There are three types of businesses that can be commenced, they are sole proprietorship, partnership, and joint-stock company. As we all know, to start any business a certain sum of money has to be invested by the owner which is known as the capital of the business in terms of accounting. In companiRead more
There are three types of businesses that can be commenced, they are sole proprietorship, partnership, and joint-stock company. As we all know, to start any business a certain sum of money has to be invested by the owner which is known as the capital of the business in terms of accounting.
In companies, commencement is a declaration issued by the company’s directors with the registrar stating that the subscribers of the company have paid the amount agreed. In a sole proprietorship, the business can be commenced with the introduction of any asset such as cash, stock, furniture, etc.
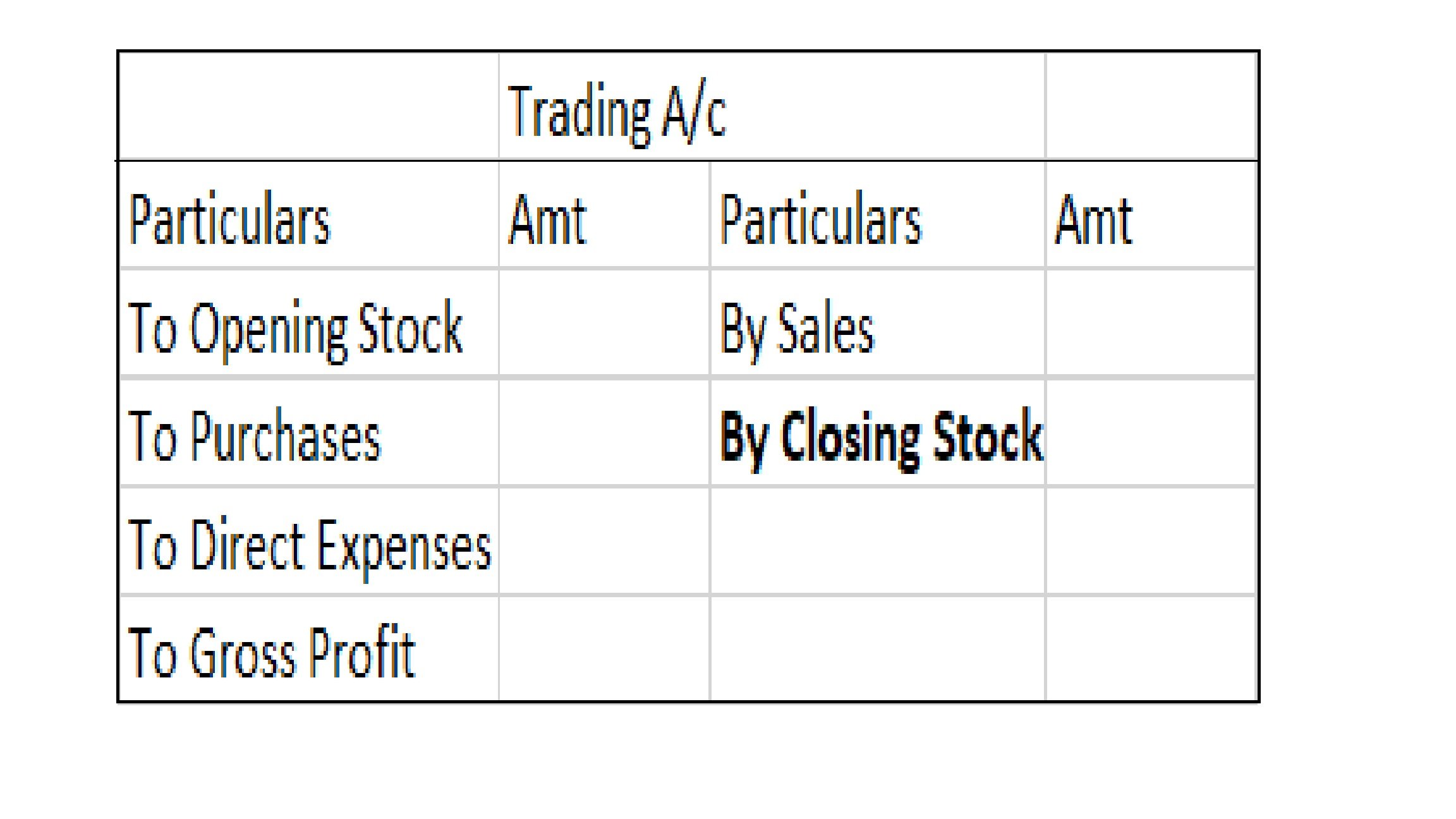
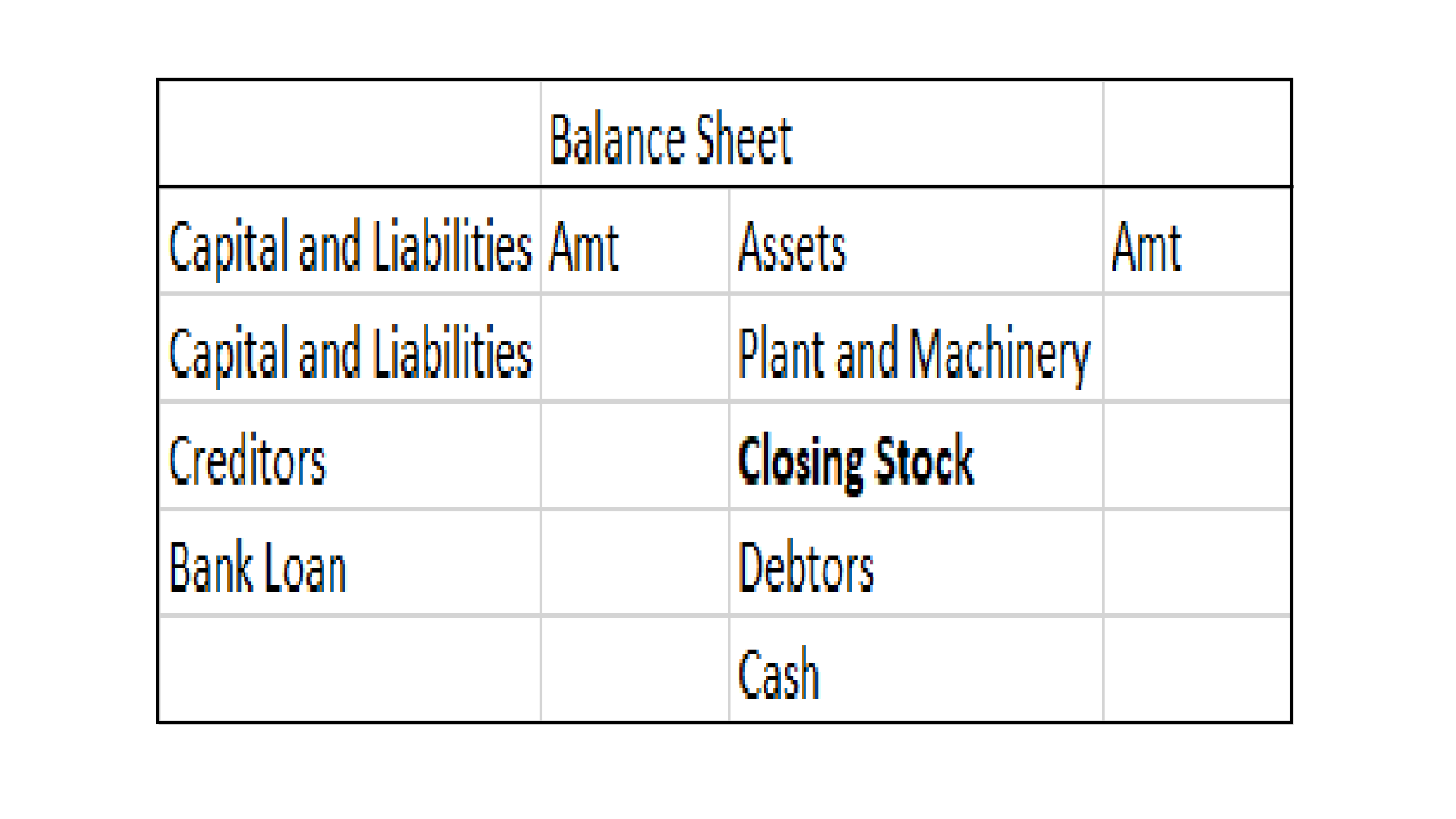
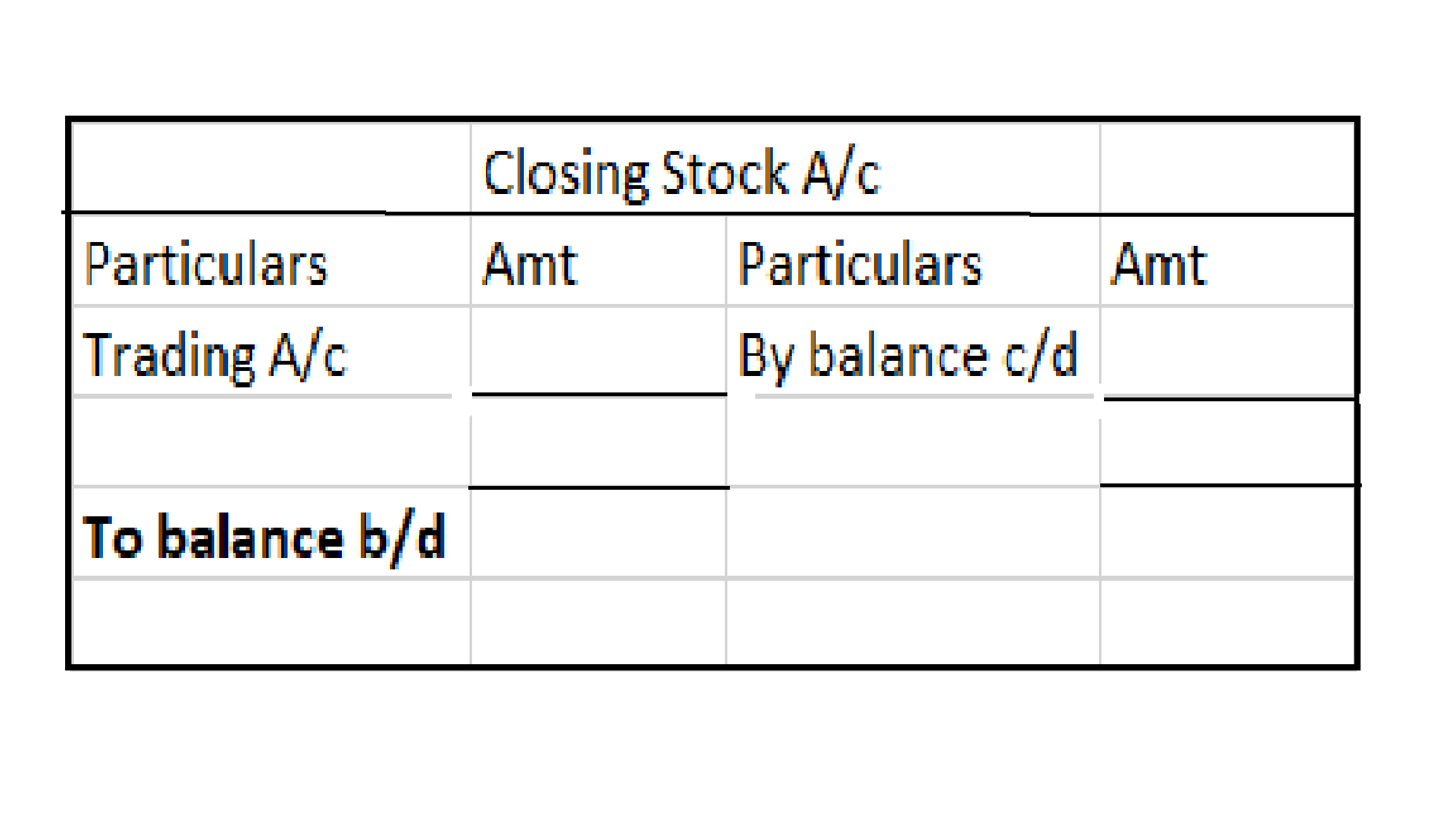
Journal entry
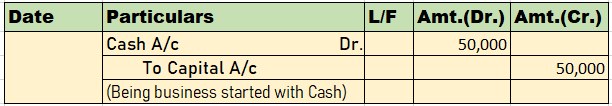
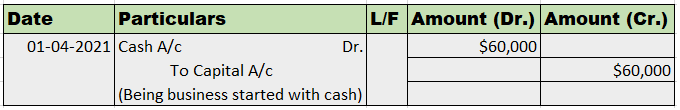
In the journal entry, “Started business with Cash”
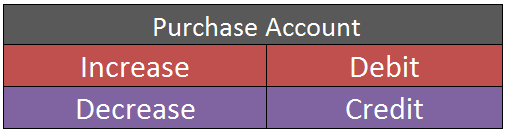
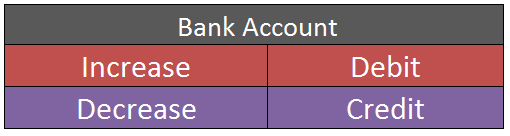
As per the golden rules of accounting, the cash a/c is debited because we bring in cash to the business, and as the rule says “debit what comes in, credit what goes out.” Whereas the capital a/c is credited because “debit all expenses and losses, credit all incomes and gains”
As per modern rules of accounting, cash a/c is debited as cash is a current asset, and assets are debited when they increase. Whereas, on the increment on liabilities, they are credited, therefore, capital a/c is credited.
