The rate of depreciation on a car as per the Income Tax Act depends upon the purpose for which it has been purchased and the year on which it was acquired. As per the Income Tax Act, cars come under the Plant and Machinery block of assets. The Act classifies cars into two categories, Group 1 - MotorRead more
The rate of depreciation on a car as per the Income Tax Act depends upon the purpose for which it has been purchased and the year on which it was acquired.
As per the Income Tax Act, cars come under the Plant and Machinery block of assets.
The Act classifies cars into two categories,
- Group 1 – Motor cars other than those used in the business of running them on hire.
- Group 2 – Motor taxis used in the business of running them on hire.
Group 1:
- If the motor car is acquired and put to use on or after 23rd August 2019 but before 1st April 2020, then the rate applicable is 30%.
- If the motor car is acquired and put to use on or after 1st April 1990, then the rate applicable is 15%. (All the cars which are not covered under the category (1) comes under this category.)
Group 2:
- If the motor taxi is acquired and put to use on or after 23rd August 2019 but before 1st April 2020, then the rate applicable is 45%.
- The rate applicable for motor taxis not covered under category (1) is 30%.
Here is a summarised version of the rates applicable to cars,
The rates can also be found on the Income Tax India website.
See less

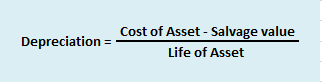


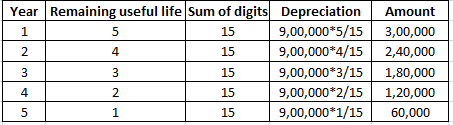

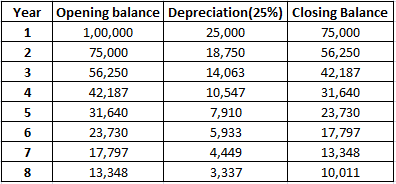
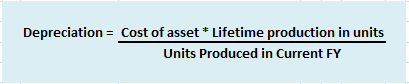
Depreciation is an accounting method that is used to write off the cost of an asset. The company must record depreciation in the profit and loss account. It is done so that the cost of an asset can be realised over the years rather than one single year. Furniture is an important asset for a businessRead more
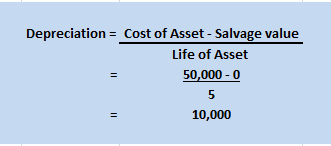
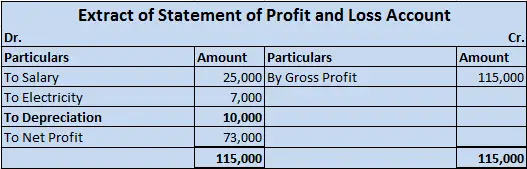
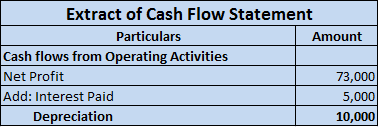
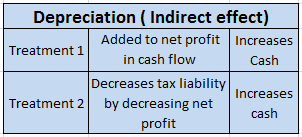
Depreciation is an accounting method that is used to write off the cost of an asset. The company must record depreciation in the profit and loss account. It is done so that the cost of an asset can be realised over the years rather than one single year.
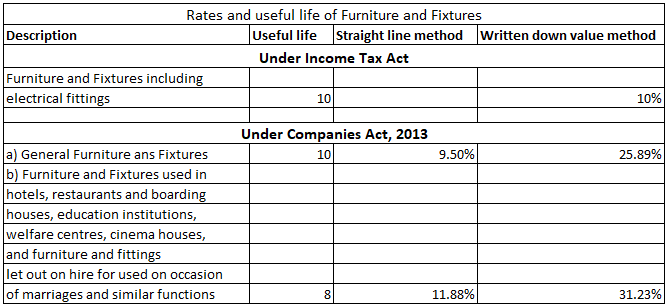
Furniture is an important asset for a business. As per the Income Tax Act, the rate of depreciation for furniture and fittings is 10%. However, for accounting purposes, the company is free to set its own rate.
JOURNAL ENTRY
Journal entry for depreciation of furniture is:
Here, depreciation is debited since it is an expense and as per the rules of accounting, “increase in expenses are debited”. Furniture is credited because a “ decrease in assets is credited”, and the value of furniture is reducing.
TYPES OF DEPRECIATION
Furniture can be depreciated in any of the following ways:
For accounting purposes, the two many methods used for depreciating furniture is the straight-line method and the diminishing value method. However, for tax purposes, they are combined into a block of furniture, where the purchase of new furniture is added and the sale of furniture is subtracted and the resulting amount is depreciated by 10% based on the written downvalue method.
EXAMPLE
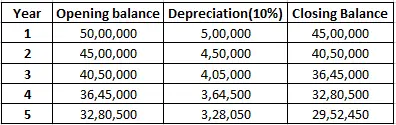
If a company buys furniture worth Rs 30,000 and charges depreciation of 10%, then by straight-line method, Rs 3,000 would be depreciated every year for 10 years.
Now if the company decided to use the diminishing value method (or written down value method), then Rs 3,000 (30,000 x 10%) would be depreciated in the first year, and in the second year, the book value of the furniture would be Rs 27,000 (30,000-3,000). Hence depreciation for the second year would be Rs 2,700 (27,000 x 10%) and so on.
See less