A Consignment Account is a Nominal Account. It is classified as a nominal A/c because it is prepared to ascertain the profit earned or loss incurred on the consignment. The accounting rule applied to consignment A/c: Debit all Expenses & Losses and Credit all Incomes & Gains. As per the modeRead more
A Consignment Account is a Nominal Account. It is classified as a nominal A/c because it is prepared to ascertain the profit earned or loss incurred on the consignment.
The accounting rule applied to consignment A/c: Debit all Expenses & Losses and Credit all Incomes & Gains.
As per the modern rules, there is no clear-cut classification of consignment A/c. It is prepared from the perspective of the consignor, hence it cannot be outrightly classified as an expense/revenue.
In the context of accounting, consignment refers to an arrangement of goods wherein the consignor sends the goods to the consignee so that the consignee can sell/distribute the goods on behalf of the consignor.
The relationship between the consignor and consignee is that of a principal and agent. The consignee gets a commission for his services.
You should keep in mind that the consignee does not get ownership of the goods even though the goods are in his possession. The ownership remains with the consignor till the sale is made. On sale, the buyer will become the owner.
A Consignment A/c is an account prepared to record the transactions happening in a consignment business. This account is maintained by the consignor. It shows the profit earned or loss incurred by the consignor on a specific consignment.
A consignor may send goods to more than one consignee. In such a case, a separate consignment A/c is prepared for each consignment.
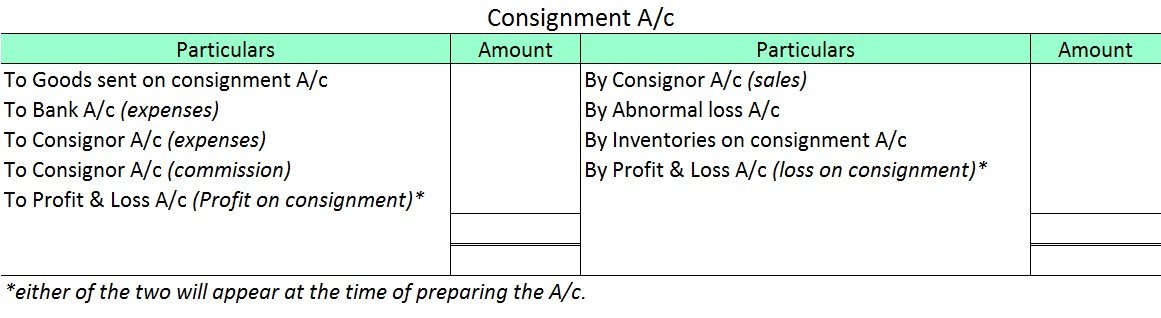
The following items appear on the debit side of the consignment A/c:
- Cost of goods sent on consignment.
- Expenses incurred by the consignor (freight, insurance, etc.)
- Expenses paid by the consignee (storage and warehousing, marketing expenses, packaging and selling expenses, etc.)
- Bad debts in consignment.
- Commission paid to consignee.
The entries appearing on the credit side of the consignment A/c are as follows:
- Gross sales.
- Abnormal loss of goods.
- Inventories on consignment (stock in transit).
The balance in the consignment A/c represents the profit or loss made on the consignment. It is transferred to the P&L A/c and the account is closed.
Below is the format for Consignment A/c:

Consignment is "goods sent by its owners to his agent for the purpose of sale". In simple language, the word consignment means to send goods to another person for sale on his behalf without transfer of ownership. In accounting terms, consignment is the process where the owner (consignor) transfers tRead more
Consignment is “goods sent by its owners to his agent for the purpose of sale”. In simple language, the word consignment means to send goods to another person for sale on his behalf without transfer of ownership.
In accounting terms, consignment is the process where the owner (consignor) transfers the possession of the goods to the agent (consignee) to make a sale on his behalf while the ownership of goods remains with the owner until the sale is made by the agent. In return, the agent receives an agreed percentage of the sum in the form of commission.
Generally, there are two parties involved in consignment, those are as follows:
The relationship between consignor and consignee is that of principal and agent.
Let me give you a simple example of how consignment works.
Mr. John (consignor) sends goods to Mr. Jeh (consignee) worth Rs 20,000 to sell these goods at a cost plus 10%. Mr. Jeh agrees to sell these goods on his behalf for a commission of 1% on the sale. Therefore Mr. Jeh sold these goods at the agreed amount i.e Rs 22,000 [20,000+ 10% of 20,000] and charges Rs 220 [1% of Rs 22,000] as commission made on such sale and remit the remaining balance to the owner Mr. John.
There is a lot of confusion regarding “is consignment the same as the sale of goods?“. The answer is NO.
The reason what makes it different from the sale is
a) In sale the ownership gets transferred from seller to buyer but in case of consignment the ownership remains with the consignor until the sale is made by the agent.
b) In sale the risk gets transferred with the transfer of goods, whereas in consignment the risk remains with the owner till the sale is made.
c) Also goods once sold cannot be returned on damages /defaults, but in case of consignment goods that come to be faulty can be returned to the consignor.

See less