To understand the accounting treatment of fixed assets under IFRS let us first understand what fixed assets are. What are Fixed Assets? Fixed assets are the assets that are purchased for long-term use by a business and not for resale. Some examples of fixed assets are land, buildings, machinery, furRead more
To understand the accounting treatment of fixed assets under IFRS let us first understand what fixed assets are.
What are Fixed Assets?
Fixed assets are the assets that are purchased for long-term use by a business and not for resale. Some examples of fixed assets are land, buildings, machinery, furniture and fixtures, etc.
Fixed assets are essential for the smooth operations of the business. It often shows the value of the business. The value of fixed assets usually decreases with time, obsolescence, damage, etc.
As per IAS-16 Property, Plant and Equipment, an asset is identified as a fixed asset if it satisfies the following conditions:
- the future economic benefits associated with the asset will probably flow to the entity, and
- the cost of the asset can be measured reliably.
What is IFRS?
IFRS stands for International Financial Reporting Standards. It provides a set of standards to be followed globally by all companies to ensure transparency, comparability, and consistency.
What is the accounting treatment of fixed assets under IFRS?
Under IFRS, the first step is to measure the value of the fixed assets on cost. The cost of the fixed assets includes the following:
- purchase price
- any direct cost related to the asset (such as transportation, installation, etc.)
- duties/taxes
After this step, the entity may choose any one of the following two primary methods:
- Cost Model: According to this model the value is first recognized on a cost basis. This includes the purchase price and direct costs attributable to the asset. Subsequently, depreciation is calculated on the cost of the asset. Depreciation spreads the cost of an asset over its useful life. Impairment checks are conducted to ensure the asset’s value on the books doesn’t exceed what it’s worth.
For example, a company bought a piece of machinery for 60,000. 5,000 were spent on its installation. It has a useful life of 10 years. The machinery would be depreciated over its useful life of 10 years based on its cost which is 65,000.
2. Revaluation model: As per this model, the fixed assets are valued on their fair value, as on the revaluation date. The amount of depreciation and impairment losses is subtracted from the fair value.
If the value of an asset increases, the gain goes to equity (revaluation surplus) unless it can be set off with a past loss recorded in profit or loss.
On the other hand, if the value decreases, the loss goes to profit or loss unless it offsets a past surplus in equity.
For example, a building was purchased for 100,000. On the revaluation date, the fair value of this building was 150,000. Hence, there is a revaluation surplus of 50,000 which shall be credited to the revaluation surplus account.
Impact on Financial Statements
Fixed assets are shown on the Assets side of the Balance Sheet.

Conclusion
From the above discussion, it may be concluded that:
- Fixed assets are the assets that are purchased for long-term use by a business and not for resale.
- Some examples of fixed assets are land, buildings, machinery, furniture and fixtures, etc.
- IFRS provides a set of standards to be followed globally by all companies to ensure transparency, comparability, and consistency.
- Under IFRS, the first step is to measure the value of the fixed assets on cost.
- After this step, the entity may choose any one of the two primary methods which are cost model and the revaluation model.
- Fixed assets are shown on the Assets side of the Balance Sheet.
See less

Every business requires research and development to create innovative products for consumers. More innovative and creative products and services are more popular among customers, leading to increased revenue and profits for the business. Creating new products or designing changes and testing existinRead more
Every business requires research and development to create innovative products for consumers. More innovative and creative products and services are more popular among customers, leading to increased revenue and profits for the business.
Creating new products or designing changes and testing existing products also forms a part of research and development.
Examples of Research and Development costs are –
Let us now understand how research and development costs are treated in Financial Statements.
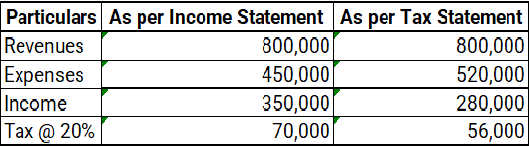
Research and Development Costs are generally shown as an expense in the Income Statement.
IAS-38
IAS-38 majorly governs the accounting of research and development costs. There are two phases in R&D:
1. it is developed with the intention of putting it to use in the future
2. the asset shall hold an economic value
3. the costs can be measured reliably
Treatment of R&D costs in the Financial statements:
Conclusion
The above discussion can be summarised as follows:
- Research and development is essential for creating innovative and creative products and services.
- Accounting standard IAS-38 governs the accounting for Research and Development.
- Research costs are usually shown as an expense in the Income statement of the business.
- Development costs when capitalised can be shown as Intangible assets in the Balance Sheet.
See less