Introduction Working capital refers to the capital which is required by an enterprise to smoothly run its daily operations. It is the measure of the short-term liquidity of a business. Working capital is the total of the current assets of a business, net of its current liabilities. Working capitalRead more
Introduction
Working capital refers to the capital which is required by an enterprise to smoothly run its daily operations.
It is the measure of the short-term liquidity of a business.
Working capital is the total of the current assets of a business, net of its current liabilities.
Working capital = Current Assets – Current Liabilities
The working capital consists of cash, accounts receivable and inventory of raw materials and finished goods fewer accounts payable and other short-term liabilities.
Without a proper level of working capital, a business cannot maintain regular production and pay its creditors and expenses.
Hence, for proper management of working capital, it is divided into types:
- Permanent working capital
- Temporary working capital
I have discussed them below:
Permanent Working Capital
It is the fixed level or minimum level of working capital that an enterprise needs to maintain to ensure production at the normal capacity and pay for its daily expenses. It is independent of the level of production.
It is also known as fixed working capital.
By ‘permanent’, it does not mean that it will forever remain at the same level or amount but it may change if the overall production capacity changes. But such changes in permanent working capital are not often.
Temporary Working Capital
It is the level of working capital that depends upon the level of production of a business. It is the excess working capital over the permanent capital that is required to meet seasonal high demand.
It is also known as fluctuating working capital because it tends to change often depending on the level of production.
Temporary working capital is required when high production is required to meet seasonal demands.
For example, a bakery will need more working capital to meet the increased demand for cakes and pastry during Christmas season
Graph showing permanent and temporary working capital
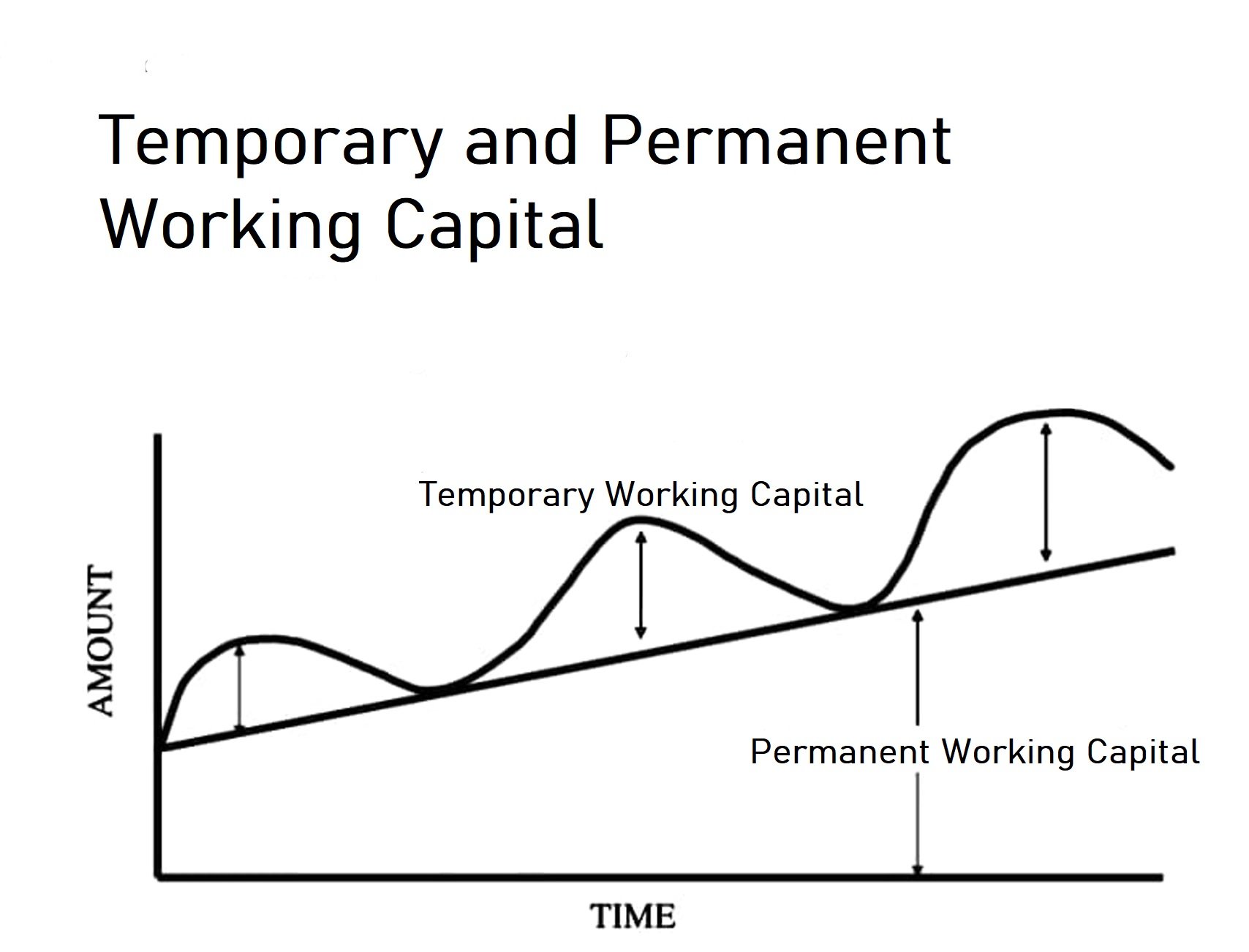
Here, the temporary working capital is fluctuating whereas the permanent working capital is gradually increasing with time.
