Therefore, 2) Asset is the correct option. Explanation The petty cash book is managed and made by not an accountant but the petty cashier and is done to record small incomes and expenditures that are not recordable in the cash book. Therefore, the desired result we obtain from the deduction oRead more
Therefore, 2) Asset is the correct option.
Explanation
The petty cash book is managed and made by not an accountant but the petty cashier and is done to record small incomes and expenditures that are not recordable in the cash book. Therefore, the desired result we obtain from the deduction of the total expenditure and total cash receipt is the closing balance of the petty cash book.
Petty cash refers to the in-hand physical cash that a business holds to pay for small and unplanned expenses.
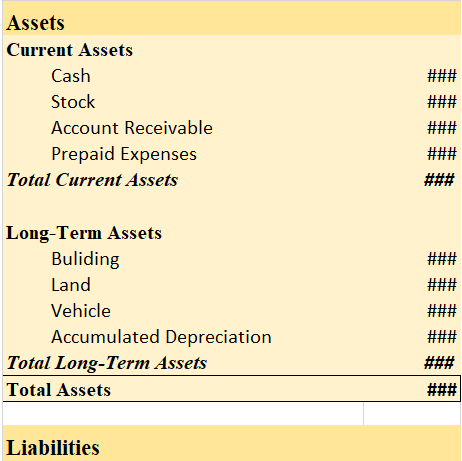
Asset: The closing balance of the petty cash book is considered an asset because the petty cash book is a type of cash book. The petty cash book also deals in outflow and inflow of the cash, it also maintains and records income and expenditure that are similar to the cash book.
