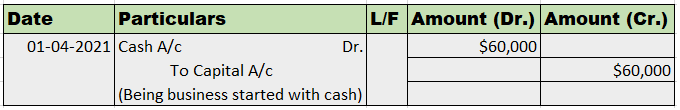
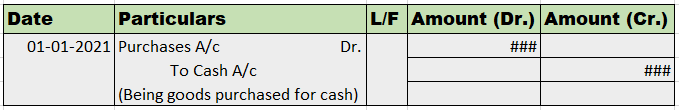
Journal entry for goods purchased by cheque The journal entry for goods purchased by cheque is as follows: In this journal entry, purchase account and bank account are involved. The explanation is given below. Explanation Purchase Whenever there is a purchase of goods, the purchase account is debiteRead more
Journal entry for goods purchased by cheque
The journal entry for goods purchased by cheque is as follows:

In this journal entry, purchase account and bank account are involved. The explanation is given below.
Explanation
Purchase
Whenever there is a purchase of goods, the purchase account is debited.
Goods refer to the items which an enterprise manufactures or purchases and sells to generate its business revenue.
If there is a purchase of any other item which does not satisfy the above definition of goods, then the purchase account is not involved.
For example, if stationery is purchased and the enterprise does not trade in stationery items, then the purchase account will not appear in the journal entry.
Payment by cheque
Payment by cheque means the payment amount will be deducted from the bank account balance. Hence, in the given journal entry, the bank account is involved.
The logic behind the debit and credit
The golden rules of accounting
Purchase is an expense hence it is a nominal account. The golden rule for nominal accounts is “Debit all expense and loss and credit all incomes and gains”
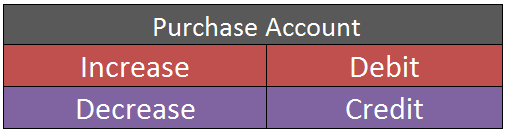
Hence, the purchase account is debited.
Bank is a real account and the golden rule of accounting for real accounts is, “Debit what comes in, credit what goes out”.
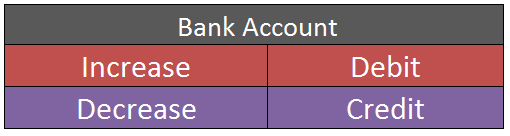
Hence, the bank account is credited as money is going out of the bank.
Modern rules of accounting
Purchase is an expense account, and expenses are debited when increased and credited when decreased.
Hence, the purchase account is debited here.
A bank account is an asset account. Asset accounts are debited in case of an increase and credited in case of a decrease. Hence, the bank account is credited here.
See less
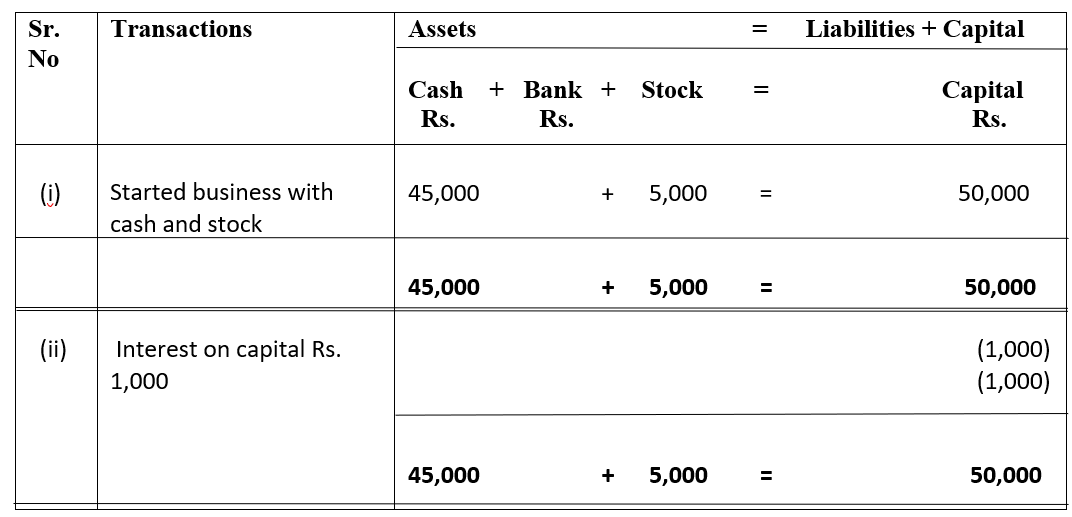
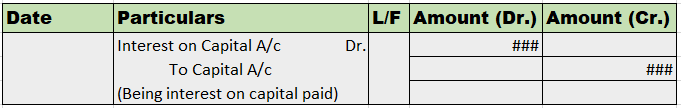
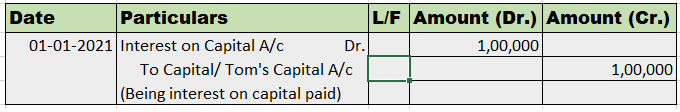
Introduction The term 'gain ratio' is related to partnership accounting. Gain ratio refers to the ratio in which existing partners of a partnership firm, divide among themselves, the share of profit and loss of the outgoing partners. There is a method of calculating this gain ratio. The method alongRead more
Introduction
The term ‘gain ratio’ is related to partnership accounting. Gain ratio refers to the ratio in which existing partners of a partnership firm, divide among themselves, the share of profit and loss of the outgoing partners.
There is a method of calculating this gain ratio. The method along with the concept behind gain ration is discussed below.
Concept behind gain ratio
A partnership firm is a form of business organisation which is conducted and carried on by members known as partners. It requires at least two partners to start a firm and the maximum limit is 50.
The partners share the profit and loss of a business in a ratio known as Profit and loss sharing ratio.
For example, Amanda, Bill and Chang are partners, having a P/L sharing ratio of 3:2:1 i.e. Amanda is getting 3/6, Bill is getting 2/6 of the same and Chang is getting ⅓ of the profit and loss
If the profit is $6,000 , then Amanda will get $3,000 (3/6 of $6,000) and Bill will get $2,000 (2/6 of $6,000) and Chang will get $1,000 (1/6 of $6,000).
Now if Amanda retires from the firm, then naturally, Bill and Chang’s share of profit will increase.
The profit and loss sharing ratio will now be 2:1 (earlier it was 3:2:1) and the share of profit of Bill will be $4,000 and of Chang will be $2,000.
Calculation of gain ratio
The formula for calculating gain ratio = New ratio – Old Ratio
As per the above case:
Therefore the gain ratio in which Bill and Chang gained the share of profit of Amanda is 2/6 : 1/6 or simply 2:1
This is how we can calculate the gain ratio. But one thing to notice is that the gain ratio is equal to the P/L sharing ratio of the partnership between Bill and Chang.
Hence, whenever a partner retires and the existing partner keep the P/L sharing ratio unchanged among themselves then, the gain ratio will be equal to their P/L sharing ratio. In that case, there is no need to calculate the gain ratio from the formula given above.
But, when the remaining partners change the P/L sharing ratio among themselves after a partner retires, then the gain ratio is to be calculated using the formula given above.
Suppose, upon retirement of Amanda, Bill and Chang change the P/L sharing between them to from 2:1 to 3:2
In that case,
Therefore the gain ratio in which Bill and Chang will gain the share of profit of Amanda is 8/30 : 7/30 or simply 8:7

See less