Definition Gross profit is the excess of the proceeds of goods and services rendered during a period over their cost, before taking into account administration, selling, distribution, and financial expenses. Gross profit and net profit are gross profit estimates of the profitability of a company. WhRead more
Definition
Gross profit is the excess of the proceeds of goods and services rendered during a period over their cost, before taking into account administration, selling, distribution, and financial expenses.
Gross profit and net profit are gross profit estimates of the profitability of a company.
When the result of this computation is negative it is referred to as gross loss
Formula :
Total Revenues – Cost Of Goods Sold
Net profit is defined as the excess of revenues over expenses during a particular period.
Net profit is to show the performance of the company.
When the result of this computation is negative it is called a net loss.
Net profit may be shown before or after tax.
Formula :
Total Revenues – Expenses
Or
Total Revenues – Total Cost ( Implicit And Explicit Cost )
Examples
Now let me explain to you by taking an example which is as follows :
In a business organization there were the following data given as purchases made Rs 73000, inventory, in the beginning, was Rs 10000, direct expenses made were Rs 7000, closing inventory which was Rs 5000, revenue from operation during the period was Rs 100000.
Then,
COST OF GOODS SOLD = Purchases + Opening Inventory + Direct Expenses – Closing Inventory.
= Rs ( 73000 + 10000+ 7000- 5000)
= Rs 85000
GROSS PROFIT = REVENUE – COST OF GOODS SOLD
= Rs ( 100000 – 85000 )
= Rs 15000
Now from the above question keeping the gross profit same if the indirect expenses of the organization are Rs 2000 and the other income is Rs 1000.
Then,
NET PROFIT = GROSS PROFIT – INDIRECT EXPENSES + OTHER INCOMES
= Rs ( 15000 – 2000 + 1000)
= Rs 14000
Treatment
Treatment of gross profit and net profit is given as follows :
Gross profit
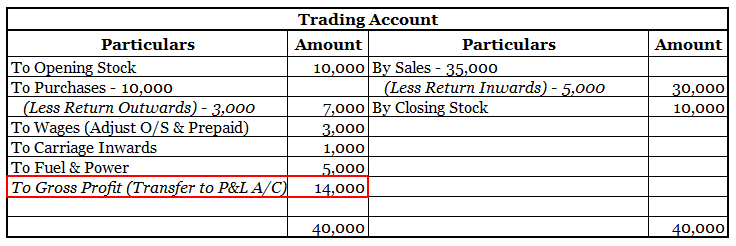
• Gross profit appears on the credit side of the trading account.
• Gross profit is located in the upper portion beneath revenue and cost of goods sold.
Net profit
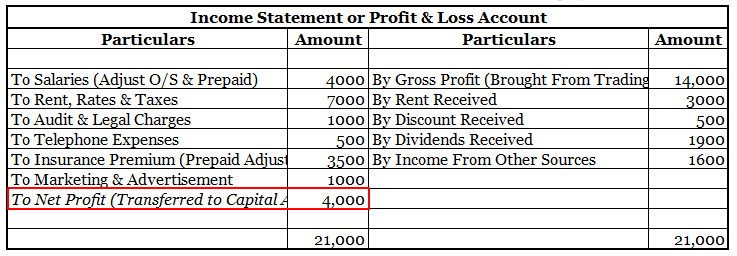
• Net profit appears on the credit side of the profit and loss account.
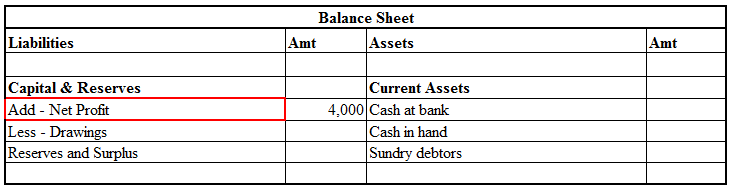
• It is treated directly in the balance sheet by adding or subtracting from the capital.
Here is an extract of the trading and profit/loss account and balance sheet showing GROSS PROFIT & NET PROFIT :

Definition A ledger may be defined as a book that contains, in a summarized and classified form, a permanent record of all transactions. Or in other words, we can say a group of accounts with different characteristics. It is also called the Principal Book of accounts. For example:- salary account, aRead more
Definition
A ledger may be defined as a book that contains, in a summarized and classified form, a permanent record of all transactions.
Or in other words, we can say a group of accounts with different characteristics.
It is also called the Principal Book of accounts.
For example:– salary account, and debtor account.
Sub- ledger it is defined as a group of accounts with common characteristics. And is a part of ledger accounts.
For example:- customer account, vendor account, etc.
The difference between a ledger and a sub-ledger is that ledger accounts control sub-ledger accounts whereas a sub-ledger is a part of the ledger account.
Features Of Ledger
Features Of Sub-Ledger
Utilities of ledger
The main utilities of a ledger are summarized as follows :
• Provides complete information about a particular account: Complete information relating to a particular account is available in one place in the ledger.
• Information on income and expenses: In the ledger, a separate account is maintained for each income and expense. The amount of total income and total expenses are known from the ledger accounts.
• Preparation of trial balance: Ledger helps in preparing trial balances which ensure arithmetical accuracy of the transaction recorded in the books of account.
• Helps in preparing final accounts: After preparing the trial balance, final accounts are prepared to know the profitability and financial position of the business.
Utilities of sub-ledger
The utilities of the sub-ledger are as follows :
• Track customer information: If a client has an outstanding credit debt or needs money refunded, a company can use a sub-ledger to verify the information quickly.
• Protect financial information: A sub-ledger allows a financial supervisor to isolate certain records so that employees can view only parts of the company’s financial information. This added level of security is important for large corporations.
• Create separate databases: Large companies usually process large amounts of financial data that may be too big for one database. Software programs organize this data into isolated files to calculate financial information in the general ledger of a business.
Conclusion
So here I conclude that a ledger is compulsory in the recording process whereas a sub-ledger is optional.
The ledger is used for preparing trial balance but the sub-ledger is not used for the same.
Sub ledger is controlled by the ledger.
The sub-ledger supports the transaction of each specific account indicated on the ledger.
See less