A. Normal wear and tear B. Foreseen obsolescence C. Normal wear & tear & foreseen obsolescence D. Unforeseen obsolescence
Buildings S.No. Particulars Rate 1 Buildings which are used mainly for residential purposes except hotels and boarding houses. 5% 2 Buildings other than those used mainly for residential purposes and not covered by sub-items (1) above and (3) below. 10% 3 Buildings acquired on or after the 1st day oRead more
| Buildings | ||
| S.No. | Particulars | Rate |
| 1 | Buildings which are used mainly for residential purposes except hotels and boarding houses. | 5% |
| 2 | Buildings other than those used mainly for residential purposes and not covered by sub-items (1) above and (3) below. | 10% |
| 3 | Buildings acquired on or after the 1st day of September, 2002 for installing machinery and plant forming part of water supply project or water treatment system and which is put to use for the purpose of business of providing infra- structure facilities. | 40% |
| 4 | Purely temporary erections such as wooden structures. | 40% |
| Furniture & Fittings | ||
| S.No. | Particulars | Rate |
| Furniture and fittings including electrical fittings. | 10% | |
| Machinery & Plant | ||
| S.No. | Particulars | Rate |
| 1 | Machinery and plant other than those covered by sub-items (2), (3) and (8) below. | 15% |
| 2 (i) | Motor cars, other than those used in a business of running them on hire, acquired or put to use on or after the 1st day of April, 1990 except those covered under entry (ii). | 15% |
| 2 (ii) | Motor cars, other than those used in a business of running them on hire, acquired on or after the 23rd day of August, 2019 but before the 1st day of April, 2020 and is put to use before the 1st day of April, 2020. | 30% |
| 3 (i) | Aeroplanes – Aero engines. | 40% |
| 3 (ii) | (a) Motor buses, motor lorries and motor taxis used in a business of running them on hire other than those covered under entry (b). | 30% |
| (b) Motor buses, motor lorries and motor taxis used in a business of running them on hire, acquired on or after the 23rd day of August, 2019 but before the 1st day of April, 2020 and is put to use before the 1st day of April, 2020. | 45% | |
| 3 (iii) | Commercial vehicle which is acquired by the assessee on or after the 1st day of October, 1998, but before the 1st day of April, 1999 and is put to use for any period before the 1st day of April, 1999 for the purposes of business or profession. | 40% |
| 3 (iv) | New commercial vehicle which is acquired on or after the 1st October, 1998, but before the 1st April, 1999 in replacement of condemned vehicle of over 15 years of age and is put to use for any period before the 1st day of April, 1999 for the purposes of business or profession. | 40% |
| 3 (v) | New commercial vehicle which is acquired on or after the 1st April, 1999 but before the 1st April, 2000 in replacement of condemned vehicle of over 15 years of age and is put to use before the 1st April, 2000 for the purposes of business or profession. | 40% |