Therefore, the entry we’ll be passing is-
See less





Before starting with the main discussion, let me give you a brief explanation of what rent received is When a business or an organization rents out its unused property to earn some extra income and receive some amount from it, that amount of money is said to be rent received. Rent can be monthly, quRead more
Before starting with the main discussion, let me give you a brief explanation of what rent received is
When a business or an organization rents out its unused property to earn some extra income and receive some amount from it, that amount of money is said to be rent received.
Rent can be monthly, quarterly, half-yearly, or yearly rent depending upon the organization’s agreement.
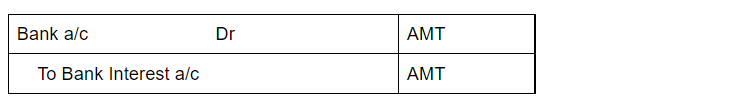
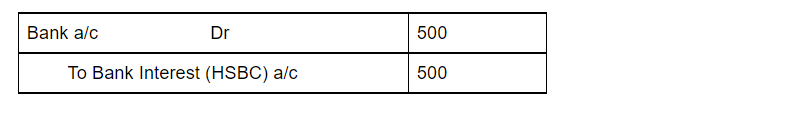
The journal entry for rent received will be
Here, Cash account is debited due to the increase in assets or because of a real account. Rent account is credited due to the increase in income or because of the nominal account.
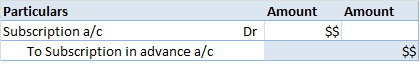
However, Rent received in advance means the amount of rent that is not yet due but is received in advance. It is treated as a current liability because the benefit related is yet to be provided to the tenant.
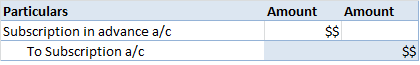
The Journal entry for Rent received in advance will be-
Here, rent is debited due to a decrease in income.
Rent received in Advance is credited due to an increase in liability.
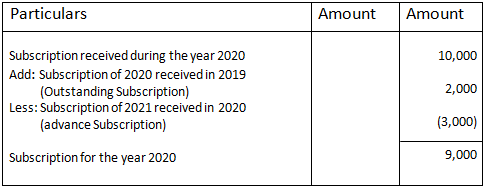
For Example, Johnson company rented out a part of its building that was not used to earn some extra income from it. The monthly rent was fixed as 20000. Johnson company follows calendar year as their accounting year. The tenant, therefore, paid 4 months advance rent to Johnson company i.e. the tenant in January gave his advance rent for February, March, April, and May.
While receiving the rent in the month of January. The journal entry would be
Now, the adjustment entry of rent received in advance would be
The rent received in advance will also be posted individually in each month of February, March, April, and May as
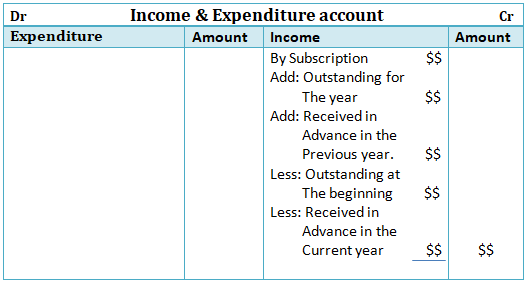
Furthermore, Rent received in advance is deducted from the amount of rent in the income and expenditure account and thereafter the amount received in advance is posted on the liability side of the Balance sheet.
See less