The petty cash book since being a part of the cash book, which records all the inflow and outflow of cash in a business, which is an asset, thus petty cash book’s closing balance is considered an asset. Also, the balance of the petty cash book is never closed. Their closing balance is carried forward to the next year.
Liability: The closing balance of the petty cash book is not considered a liability because that closing balance of the petty cash book doesn’t create a liability for the business. In fact, the closing of the petty cash book is placed under the head current asset in the balance sheet as mentioned above, it’s a part of the cash book which records the transactions of cash a/c which is an asset itself.
Expenses or Income: It is not an expense because the closing balance of the petty cash book is calculated by deducting the total expenditure from the total cash receipt.
That is an asset and it is considered to be a current asset, neither an income nor an expense. It is used for paying out petty expenses.
Therefore, the closing balance of the petty cash book is considered an asset.
See less

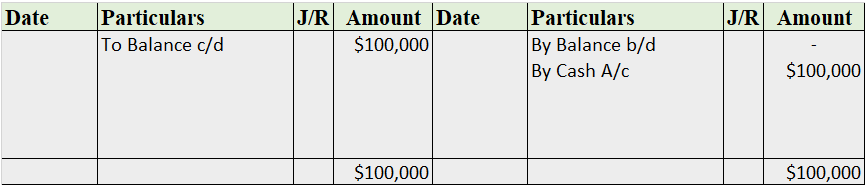
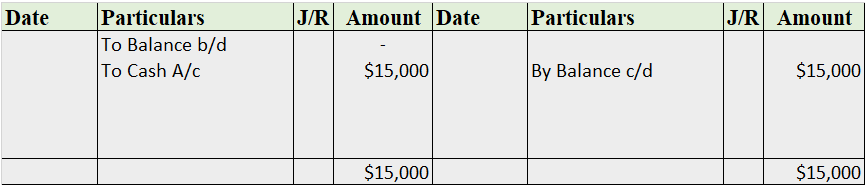
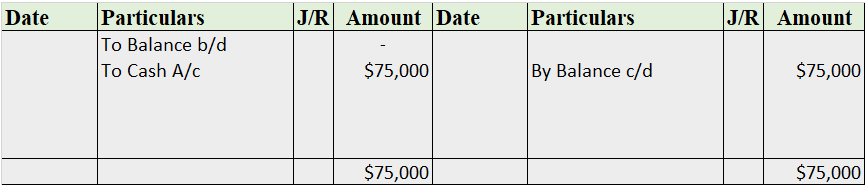
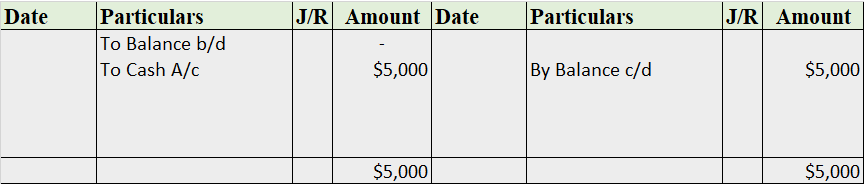
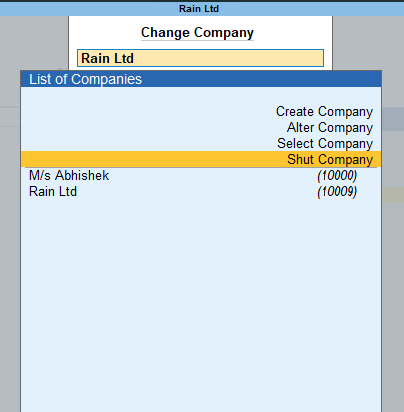
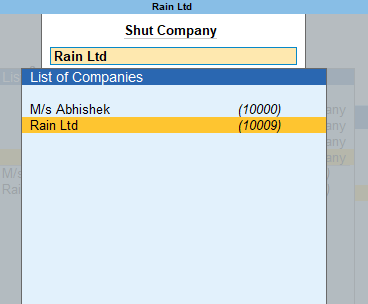
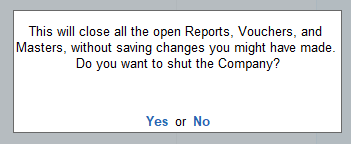
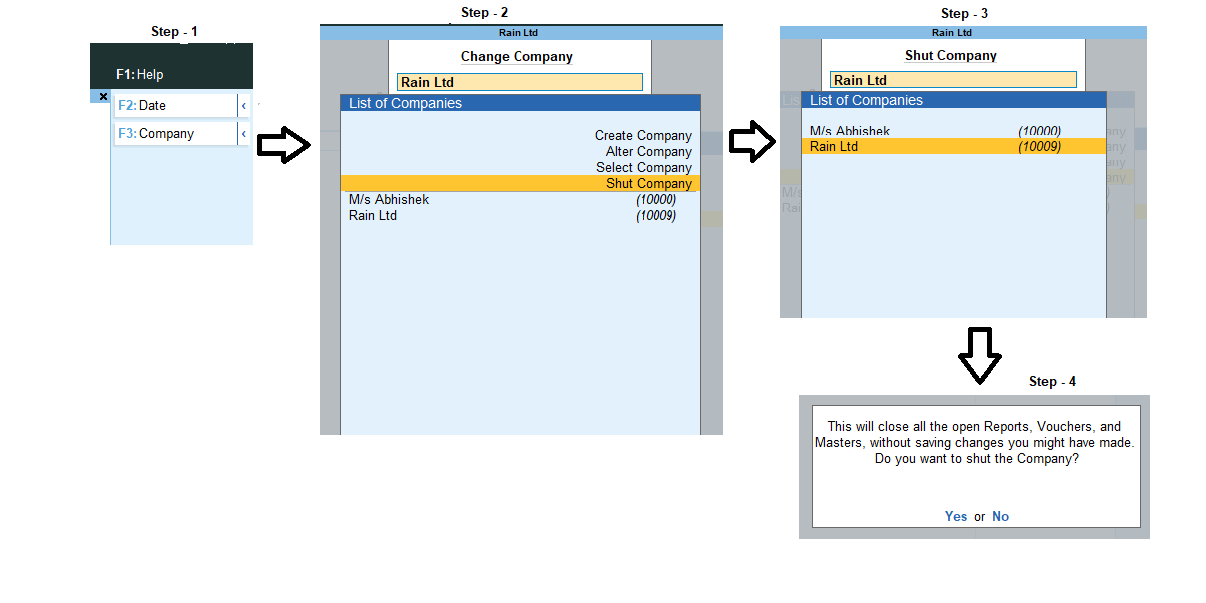
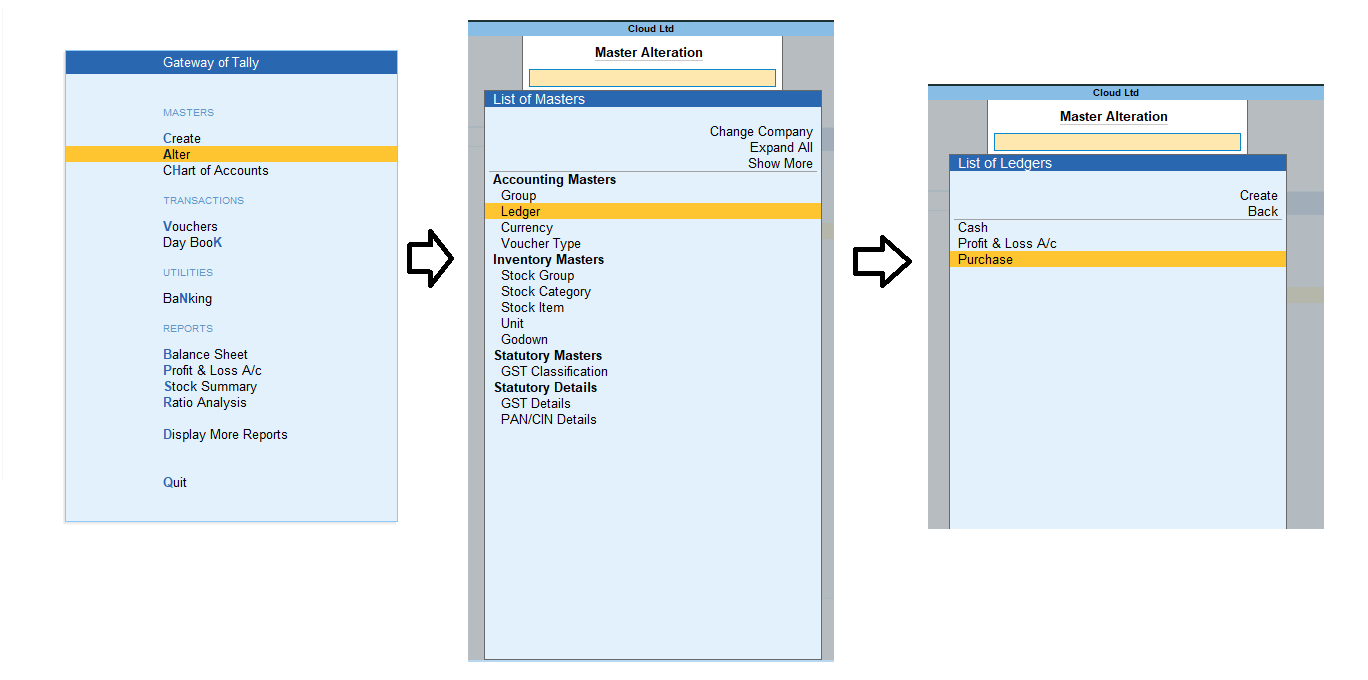
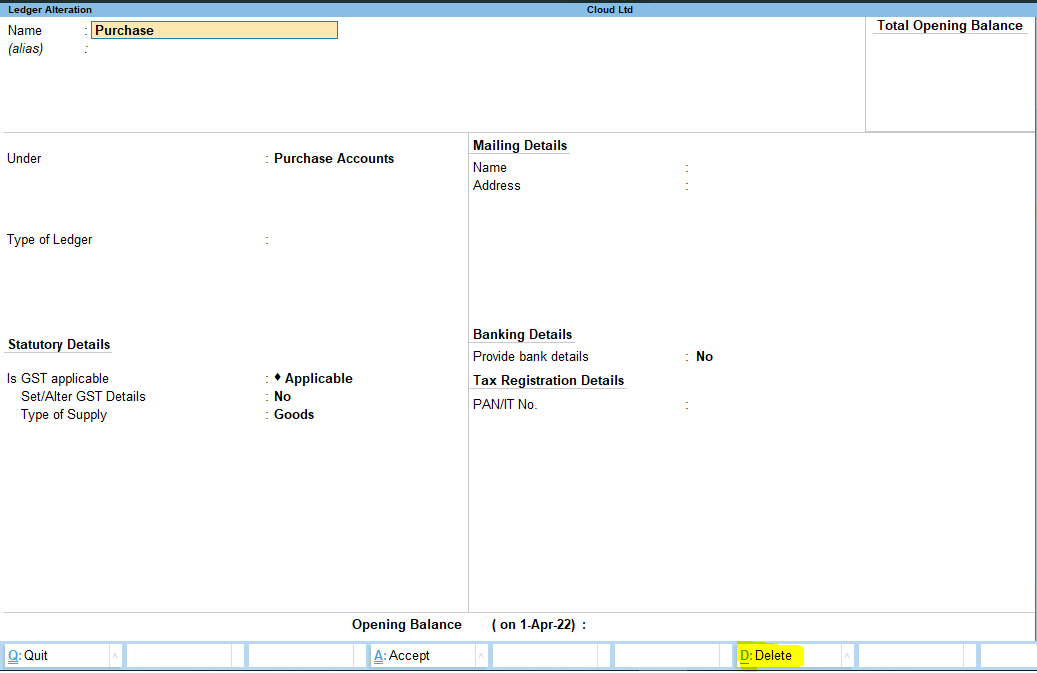

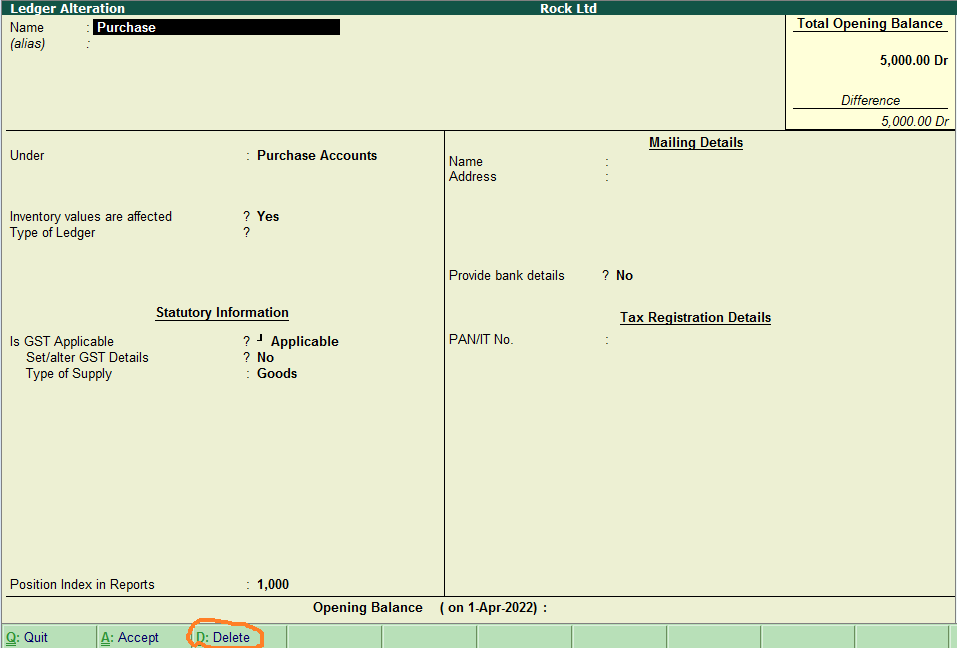
Subsidiary Books Introduction & Definition In large business organizations, it is practically impossible to keep a record of every single business affair, while neglecting them and not recording them wouldn't be an ideal choice, this is where subsidiary books come into the role. As we were introRead more
Subsidiary Books
Introduction & Definition
In large business organizations, it is practically impossible to keep a record of every single business affair, while neglecting them and not recording them wouldn’t be an ideal choice, this is where subsidiary books come into the role. As we were introduced to the basics of accounting in the 11th standard, we learned about different elements like journals, ledgers, trial balances, etc. It is practically impossible for a business to keep track of every single affair just through only those elements. Thus, the Subsidiary book is the next step here.
Subsidiary books are the books of original entry. They are a dedicated form of books that maintains an analysis of a specific account. It records financial transactions of a similar nature. They are sub-division of a journal.
In big business organizations, it’s very hard for a bookkeeper or accountant to record all the transactions in one journal and post them into various accounts. This is where special purpose books or subsidiary books may be required for more efficient bookkeeping. They are a subdivision of journals and for every type of transaction, there is a separate book.
Types of Subsidiary Books
There are eight types of subsidiary books that are required for recording transactions. The list of various subsidiary books is as follows:
Types of Subsidiary Books
Now, we’ll be taking a closer look at each and every subsidiary book.
