Introduction & Definition Firstly, let's see what the term 'petty cash book' means. The word ‘petty’ means small. A petty cash book is identical to a cash book, maintained to record the small expenses of a business like stationery, postage, stamps, carriage, etc. The cash received by a petty casRead more
Introduction & Definition
Firstly, let’s see what the term ‘petty cash book’ means. The word ‘petty’ means small. A petty cash book is identical to a cash book, maintained to record the small expenses of a business like stationery, postage, stamps, carriage, etc. The cash received by a petty cashier is recorded on the debit/ receipt side whereas, the money he pays is recorded on the credit/ payment side. The difference between the sum of the debit and credit items represents the balance of the petty cash in hand.
The reason the petty cash book is maintained is that it records small expenses that are inconvenient or too small to be registered in the cash book. This is also called a simple petty cash book. Just like a cash book is maintained by the accountant, the petty cash book is maintained by a petty cashier.
When it comes to the format, there are two types of petty cash book formats. They are-
- Simple Petty Cash Book
- Analytical Petty Cash Book
We have been discussing the simple petty cash book so far. Thus,
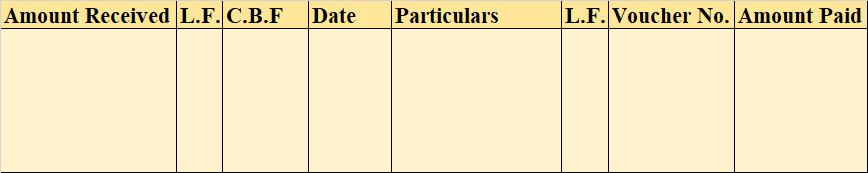
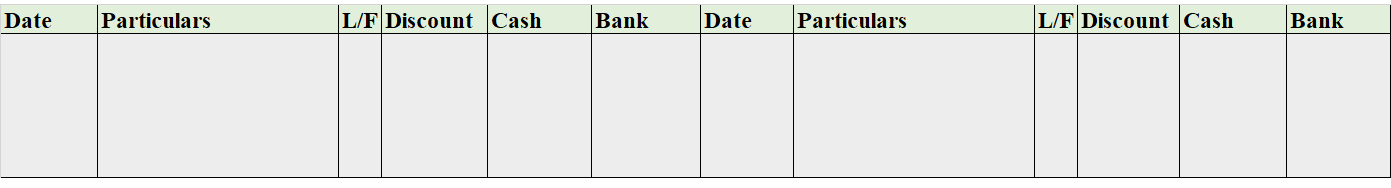
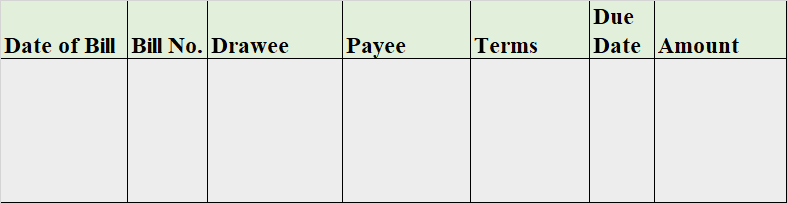
Format of Simple Petty Cash Book
Analytical Petty Cash Book
The analytical petty cash book has numerous columns for the recording of monetary transactions. In the analytical petty cash book, there are pre-existing columns for the usual expenses that are recorded frequently in the business which makes it easier for a business that has daily expenses for food, stationery, postage, etc. They’ll be having individual columns. It has numerous columns in it for the recording of expenses in it.
The key advantages of an analytical petty cash book are-
- One of the major key advantages is that the analytical petty cash book due to its format and structure saves time.
- The other advantage is that it helps the business in easy comparisons.
- It requires lesser time in recording.
