A cash flow statement presents the changes in the cash and cash equivalents of a business. It classifies the cash flow items into either operating, investing, or financing activities. The cash flow statement provides information about the flow of cash over a period of time. General reserve is a reseRead more
A cash flow statement presents the changes in the cash and cash equivalents of a business. It classifies the cash flow items into either operating, investing, or financing activities. The cash flow statement provides information about the flow of cash over a period of time.
General reserve is a reserve created by taking a portion of the profits for future requirements.
TREATMENT OF GENERAL RESERVE
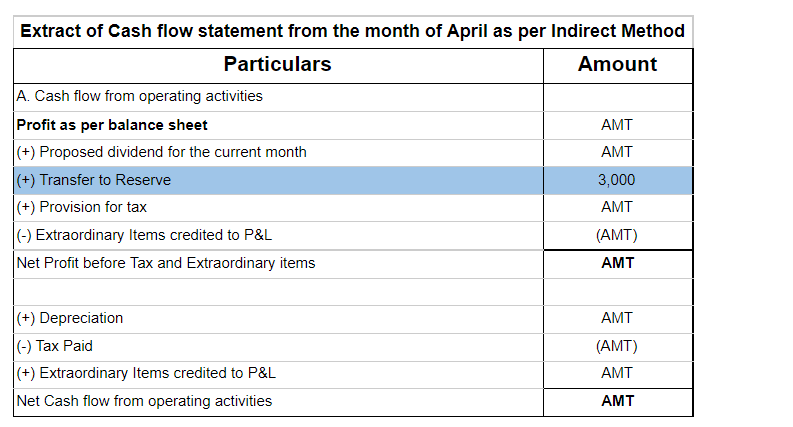
As per the indirect method, Since there is no actual flow of cash, any addition to reserves is added back to net profit for calculation of net profit before tax and extraordinary items. This net profit before tax will appear under cash flow from operating activities. If there is a reduction in reserve, then they are subtracted from net profit.
As per the Direct method, an increase or decrease in general reserve will not affect the cash flow statement since non-cash items are not recorded. Only cash receipts and payments that come under operating activities are recorded. So, net profit is not shown in the direct method and hence neither is general reserve.
General reserve does not fall under the head investing activities as investing activities involve the acquisition or disposal of long-term assets or investments. They do not fit in financing activities either as financing activities relate to change in capital or borrowings of the company.
EXAMPLE
If the balance in general reserve for the period of March was Rs 4,000 and in April the balance was Rs 7,000, then its treatment in cash flow would be:
See less


General reserve is the part of profits or money kept aside to meet future uncertainties and obligations of the entity. General reserve is created out of revenue profits for unspecified purposes and therefore is also a part of free reserves. General reserve forms a part of the Profit & Loss ApprRead more
General reserve is the part of profits or money kept aside to meet future uncertainties and obligations of the entity. General reserve is created out of revenue profits for unspecified purposes and therefore is also a part of free reserves.
General reserve forms a part of the Profit & Loss Appropriation account and is created to strengthen the financial position of the entity and serves as a sources of internal financing. It is upon the discretion of the management as to how much of a reserve is to be created. No reserve is created when the entity incurs losses.
General reserve is shown in the Reserves & Surplus head on the liability side of the balance sheet of the entity and carries a credit balance.
Suppose, an entity, ABC Ltd engaged in the business of electronics earns a profit of 85000 in the current financial year and has an existing general reserve amounting to 100000. The management decides to keep aside 20% of its profits as general reserve.
Then the amount to be transferred to general reserve will be = 85000*20% = 17000.
In the financial statements it will be shown as follows-
Now, in the next financial year, the entity incurs losses amounting to 45000. In this case, no amount shall be transferred to the general reserve of the entity and will be shown in the financial statement as follows-
The creation of general reserve can sometimes be deceiving since it does not show the clear picture of the entity and absorbs losses incurred.
See less