Specimen of Bill of Exchange Important points of Bill of Exchange: Date: When a bill of exchange is drawn, the drawer has to specify the date in the top right corner. The date is important for the purpose of calculating the due date of the bill. Generally, the drawee is given three days as a grace pRead more
Specimen of Bill of Exchange

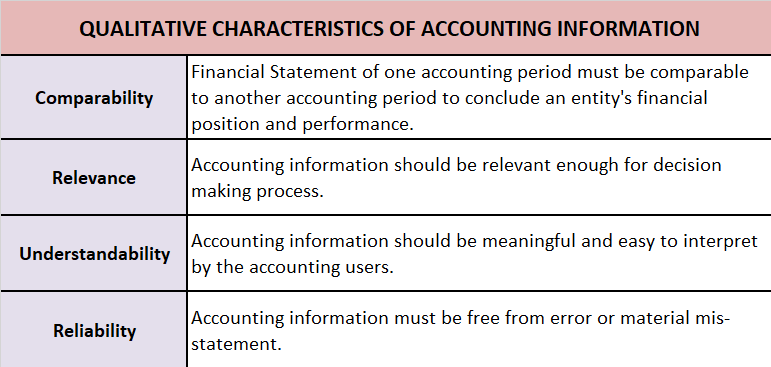
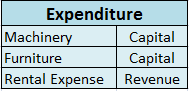
Important points of Bill of Exchange:
Date: When a bill of exchange is drawn, the drawer has to specify the date in the top right corner. The date is important for the purpose of calculating the due date of the bill. Generally, the drawee is given three days as a grace period over and above the due date of maturity.
In the above specimen, the date mentioned is 25th July 2021, so the due date will be three months + 3 days( grace period) i.e. to say 28th October 2021.
Term: In the above, the term as agreed by the drawer and drawee is 3 months. So the maturity date will be after 3 months.
Stamp: The Stamp is affixed in the left corner in every bill of exchange, the value of which depends upon the amount specified in the bill.
Parties involved in Bill of Exchange:
- Drawer: The one who makes the bill, i.e. the creditor.
- Drawee: The one on whom the bill is drawn, i.e. the debtor.
- Payee: The one to whom the amount is to be paid is the payee.
Sometimes, the drawer and the payee are the same people.
For Example,
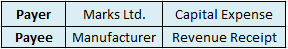
i) A bill of exchange for Rs 10,000 is drawn by Sandy on Karan which is due after three months. Karan accepted the bill which is met at maturity and hence becomes the acceptor of the bill by putting his signature.
Here, Sandy is the drawer and Karan is the drawee. As the payment on maturity is received by Sandy so the payee will be Sandy.
ii) A bill of exchange for Rs 10,000 is drawn by Sandy on Karan which is due after three months. Karan accepted the bill. Thereafter Sandy endorsed the bill in favor of his creditor, Vikash. The bill is met at maturity.
So in this case, Sandy is the drawer, Karan is the drawee and Vikash is the payee as he received the amount at maturity.
Acceptance: Acceptance by the drawee is given on the face of the bill as-

Meaning of BOE:
In a business, in the case of credit sales, the payment is received after a certain period of time. In such a case the seller i.e. the creditor makes a credit note and the purchaser i.e. the debtor accepts the same by giving his acceptance by signing the instrument, to pay the amount of money mentioned to a certain person or the bearer of the instrument.
It is generally a negotiable instrument i.e. can be transferred from one person to another.
Features of Bill of Exchange.
- It is a written document.
- It is an unconditional order to pay.
- It must be signed by the maker of the bill i.e. the drawer.
- It must be properly stamped.
- The amount is payable either to a specified person or to his order or to the bearer.
- It contains an order to pay the amount mentioned in the instrument both in figures and words.
- The amount is to be paid either on the expiry of a fixed period from the date of the bill or on-demand.
See less

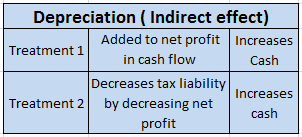

As per the companies act 2013, the rate of depreciation for cars/vehicles and their useful life is mentioned below They are categorized by the companies act as follows: when these car/ motor vehicles are owned with no intention to sell within the accounting period and are generally used to generateRead more
As per the companies act 2013, the rate of depreciation for cars/vehicles and their useful life is mentioned below
They are categorized by the companies act as follows:
Car/motor vehicles are considered as fixed tangible assets. Treatment of these cars/ motor vehicles is similar to those of other fixed assets. The depreciation will be shown as an expense in the profit and loss account and also the value of these assets will be adjusted in the balance sheet.
Explaining with a simple example: Mars.Ltd purchased a car for Rs 10,00,000, and use it for its official purpose. Its useful life as per act is taken as 6 years and the rate of depreciation as 31.23% as per the WDV method.
Therefore depreciation as per WDV is calculated as follows
Cost of car = Rs 10,00,000
Residual value = NIL
Rate of depreciation = 31.23%
depreciation for first-year = Rs (10,00,000 – NIL)*31.23%
= Rs 3,12,300
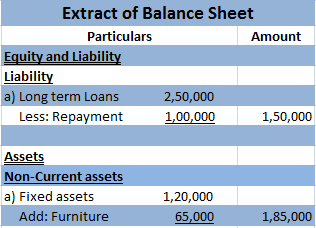
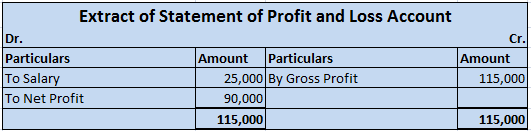
Calculated depreciation on this car will be shown in the profit and loss account as an expense and the same will be treated under the balance sheet every year. Here is the extract of profit and loss and the balance sheet for the above example.


See less