Trading A/c is a Nominal A/c which follows the rule “Debit the expenses and losses, Credit the incomes and gains” So, the Credit side of Trading A/c shows income from the sale of goods. It includes Sales, Closing stock (if adjustment for it has not been made yet) and Gross Loss (if any). TRADRead more
Trading A/c is a Nominal A/c which follows the rule “Debit the expenses and losses, Credit the incomes and gains”
So, the Credit side of Trading A/c shows income from the sale of goods. It includes Sales, Closing stock (if adjustment for it has not been made yet) and Gross Loss (if any).
TRADING ACCOUNT
Trading A/c is prepared for calculating the Gross Profit or Gross Loss arising from the trading activities of a business.
Trading activities are mostly related to buying and selling of goods. However, in between buying and selling, a lot of activities are involved like transportation, warehousing, etc. So, all the expenses that are directly related to manufacturing or purchase of goods are also recorded in the Trading A/c.
CREDIT SIDE OF TRADING ACCOUNT
It includes,
SALES – When goods are sold to earn a profit, it is called sales. It can be cash sales or credit sales.
Suppose you are in the business of manufacturing and trading shirts. You sold shirts worth $ 20,000 during the year. This $20,000 is your sales.
SALES RETURN – When the goods sold by you are returned by the customer, it is known as sales return. Sales return is deducted from the sales.
Continuing with the above example, the customers returned shirts of $1,000 because they didn’t like them. This return is known as sales return or return inward (as goods are coming back i.e. in)
CLOSING STOCK – Stock is nothing but goods that are either obtained for resale or manufactured for sale and are yet unsold on any particular date.
The value of stock at the beginning of an accounting year is called Opening stock while the value of the stock at the end of an accounting year is called Closing stock.
Closing stock is valued at cost price or market price whichever is less.
It includes,
- Closing stock of raw materials
- Closing stock of semi-finished goods
- Closing stock of finished goods
For example – On 31st March 2023, there was unused raw material worth $1,000 and shirts worth $5,000 remained unsold.
So, we have Closing Stock of Raw material – $1,000
Closing Stock of Finished Goods – $5,000
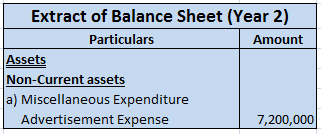
Normally, the closing stock is given outside the Trial Balance because its valuation is made after accounts have been closed. It is incorporated in the books by transferring it to the Trading A/c. So, it is shown on the credit side of Trading A/c as well as on the assets side of the Balance sheet.
However, if the closing stock is given inside the Trail Balance, it means that the closing stock must have already been deducted from the Purchases account. So, closing stock will only be shown on the assets side of the Balance sheet.
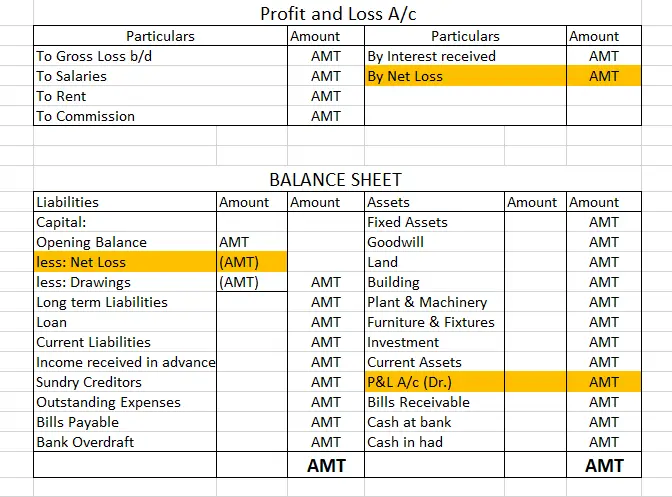
GROSS LOSS – If purchases and direct expenses exceed sales, then it is a Gross loss. In other words, when Debit side > credit side.
DEBIT SIDE OF TRADING ACCOUNT
It includes
OPENING STOCK – The value of the stock at the beginning of an accounting year is called Opening stock.
The closing stock of the last year becomes the opening stock of the current year.
PURCHASES – Goods that have been bought for resale or raw materials purchased for the manufacturing of the product are terms as Purchases. These goods must be related to the business you are doing. It includes cash as well as credit Purchases.
PURCHASES RETURN – When goods bought are returned to the suppliers due to any reason. This is known as Purchase return. Purchase return is deducted from the Purchases.