| 3 (vi) | New commercial vehicle which is acquired on or after the 1st April, 2001 but before the 1st April, 2002 and is put to use before the 1st day of April, 2002 for the purposes of business or profession. | 40% |
| 3 (via) | New commercial vehicle which is acquired on or after the 1st January, 2009 but before the 1st October, 2009 and is put to use before the 1st October, 2009 for the purposes of business or profession. | 40% |
| 3 (vii) | Moulds used in rubber and plastic goods factories. | 30% |
| 3 (viii) | Air pollution control equipment. | 40% |
| 3 (ix) | Water pollution control equipment. | 40% |
| 3 (x) | Solid waste control equipments & solid waste recycling and resource recovery systems. | 40% |
| 3 (xi) | Machinery and plant, used in semi-conductor industry covering all integrated circuits (ICs). | 30% |
| 3 (xia) | Life saving medical equipment. | 40% |
| 4 | Containers made of glass or plastic used as re-fills. | 40% |
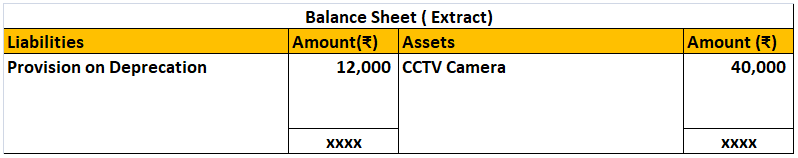
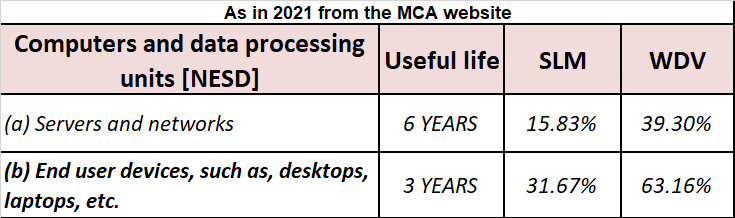
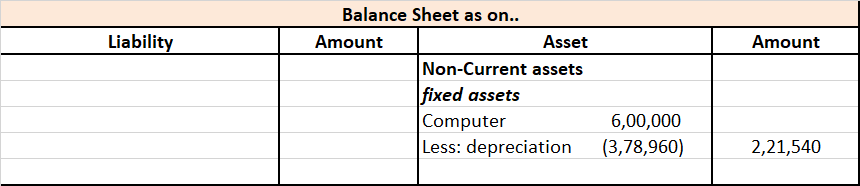
| 5 | Computers including computer software. | 40% |
| 6 | Machinery and plant, used in weaving, processing and garment sector of textile industry, which is purchased & put to use under TUFS on or after the 1st April, 2001 but before the 1st April, 2004. | 40% |
| 7 | Machinery and plant, acquired and installed on or after the 1st September, 2002 in a water supply project or a water treatment system and which is put to use for the purpose of business of providing infrastructure facility. | 40% |
| 8 (i) | Wooden parts used in artificial silk manufacturing machinery. | 40% |
| 8 (ii) | Cinematograph films – bulbs of studio lights. | 40% |
| 8 (iii) | Match factories – Wooden match frames. | 40% |
| 8 (iv) | Mines and quarries. | 40% |
| 8 (v) | Salt works – Salt pans, reservoirs and condensers, etc., made of earthy, sandy or clayey material or any other similar material. | 40% |
| 8 (vi) | Flour mills – Rollers. | 40% |
| 8 (vii) | Iron and steel industry – Rolling mill rolls. | 40% |
| 8 (viii) | Sugar works – Rollers. | 40% |
| 8 (ix) | Energy saving devices: (a) Specialised boilers and furnaces. | 40% |
| (b) Instrumentation and monitoring system for monitoring energy flows. | 40% | |
| (c) Waste heat recovery equipment. | 40% | |
| (d) Co-generation systems. | 40% | |
| (e) Electrical equipment. | 40% | |
| (f) Burners. | 40% | |
| (g) Other equipment. | 40% | |
| 8 (x) | Gas cylinders including valves and regulators. | 40% |
| 8 (xi) | Glass manufacturing concerns – Direct fire glass melting furnaces. | 40% |
| 8 (xii) | Mineral oil concerns: (a) Plant used in field operations (above ground) distribution – Returnable packages. | 40% |
| (b) Plant used in field operations (below ground), but not including kerbside pumps including underground tanks and fittings used in field operations (distribution) by mineral oil concerns. | 40% | |
| (c) Oil wells not covered in clauses (a) and (b). | 15% | |
| 8 (ix) | Renewal energy devices. | 40% |
| 9 (i) | Books owned by assessees carrying on a profession. | 40% |
