real account as represents an asset. For real accounts, the rule, “Debit the receiver and credit the giver” applies.
Hence, when cash is received, cash is debited and the source (giver) is credited.
As per modern rules of accounting, the cash account is an asset account. Assets accounts are debited when increased and credited when decreased.
Hence, at receipt of cash, cash is debited as cash is increased.
See less





First, let us understand the meaning of a provision of depreciation. It is nothing but the total collection of all the depreciation over the years. This account is not like a normal account but a contra asset account. It is also called accumulated depreciation. Annual depreciation charged is an expeRead more
First, let us understand the meaning of a provision of depreciation. It is nothing but the total collection of all the depreciation over the years. This account is not like a normal account but a contra asset account. It is also called accumulated depreciation.
Annual depreciation charged is an expense for the business and hence has a debit balance. Whereas provision for depreciation as a contra asset account has a credit balance.
The journal entry for provision for depreciation is
Explaining the credit nature of this account. As we know that the depreciation is an expense for the business hence as per modern rules “Debit all the expenses and losses and credit all incomes and gains” therefore it is debited whereas the provision of depreciation is contra account it has a credit balance as it reduces the value of assets. So according to modern rule, we know a decrease in assets has a credit balance, hence shown in a negative balance on the balance sheet under long-term assets.
With the preparation of this account, we do not credit depreciation in the asset account but transfer every year to the accumulated depreciation account, and when assets are disposed of or sold we credit the ‘total’ of the provision on depreciation to the credit of the asset account just to calculate the actual profit or loss on a sale of the asset.
See less