The correct option is (A) Original. Journal entry is the book of the original entry. It is because every event or transaction which is of monetary nature is first recorded in the journal. The transactions recorded in the journal are known as journal entries. Journal follows the double-entry system oRead more
The correct option is (A) Original. Journal entry is the book of the original entry. It is because every event or transaction which is of monetary nature is first recorded in the journal. The transactions recorded in the journal are known as journal entries.
Journal follows the double-entry system of accounting. It means a journal entry affects at least two accounts. It is from the journal entries, the ledger accounts are prepared. For example, the transaction, ‘sale of goods for Rs 1000 for cash’ affects two accounts. The journal entry is:

There are many special journals that record some special set of transactions which are called subsidiary journals or daybooks. Such special journals are not considered the books of original entry.
Option (B) Duplicate is wrong. It is because the journal is the book where monetary events and transactions are recorded. It cannot be the book of duplicate entries. There is no such thing as ‘book of duplicate entry.’
Option (C) Personal is wrong. Personal is a type of account under the golden rules of accounting. A personal account is a type of account that represents a person. But, the journal is not an account, it is a book. Also, there is no such thing as book of personal entry.
Option (D) Nominal is wrong. Nominal is also a type of account under the golden rules of accounting. The nominal account is a type of account that represents an income, expense, gain or loss. Journal is a type of account but a book.
See less
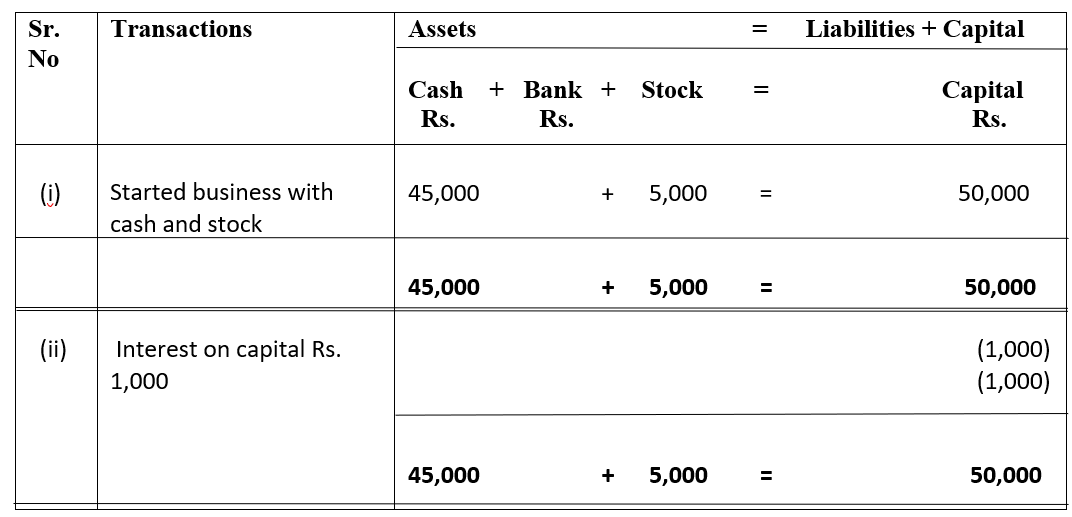
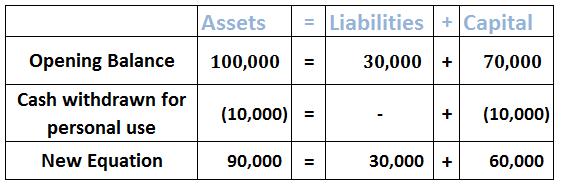
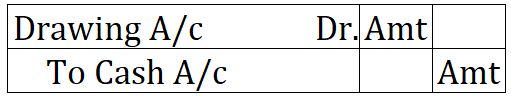
Interest on drawings Drawings refer to the money withdrawn by owners/partners for personal use from the business. The drawings, in accounting terms, can be of any type. It can be cash withdrawn from business or furniture or car etc. Drawings are money or assets that are withdrawn from a company by iRead more
Interest on drawings
Drawings refer to the money withdrawn by owners/partners for personal use from the business. The drawings, in accounting terms, can be of any type. It can be cash withdrawn from business or furniture or car etc. Drawings are money or assets that are withdrawn from a company by its owners for personal use and must be recorded as a reduction of assets. It’s paid back to the business with some interest.
Interest on drawings is an income for the business and reduces the capital of the owner. Interest on drawings is the amount of interest paid by the partners, calculated concerning the period for which the money was withdrawn.
Formulae for Interest on drawings
There are three formulae used for calculating the interest on drawings. They are:
1. Simple Method: In this method, as the name suggests, the amount of interest on drawings is calculated simply for the time the amount has been utilized.
Interest on Drawings = Amount of drawings × Rate/100 × No. of Months/12
2. Product Method: This method is used when-
Interest on Drawings = Total of Products × Rate/100 × 1/12
Interest on Drawings= Total amount of drawings × Rate/ 100 × Average Period/12
Also, note-
Average Period = (No. of months left after first drawings+ No. of months left after last drawings)/2
Example:
Harish withdrew equal amounts at the beginning of every month for 9 months. Total drawings amounted to ₹6,000. Calculate the interest on drawings charged if the rate was 6% p.a.
Solution:
Average period = (No. of months left after first drawings+ No. of months left after last drawings)/2 = (9+1)/2 = 5 months
Interest on Drawings = Total of drawings × Rate/100 × 5/12
Journal entry for interest on drawings:
Interest transferred to Profit & Loss A/c:
See less