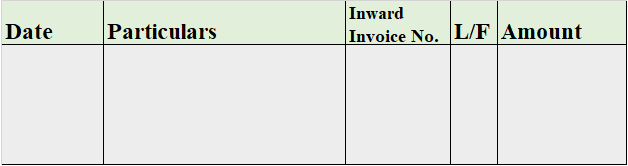
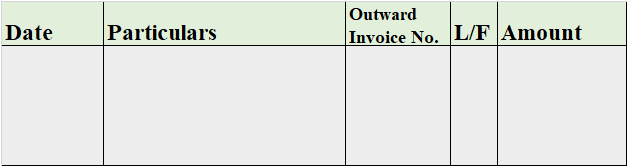
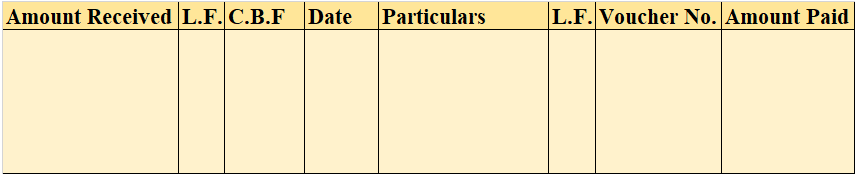
Format of Analytical Petty Cash Book
See less



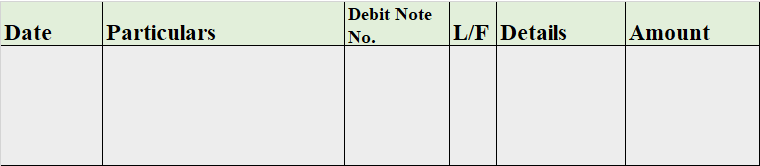
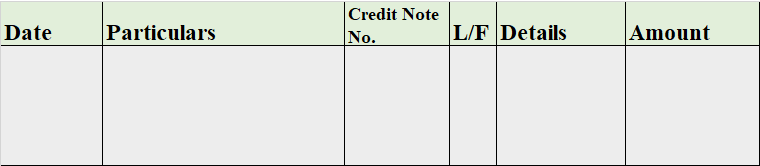
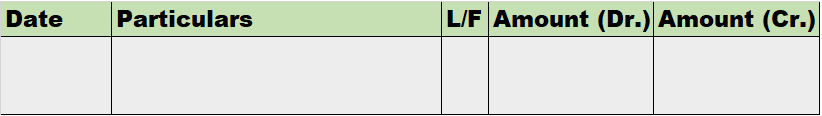
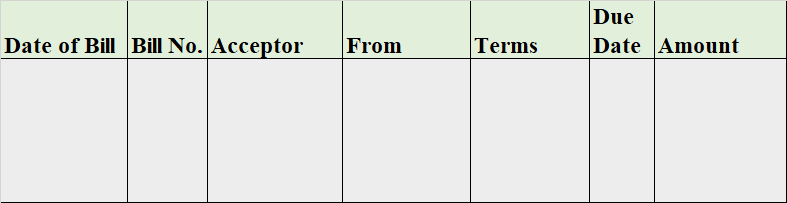
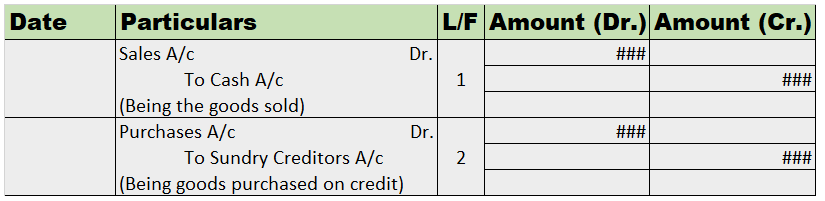
Debts are of two types one is Good Debt, and another one is Bad debt. Bad Debts The amount which is not recoverable from the debtors is called Bad debt. It is an uncollectable amount from the organization's customers due to the customer's inability to pay the amount of money taken on credit. Read more
Debts are of two types one is Good Debt, and another one is Bad debt.
Bad Debts
The amount which is not recoverable from the debtors is called Bad debt. It is an uncollectable amount from the organization’s customers due to the customer’s inability to pay the amount of money taken on credit.
Example 1
Mr A borrowed $100 from Mr B for his college fee and agrees to pay in 2 months. After the time period is complete Mr A failed to repay the borrowed amount. This is a Bad Debt for Mr B.
Example 2
XYZ Co. had made a credit sale of $50,000. A debtor who has to pay $1000 has been bankrupted. XYZ co. cannot recover the amount from the Debtor, so it records the irrecoverable amount as a bad debt.
Journal Entry
In this entry, “Bad debts are written off of Rs. 2000.”
Bad debt is the amount not recoverable from debtors, which is a loss for the organization.
Modern Rule
The Modern rules of accounting for Expenses are “Debit the increase in expenses and Credit the decrease in expenses.”
Golden Rule
The Golden rules of accounting for expenses and losses are “Debit all expenses and losses, Credit all incomes and gains.”
Bad Debts A/c Dr. 2,000
To Debtor’s A/c 2000
Bad debt is treated as a loss for the organization. As per the rule, this should be debited to the profit and loss account.
Profit and Loss A/c Dr. – 2000
To Bad Debts A/c – 2000
Instead of passing two separate entries for writing off, we can combine the entries and pass one entry.
Profit and Loss A/c Dr. 2000
To Debtor’s A/c 2000
Recovery of Bad debts
Recovery of Bad debt is the amount received for a debt that was written off in the past. It was considered uncollectable.
When we write off bad debt, it is recorded as a loss, but the recovery of bad debts is treated as an income for the business.
It is treated as an income and the recovery of bad debt is shown on the credit side of the Income statement.
Journal Entry for Recovery of Bad debts
Bank/Cash A/c Dr. – Amount
To Bad Debts Recovered A/c – Amount
Rules applied in the Journal entry are as per the Golden rules of accounting,
“Cash/Bank A/C” is a real account therefore debit what comes in and credit what goes out.
“Bad Debts Recovered A/C” is a nominal account therefore debit all expenses and losses, and credit all incomes and gains.
Treatment of “Bad Debt written off of Rs.2ooo.”
In Trial Balance: No effect
In Income Statement: It is shown on the debit side as Rs.2000 (loss)
In Balance Sheet: Rs.2000 shall be deducted from the sundry debtor account.
See less