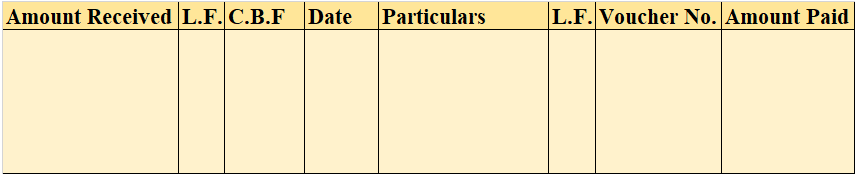
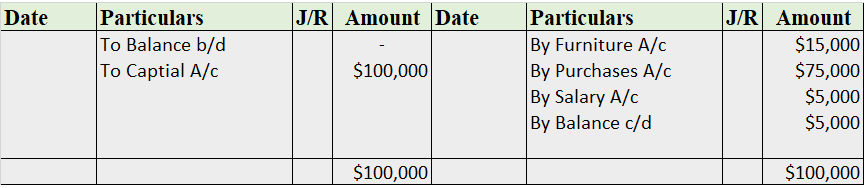
Cash Book
The cash book is the most important subsidiary book, it’s a book of a prime entry recording all the cash spent or received by the business, either in cash form or from the bank. In simple words, recording all the transactions made by the business.
It is of three types i.e single-column cash book, double-column cash book, and triple-column cash book. As the name indicates, the column of cash, bank, and discount increases/decreases as per the column of the cash book stated.
Format
Note: this is a triple-column cash book format, for the double-column cash book format, we remove the discount column from both sides, and for the single column, we may remove the bank column as well.
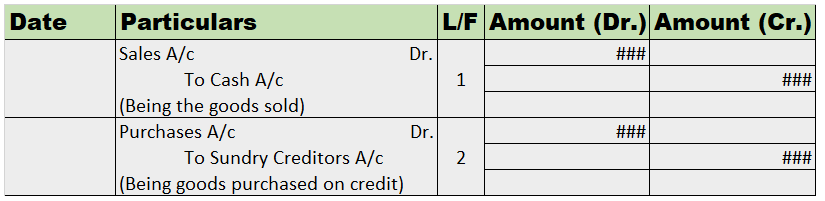
Purchase Book
A purchase book is a subsidiary book that records all the transactions related to the credit purchase in a business. Thereby, the normal purchasing of assets is never recorded in the purchase book.
The credit purchases are directly recorded in the purchase book from the journals or the source documents. The source document indicates bills payable, invoices, etc.
Format
Sales Book
A sales book, similar to a purchase book, is a special book where all the credit sales are recorded. The sales book doesn’t record the transactions related to the normal sale of assets and hence, is a special type of book, just like the purchase book.
Format
Purchase Return Book
The purchase return book, also known as the return outwards book, is that book that records the goods that were returned by us to the supplier. Thereby, called purchase return book.
When the goods are returned, a debit note is issued against every return and hence, recorded in the purchase return book.
Format
Sales Return Book
The sales return book, also known as the return inwards book, refers to that subsidiary book that records the goods which were returned to us by the customer.
For every good returned to us, a credit note is issued to the customer. And thus, it is recorded in the sales return book.
Format
Journal Proper
Just like we recently learned in class 11th about what a journal entry is and how it is made, it’s a little different from the journal proper. Journal proper is a subsidiary book that records all the transactions which are not recorded in other subsidiary books.
A journal is an original book of entries that records all the business transactions, while a journal proper is a subsidiary book in which all types of miscellaneous credit business transactions are recorded that do not fit anywhere in the other subsidiary books. Its format is the same as the journal entries’ format. Therefore, it’s also known as a miscellaneous journal.
Format
Bills Receivable Book
The bills receivable book is the book that draws the bills favorable to the business i.e when the goods or services are provided to any customer on credit, they become a debtor, and bills receivable is a written note received from the customer indicating that they formally agree to pay the sum of money owed.
Therefore, it helps in recording these types of transactions. The sum total of the bills receivable book is posted to the bills receivable account.
Format
Bills Payable Book
The bills payable book is the subsidiary book that records all the bills that are drawn on the company. The bills payable is drawn on the company when we buy a good/service on credit and agrees to pay the amount to the supplier by signing a written note with the date we agree to pay.
It’s a liability of the business and the total of the bills payable book is posted on the credit side of the bills payable account.
Format
See less