A. Events B. Transactions C. Journals D. None of These
The term ‘contra’ means 'opposite'. Therefore, a contra revenue account is an account that is opposite of the revenue accounts of a business i.e. sales account. It has the opposite balance of the revenue account i.e. debit balance. The purpose of the contra revenue account is to ascertain the actuaRead more
The term ‘contra’ means ‘opposite’. Therefore, a contra revenue account is an account that is opposite of the revenue accounts of a business i.e. sales account. It has the opposite balance of the revenue account i.e. debit balance.
The purpose of the contra revenue account is to ascertain the actual amount of sales and record the items which have reduced the sales.
These are the contra revenue accounts commonly seen in businesses:
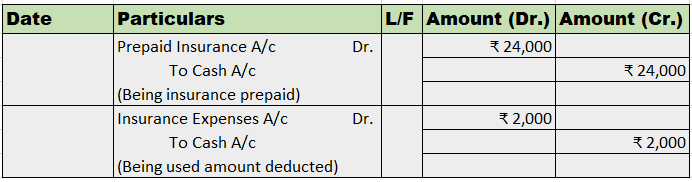
- Sales return account: This account records the amount of goods sold returned by customers. The journal entry for recording sale return is as follow:

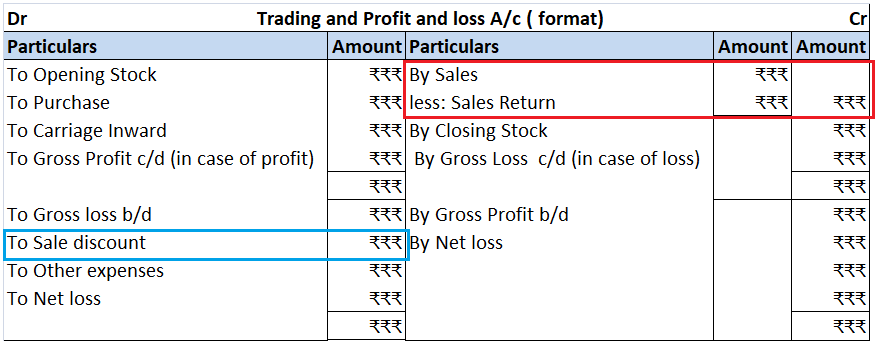
The total sales return is deducted from the sales in the balance sheet. Though being opposite of the sales account, the sale return account is not an expense account. It is considered an indirect loss as it reduces sales.
- Sale Discount account: This account records the amount of discount allowed to customers. The journal entry for recording sale discounts is as follows:

Sales discount is an expense hence it is debited to the profit and loss account.
Sales returns and sales discounts are shown in the trading and profit and loss account in the following manner:


The correct option is Option C: Journal Entries. Journal entries are the primary entries in the books of accounts and they are passed when any transaction or event takes place. Every journal entry has a dual effect i.e. two or more accounts are affected. For example, When cash is introduced in the bRead more
The correct option is Option C: Journal Entries.
Journal entries are the primary entries in the books of accounts and they are passed when any transaction or event takes place. Every journal entry has a dual effect i.e. two or more accounts are affected.
For example, When cash is introduced in the business, the journal entry passed is:
Cash A/c Dr. ₹10,000
To Capital A/c ₹10,000
The accounts affected here are Cash A/c and Capital A/c.
Cash A/c gets debited by ₹10,000,
and Capital A/c get credited by ₹10,000.
All the processes of accounting are conducted in an ordered manner known as the accounting cycle.
The first step in an accounting cycle is to identify the transactions and events which are monetary in nature.
The second step is to record the identified transactions in form of journal entries.
And the third step is to make postings in the general ledger accounts as per the journal entries.
Hence, the preparation of the ledger is the third step in the accounting cycle and is prepared from the journal entries.
See less