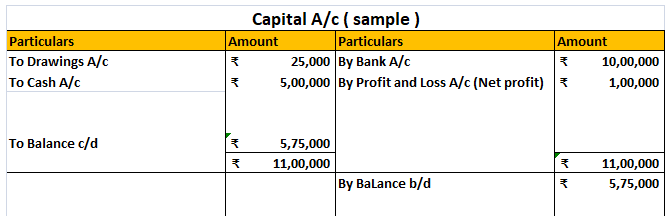
No, capital account is not a real account. Capital account represents the amount of money invested by the owner/owners of the business along with the retained earnings net of drawings or dividends. Capital account has a natural credit balance because it is an internal liability of the business. CapiRead more
No, capital account is not a real account.
Capital account represents the amount of money invested by the owner/owners of the business along with the retained earnings net of drawings or dividends. Capital account has a natural credit balance because it is an internal liability of the business.
Capital account is a personal account because, as discussed above, it represents the investment of the owner or owners. Personal account represents person or persons.
Whereas a real account represents the material assets of a business. Example:- Cash A/c, Fixed assets A/c etc. That’s why the capital account is not a real account.
Being a personal account, the following golden rule of accounting applies to capital account:-
“Debit the receiver and credit the giver”
Here, as the owner gives an amount as an investment into the business (owner and the business are separate entities), the capital account has a credit balance.


The term ‘contra’ means opposite or against. In financial accounting, we encounter the term ‘contra’ in: Contra accounts Contra entries The meaning of contra in the above mention terms is also the same as their general meaning. Contra accounts mean the account which is opposite of the account it corRead more
The term ‘contra’ means opposite or against. In financial accounting, we encounter the term ‘contra’ in:
The meaning of contra in the above mention terms is also the same as their general meaning. Contra accounts mean the account which is opposite of the account it corresponds to.
Contra entries are entries of the debit and credit aspects related to the same parent account. Let’s discuss them in detail.
Contra accounts
Any account which is created with the purpose of reducing or offsetting the balance of another account is known as a contra account.
A contra account is just the opposite of the account to which it relates. The most common examples are the sales discount account and sales return account which is the contra account of the sales account. They are just the opposite of the sales accounts.
Contra Entries
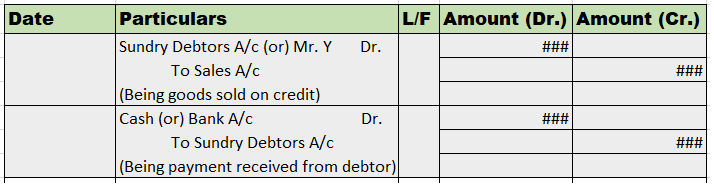
Contra entries refer to the entries which show the movement of the amount within the same parent account. Here, the debit and credit entry is posted on the debit and credit side respectively of a single parent account. Mainly, contra entries are the entries involving cash and bank accounts.
The following transactions are recorded as contra entries:
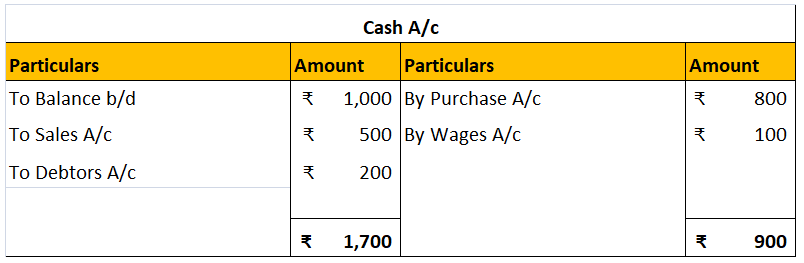
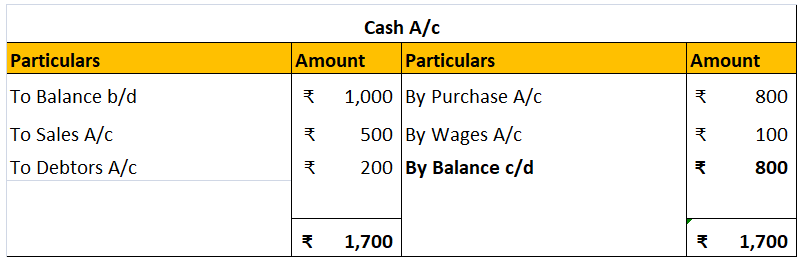
Contra entries are marked by the letter ‘C’ beside the postings in the ledger. Deposit of cash in to bank will be posted in cashbook as below:

See less