The principal book of accounting is “Ledger”. It records all types of transactions relating to a real, personal or nominal account. It records transactions relating to an income, expense, asset or a liability. A ledger classifies a transaction which is recorded in journal to their respective accountRead more
The principal book of accounting is “Ledger”. It records all types of transactions relating to a real, personal or nominal account. It records transactions relating to an income, expense, asset or a liability.
A ledger classifies a transaction which is recorded in journal to their respective accounts, and in the end calculates a closing balance for the same account. The closing balance is further transferred to the financial statements, and hence ledger is called the books of final entry as it gives true and fair picture of an account.
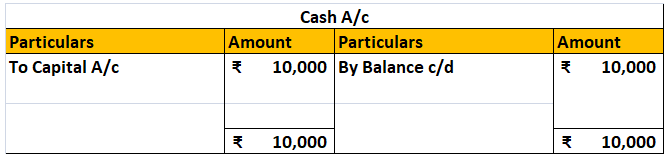
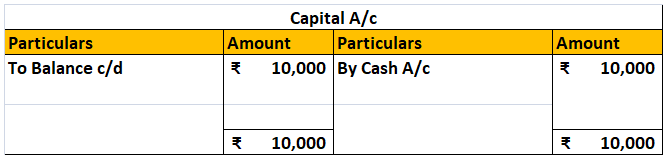
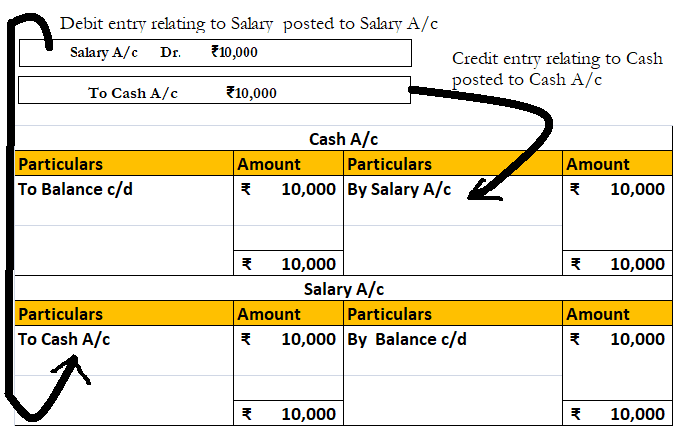
Template of Ledger:
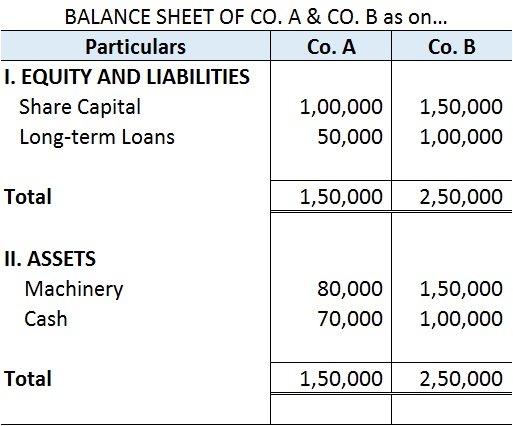
For example, ABC Ltd purchased machinery for cash amounting to Rs 1,00,000 on 1st January. This transaction will include a machinery account and a cash account. The amount will be recorded in the respective accounts for that period.
The reason being ledger is called a principal book of accounting is, it helps a business in preparation of trial balance and financial statements.
See less

Capitalize in Accounting The term 'capitalized' in accounting means to record an expenditure as an asset on the balance sheet. Capitalization takes place when a business buys an asset that has a useful life. The cost of the relevant asset is then allocated to expense over its useful life i.e charginRead more
Capitalize in Accounting
The term ‘capitalized’ in accounting means to record an expenditure as an asset on the balance sheet. Capitalization takes place when a business buys an asset that has a useful life. The cost of the relevant asset is then allocated to expense over its useful life i.e charging depreciation, etc. This means that the relevant expenditure will appear on the balance sheet instead of the income statement. The capitalizing of the expenses is a benefit for the company as the assets bought by them for the long-term are subjected to depreciation and capitalizing expenses can amortize or depreciate the costs. This process is called capitalization.
In order to capitalize any expense, we’ll have to make sure it meets the criteria stated below.
The assets exceeding the capitalization limit
The companies set a capitalization limit, below which the expenses are considered too immaterial to be capitalized. Therefore, the limit is supposed to be followed and considered as it controls the capitalization of the expenses. Generally, the capitalization limit is $1,000.
The assets have a useful life
The companies also seek to generate revenues for a long period of time. Thus, the asset should have a long and useful life at least a year or more. Thereby, the business can record it as an asset and depreciate it over its valuable life.
Most of the important principles of capitalization in accounting are from the matching principle.
Matching Principle
The matching principle states that the expenses in the accounting should be recorded when they are incurred and not when the payment is made. This helps the business identify the amounts spent to generate revenue.
For e.g, the company bought machinery for manufacturing goods with more efficiency. It is supposed to have a useful life for a period of over 10 years. Instead of expensing the entire cost of the machinery, the company will write off (depreciated) the cost of the asset over its useful life i.e 10 years. Therefore, the asset will be written off as it is used and these types of assets are automatically used as capitalized assets.
Benefits of Capitalization
Capitalization is of course recording expenses as an asset but this indeed has benefits.
See less