AS-11: The effects of changes in foreign exchange rates deal with the issues in the translation of foreign currency transactions and foreign operations. Foreign operations of a reporting enterprise mean its subsidiary, associate, joint venture or branch which is based or conducted in a country otherRead more
AS-11: The effects of changes in foreign exchange rates deal with the issues in the translation of foreign currency transactions and foreign operations.
Foreign operations of a reporting enterprise mean its subsidiary, associate, joint venture or branch which is based or conducted in a country other than the country of the reporting entity
For simple understanding let’s consider foreign operation as a branch of a business that is based in a foreign country.
Foreign Integral operations
So, integral foreign operations will be a dependent branch that works on the directions of the head office and it is like an extension of the business. The head office consigns goods to it and it sells them and remits cash and reports to the head office.
It is dependent on head office for receiving goods to sell and to cover its expenses.
Further, the difference in foreign exchange rate affects the present and future cash flows to the head office.
Foreign Non-Integral operations
A non-integral foreign operation will be like an independent branch that can operate without the aid of the head office. Apart from selling goods of the head office, it also buys goods from the local market and sells them.
Also, it covers its expenses on its own. It doesn’t remit the cash from sales regularly like a dependent branch. It is like acts an investment of the main business.
The difference in the foreign exchange rate has little or no effect on the present or future cash flows of the head office
See less
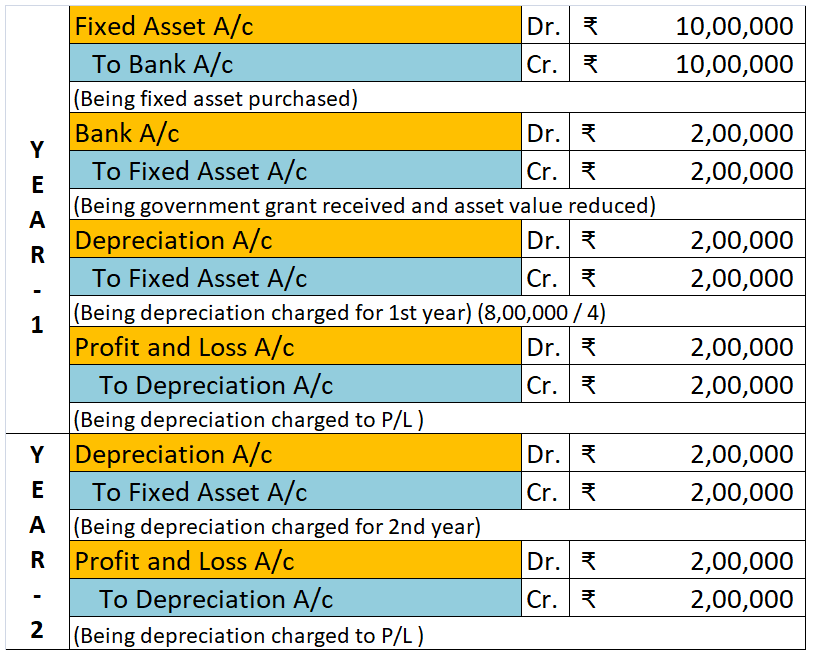
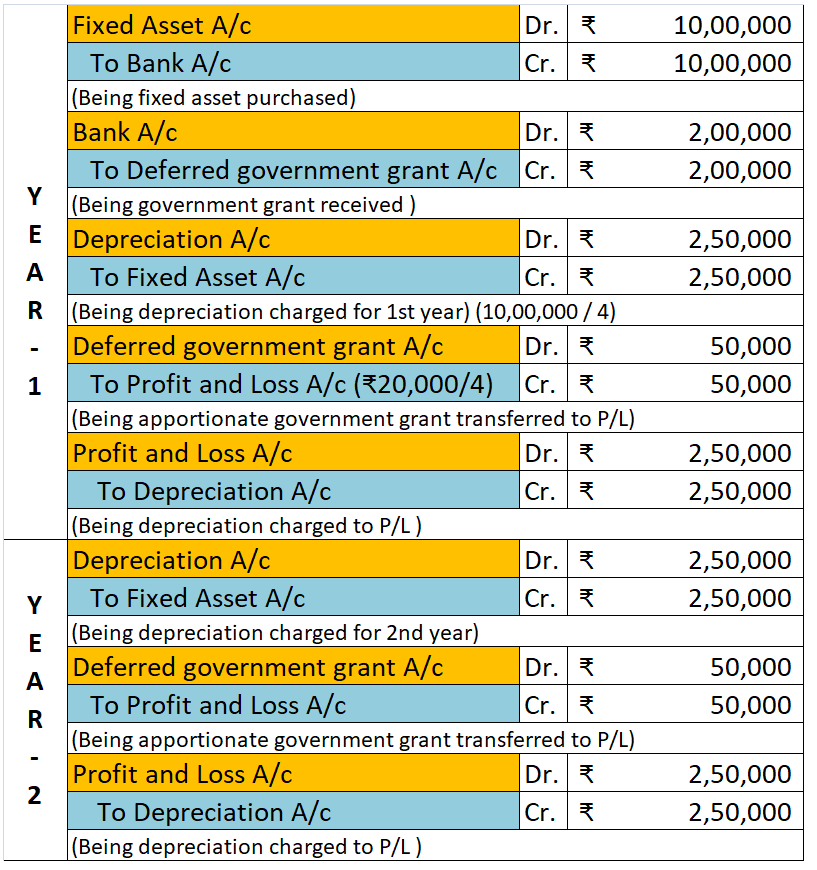
As per AS-10 ( Revised ): Property, Plant and Equipment, depreciation on an asset should begin when the asset is in the location and condition necessary for it to be capable of operating in the manner as intended by the management. This means a firm should start charging depreciation when the assetRead more
As per AS-10 ( Revised ): Property, Plant and Equipment, depreciation on an asset should begin when the asset is in the location and condition necessary for it to be capable of operating in the manner as intended by the management.
This means a firm should start charging depreciation when the asset is ready to be used as per the management’s desire.
Let’s take an example to understand this clearly:
A business bought a drinking water cooler for its office use on 1st April 2021. Now, this water cooler needs to be installed and wiped with Isopropyl Alcohol before it can be put to use.
The business completed all the required procedures by 1st May 2021, but it opened the machine for office use from 1st August 2021.
So the question arises, from when to start charging depreciation?
The answer is 1st May 2021– The date when the machine was ready to use.
It doesn’t matter whether the company started the use of an asset or not. Once an asset is in
the depreciation should begin.
See less