The correct option is C. Either Debit or Credit. Partner’s Current account is prepared when the capital account is of fixed nature. We know that partner’s capital account can be of fluctuating nature or fixed nature. In the case of fluctuating partner’s capital, all the transactions relating to theRead more
The correct option is C. Either Debit or Credit.
Partner’s Current account is prepared when the capital account is of fixed nature. We know that partner’s capital account can be of fluctuating nature or fixed nature.
In the case of fluctuating partner’s capital, all the transactions relating to the appropriation of profit, salary, commission, drawings, the introduction of capital, interest on capital etc. are passed through the partner’s capital account.
The balance of partner’s capital is generally credit but sometimes it may show debit balance indicating that the business owes to partner.
But when the partner’s capital account is of fixed nature, then separate partner’ current accounts are prepared. Through this account, all the transactions of revenue nature are passed like appropriation of profits, salary or commission paid to a partner, interest on capital and drawings. The balance of this account may be debit or credit.
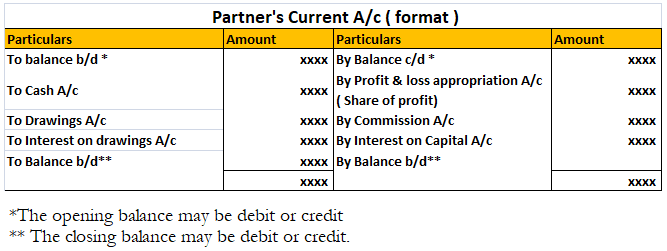
The debit balance means the partner has withdrawn a lot of amount as drawings in anticipation of profits. The credit balance means the partner owes to the business.
The partner’s capital shows a fixed amount as capital and its balance is affected only when additional capital is introduced or capital is withdrawn. The balance of this account is always credit.
The partner current account is prepared when the firm wants to show the revenue transactions and capital transactions related to the partner ‘capital separately.
See less
Secondary books of accounts are most commonly known as subsidiary books of accounts or day books. They are prepared to record the same type of journals in an ordered manner in a special book. They are nothing, but special journals. Recording all the journals entries in a single journal and these posRead more
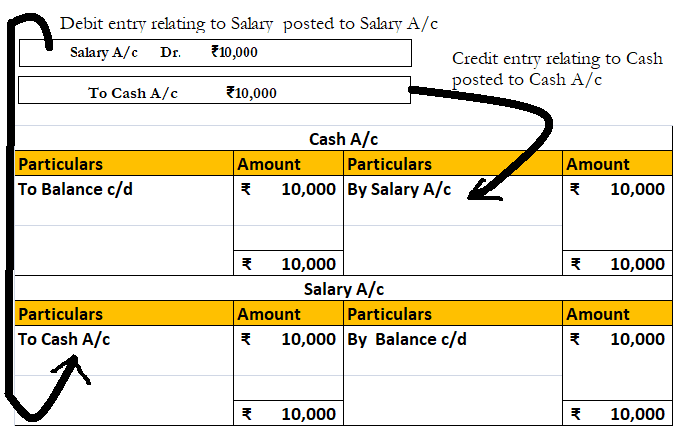
Secondary books of accounts are most commonly known as subsidiary books of accounts or day books. They are prepared to record the same type of journals in an ordered manner in a special book. They are nothing, but special journals.
Recording all the journals entries in a single journal and these posting them to different ledgers can be very difficult if the number of transactions is huge.
So, recording the same type of transactions in a special journal proves to be useful in efficient book-keeping and also information retrieval.
There are eight subsidiary books:
Also, there are a few more things to know:-
- Subsidiary books may look like ledger accounts but they are not ledgers. Ledgers are books of final entry and subsidiary books can be said to be the book of intermediate entry and are not but special journals.
- Once transactions are recorded in the subsidiary books, they are then posted to the ledgers.
See less