See less
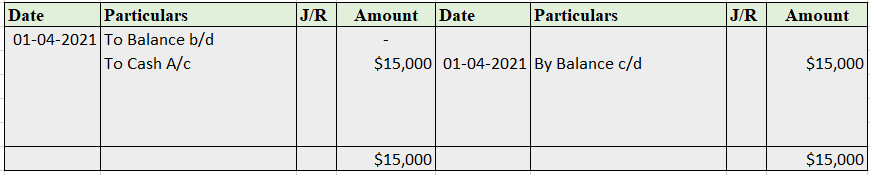
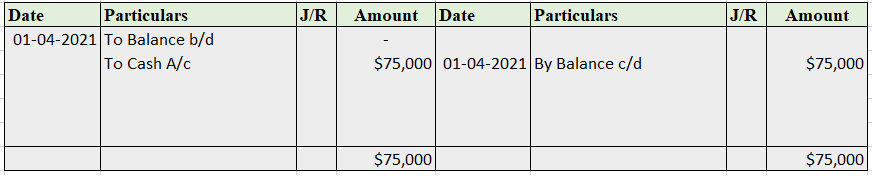
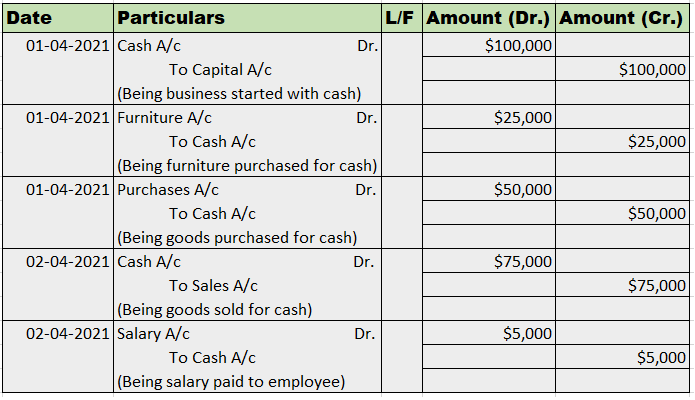
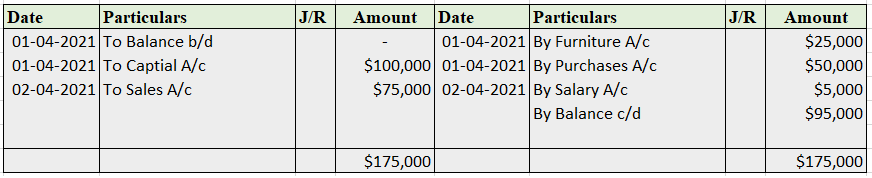
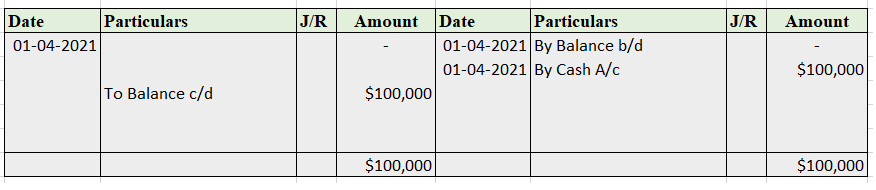
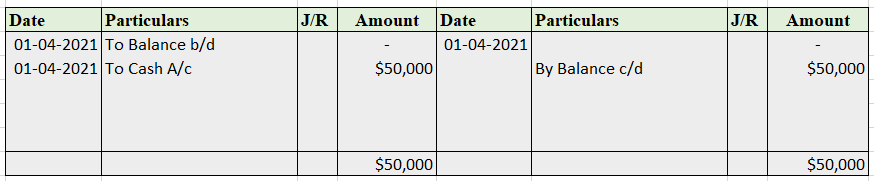
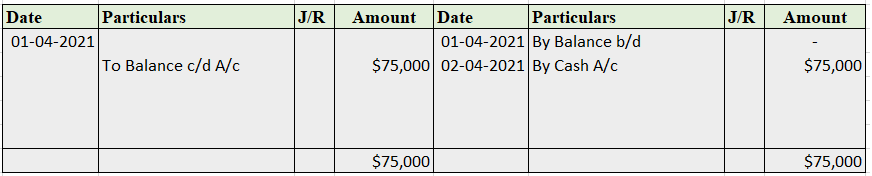
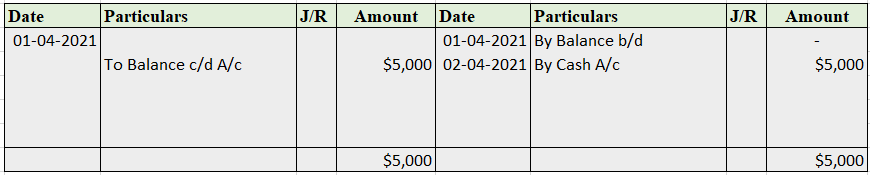
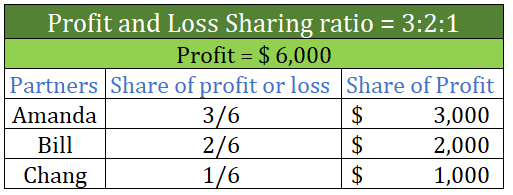
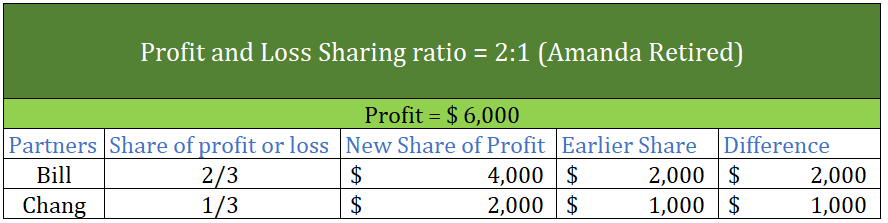
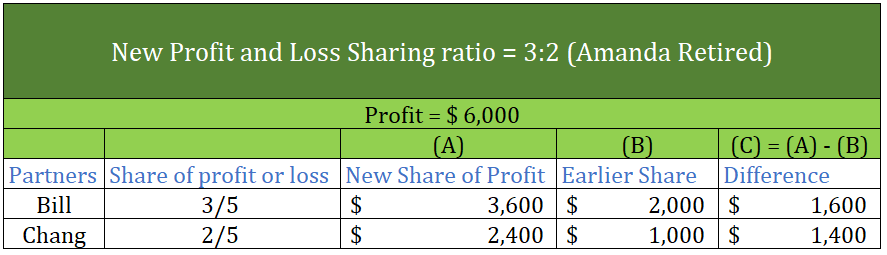
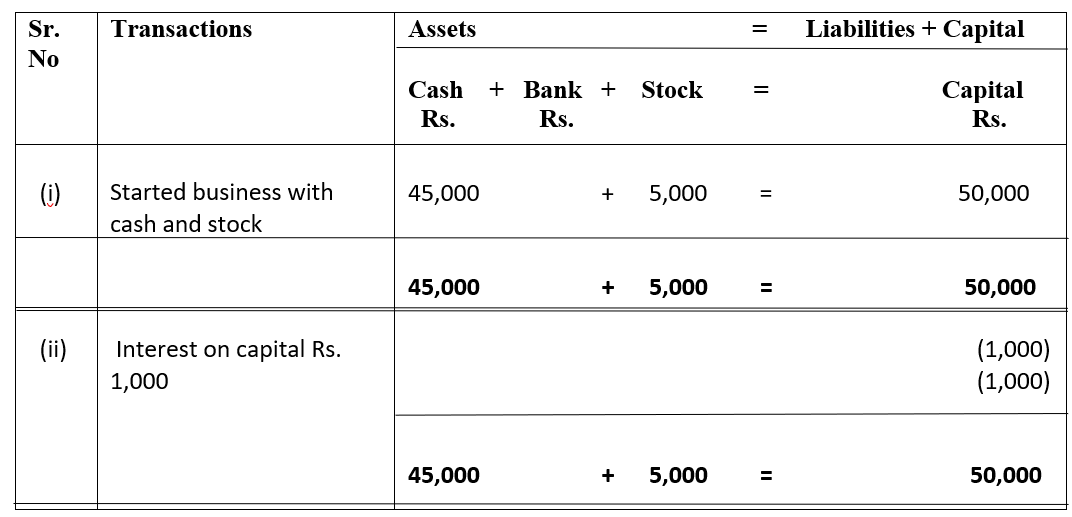
Partnership Firm Persons who have entered into a partnership with one another to carry on a business are individually called “Partners“; collectively called a “Partnership Firm”; and the name under which their business is carried on is called the “Firm Name” In simple words, A partnership is an agreRead more
Partnership Firm
Persons who have entered into a partnership with one another to carry on a business are individually called “Partners“; collectively called a “Partnership Firm”; and the name under which their business is carried on is called the “Firm Name”
In simple words, A partnership is an agreement between two or more people who comes together to run a business on a partnership deed, which is called a Partnership firm. A Partnership Deed is a written agreement between partners who are willing to form a Partnership Firm. It is also called a Partnership Agreement.
It has no separate legal entity which cannot be separated from the members. It is merely a collective name given to the individuals composing it. This means, a partnership firm cannot hold property in its name, and neither it can sue nor be sued by others.
Contents of a Partnership Deed
A Partnership Deed shall mainly include the following contents:
Types of Partners
The following are the various types o partners
Types of Partnership Firms
There are four types of partnership which are as below.
Essential characteristics of a partnership firm
See less