WAGES – Wages are paid to the workers who are directly engaged in the loading, unloading and production of goods.
CARRIAGE or CARRIAGE INWARDS or FREIGHT – It refers to the cost of transporting goods from the supplier.
MANUFACTURING EXPENSES – All expenses incurred in the manufacture of goods such as Coal, Gas, Fuel, Water, Power, Factory rent, Factory lighting etc.
DOCK CHARGES – These are charged by port authorities when unloading goods at a dock or wharf. Such charges paid in connection with goods purchased are considered direct expenses and are debited to Trading a/c.
IMPORT DUTY or CUSTOM DUTY – It is a tax collected on imports and specific exports by a country’s customs authorities.
If import duty is paid on the import of goods, then they are shown on the Dr. side of the Trading A/c.
ROYALTY – Royalty refers to the amount paid for the use of assets belonging to another person. It includes royalty for the use of intangible assets, such as copyrights, trademarks, or franchisee agreements. It is also paid for the use of natural resources, such as mining leases.
Royalty is charged to the Trading A/c as it increases the cost of production.
GROSS PROFIT – When sales exceed the amount of purchases and the expenses directly connected with such purchases i.e. when Credit side> Debit side.
See less

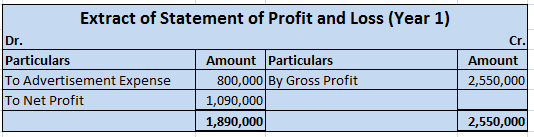
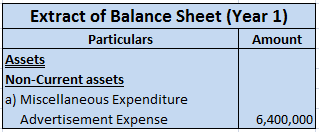
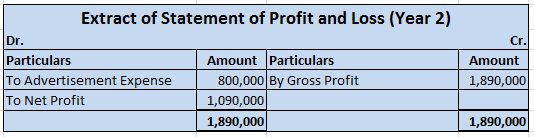
A balance sheet is a financial statement that reports the position or value of assets, liabilities and equity at a particular date, which is usually the closing date of a financial year. Formats of balance sheet A balance sheet may be presented in two formats: T-form or Horizontal format This formatRead more
A balance sheet is a financial statement that reports the position or value of assets, liabilities and equity at a particular date, which is usually the closing date of a financial year.
Formats of balance sheet
A balance sheet may be presented in two formats:
T-form or Horizontal format
This format is the same as the format of ledger accounts. There are two columns with the headings ‘Liabilities’ for the left column and ‘Assets’ for the right column and columns adjacent to both columns for amounts. The liabilities and equity (capital) are shown on the liabilities side because they both have credit balance and assets are shown on the asset side. Most of the non-corporates prepare their balance as per this format. The T-form balance sheet looks as given below:
Vertical format
The vertical format of the balance sheet is mostly prepared by corporate entities. Here, the liabilities and assets are shown in the same column as compared to two separate columns in the horizontal format. This results in having a longer shape. Hence, it is called a ‘vertical’ balance sheet. Generally, companies prepare their balance sheet as per this format.
Also, many times, there are two columns for the amount in this format presenting the amount of both the current year and the previous year. This format looks like as given below:
Grouping and marshalling
Beside the structure of the balance sheet i.e. horizontal and vertical, the grouping and marshalling of the items inside the balance sheet are also very important.
Grouping refers to the presenting of similar items under a heading or group. This is done in order to present the balance sheet in a concise manner. This is very important to do. For example, a business can have numerous creditors, but they are all presented under one ‘Creditors’ heading or two or more heading specifying different types of creditors.
The assets of a business are grouped under the heading such as Plant, Property and equipment, Current assets, Non-current investments etc.
Marshalling means the arranging of items as per a particular order. We know that a balance sheet consists of many items and to make the statement more useful and easy to comprehend, the items are arranged in one of the following orders:
In case of liabilities, the items which are due for repayment soon are kept at the top, like bank overdraft etc. The items which are due for repayment after a long time or at the time of winding capital are kept at the bottom, like long term loans and capital funds. Given below is a format of horizontal balance sheet in which the items are marshalled in order of liquidity:
- Order of permanence: This type of arrangement is just the opposite of the order of liquidity. Here the items which are least liquid are placed at the top and the more liquid items are placed at the bottom. Like in the case of assets, cash appears at the bottom and non-current assets at the top. On the liabilities side, equity and non-current liabilities are at the top while current liabilities are at the bottom. Mostly all balance sheets are marshalled in order of permanence.
See less