What is the difference between expense and revenue expenditure
Definition Goodwill is an intangible asset that places an enterprise in an advantageous position due to which the enterprise is able to earn higher profits without extra effort. For example, if the enterprise has rendered good services to its customers, it will be satisfied with the quality of its sRead more
Definition
Goodwill is an intangible asset that places an enterprise in an advantageous position due to which the enterprise is able to earn higher profits without extra effort.
For example, if the enterprise has rendered good services to its customers, it will be satisfied with the quality of its services, which will bring them back to the enterprise.
Features
The value of goodwill is a subjective assessment of the valuer.
• It helps in earning higher profits.
• It is an intangible asset.
• It is an attractive force that brings in customers to the business.
• It has realizable value when the business is sold out.
Need for goodwill valuation
The need for the valuation of goodwill arises in the following circumstances :
• When there is a change in profit sharing ratio.
• When a new partner is admitted.
• When partner retires or dies.
• When a partnership firm is sold as a going concern.
• When two or more firms amalgamate.
Classification of goodwill
Goodwill is classified into two categories:
• Purchased goodwill
• Self-generated goodwill
Purchased goodwill :
Is that goodwill acquired by the firm for consideration whether paid or kind?
For example: when a business is purchased and purchase consideration is more than the value of net assets the difference amount is the value of purchase goodwill.
Self-generated goodwill
It is that goodwill that is not purchased for consideration but is earned by the management’s efforts.
It is an internally generated goodwill that arises from a number of factors ( such as favorable location, efficient management, good quality of products, etc ) that a running business possesses due to which it is able to earn higher profits.
Methods of valuation
1. Average profit method
2. Super profit method
3. Capitalization method
Average profit method: goodwill under the average profit method can be calculated either by :
• Simple average profit method or
• Weighted average profit method
See less

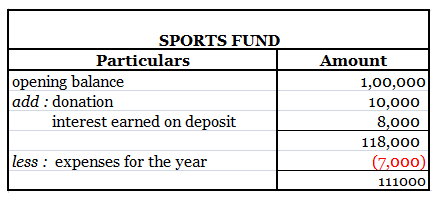
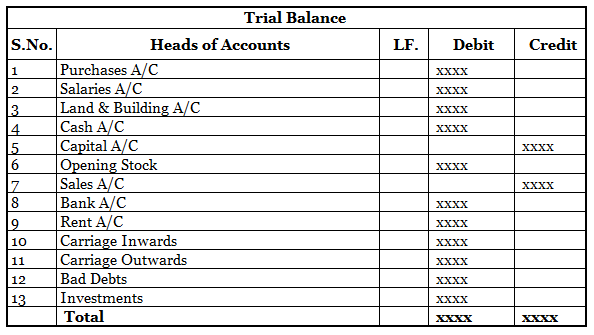
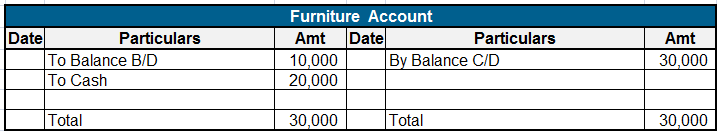
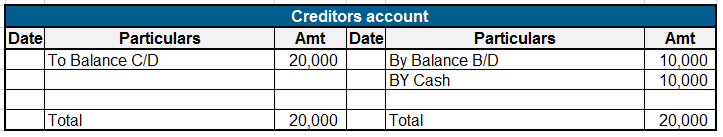
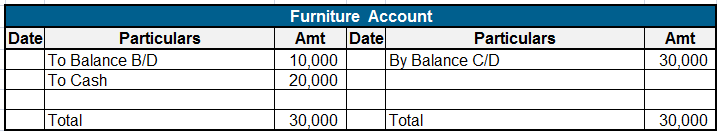
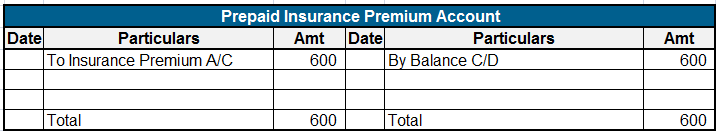
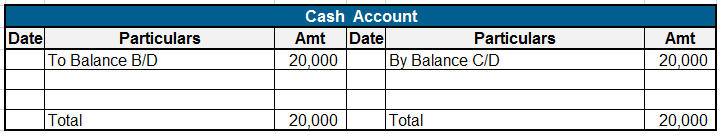
Expense Expenditure: Expense expenditures refer to the costs incurred by a company in its day-to-day operations. These expenses are deducted from revenue to calculate the net income. Here are some examples of expense expenditures: Salaries and wages: The payments made to employees for their servicesRead more
Expense Expenditure:
Expense expenditures refer to the costs incurred by a company in its day-to-day operations. These expenses are deducted from revenue to calculate the net income. Here are some examples of expense expenditures:
Salaries and wages: The payments made to employees for their services are considered expense expenditures. This includes salaries, wages, bonuses, and commissions.
Rent: The cost of leasing office space or other business premises is an expense expenditure. It includes monthly rent payments, property taxes, and insurance premiums associated with the rented space.
Utilities: Expenses related to utilities such as electricity, water, gas, and internet services are considered expense expenditures.
Office supplies: The cost of purchasing and replenishing office supplies like stationery, printer ink, pens, paper, and other consumables is categorized as an expense expenditure.
Advertising and marketing: Expenditures incurred to promote a company’s products or services, such as advertising campaigns, online marketing, social media promotions, and print media advertisements, are considered expense expenditures.
Revenue Expenditure:
Revenue expenditures are expenses incurred to acquire or improve assets that are expected to generate revenue over multiple accounting periods. Unlike expense expenditures, revenue expenditures are typically not capitalized. Here are some examples of revenue expenditures:
Repairs and maintenance: Costs incurred to repair and maintain existing assets, such as machinery, equipment, and vehicles, are considered revenue expenditures. Routine maintenance expenses, like oil changes, servicing, and small repairs, fall into this category.
Software and technology upgrades: Expenses incurred to upgrade or enhance software systems, computer hardware, or other technological infrastructure are considered revenue expenditures.
Training and development: Expenditures on employee training programs, workshops, seminars, and skill development courses that enhance the productivity and capabilities of the workforce are classified as revenue expenditures.
Advertising campaigns for new products: While advertising expenses are generally classified as expense expenditures, when they are specifically related to the launch or introduction of new products or services, they can be considered revenue expenditures.
Renovation and improvements: Costs incurred to renovate or improve existing assets, such as office spaces, stores, or warehouses, can be classified as revenue expenditures if they enhance the earning capacity or extend the useful life of the asset.
These examples highlight the distinction between expense and revenue expenditures based on their purpose and treatment in financial statements.
See less