| 9 (ii) | Books owned by assessees carrying on business in running lending libraries. | 40% |
| Ships | ||
| S.No. | Particulars | Rate |
| 1 | Ocean-going ships including dredgers, tugs, barges, survey launches and other similar ships used mainly for dredging purposes and fishing vessels with wooden hull. | 20% |
| 2 | Vessels ordinarily operating on inland waters, not covered by sub-item (3) below. | 20% |
| 3 | Vessels ordinarily operating on inland waters being speed boats. | 20% |
| Intangible Assets | ||
| S.No. | Particulars | Rate |
| 1 | Know-how, patents, copyrights, trademarks, licences, franchises or any other business or commercial rights of similar nature not being goodwill of business of profession. | 25% |
See less

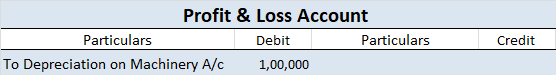
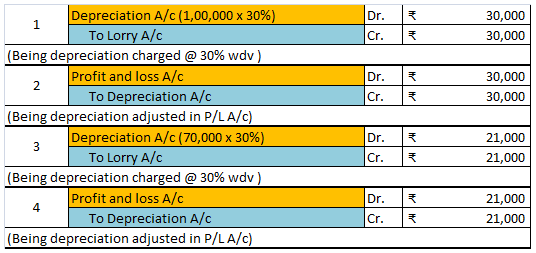

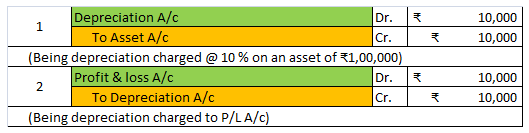
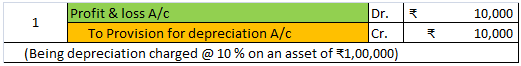
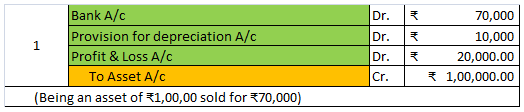
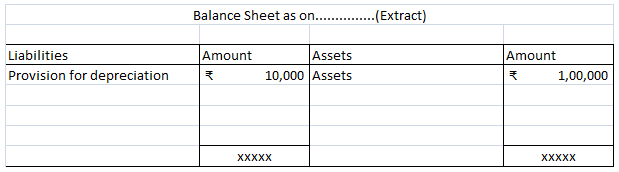
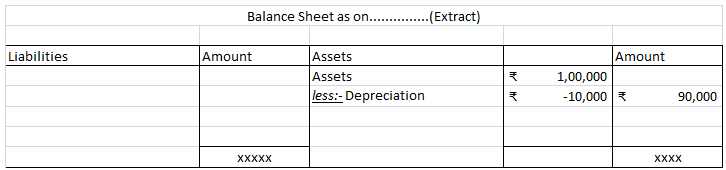
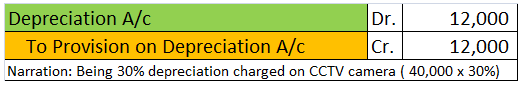
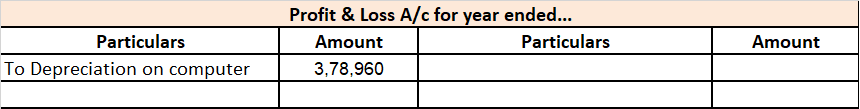
Depreciation of fixed capital assets refers to C. Normal wear & tear & foreseen obsolescence. Normal wear & tear refers to the damage caused to an asset due to its continuous usage. Even when the asset is properly maintained, wear and tear occurs. Hence, it is considered to be inevitableRead more
Depreciation of fixed capital assets refers to C. Normal wear & tear & foreseen obsolescence.
Normal wear & tear refers to the damage caused to an asset due to its continuous usage. Even when the asset is properly maintained, wear and tear occurs. Hence, it is considered to be inevitable and natural.
For example, Kumar has purchased a car for 25,00,000. After five years he wishes to sell his car. Now the market price of his used car is 12,00,000. This reduction in the value of the car from 25,00,000 to 12,00,000 is because of its usage. This fall in the value of the asset due to usage is known as normal wear & tear.
In generic terms, obsolescence means something that has become outdated or is no longer being used. Foreseen obsolescence is nothing but obsolescence that is expected.
In the context of business, whenever the value of an asset falls because it has become outdated or is replaced by a superior version, we call it obsolescence. The fall in the value of the asset due to obsolescence expected by the purchaser of the asset is known as foreseen obsolescence.
When an asset becomes obsolete it doesn’t mean it is not in working condition. Even when an asset is in good working condition it can become obsolete due to the following reasons:
For example, before the invention of computers, people used typewriters for getting their paperwork done. With the invention of computers, laptops, etc. it is easier to type as well as save our documents, spreadsheets, etc. Thus typewriters became obsolete with the invention of computers. It has become a technology of the past.
Here is a summarised version of wear & tear and obsolescence:

See less