A revaluation Account is an account created to record the changes in the value of assets and liabilities during: Change in profit sharing ratio Admission of a partner Retirement of a partner Death of a partner The realization Account is prepared to sell assets and pay liabilities in the event of theRead more
A revaluation Account is an account created to record the changes in the value of assets and liabilities during:
- Change in profit sharing ratio
- Admission of a partner
- Retirement of a partner
- Death of a partner
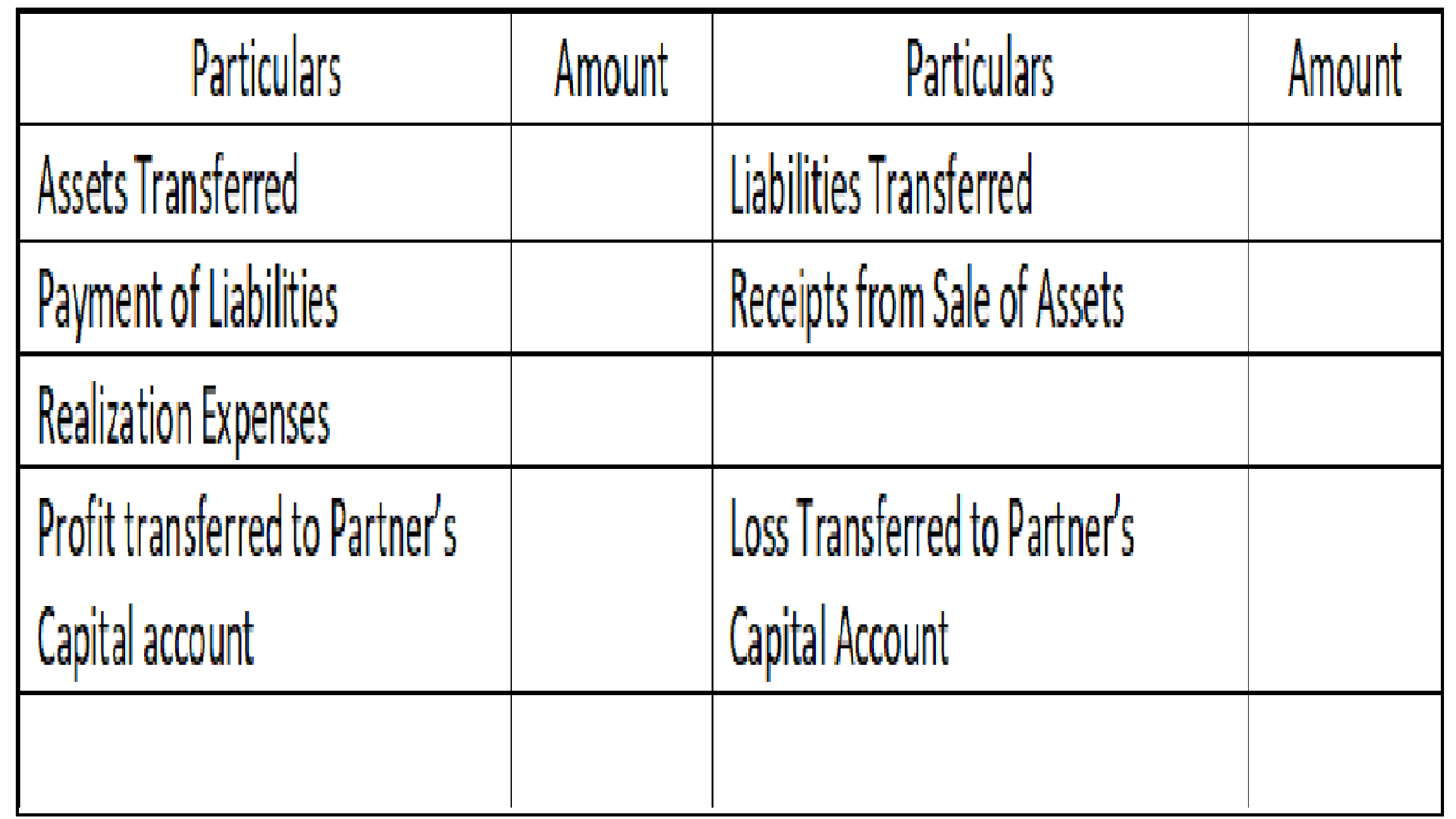
The realization Account is prepared to sell assets and pay liabilities in the event of the dissolution of the firm.
Revaluation Account is prepared for dissolution of the partnership while Realization Account is prepared for dissolution of the partnership firm.
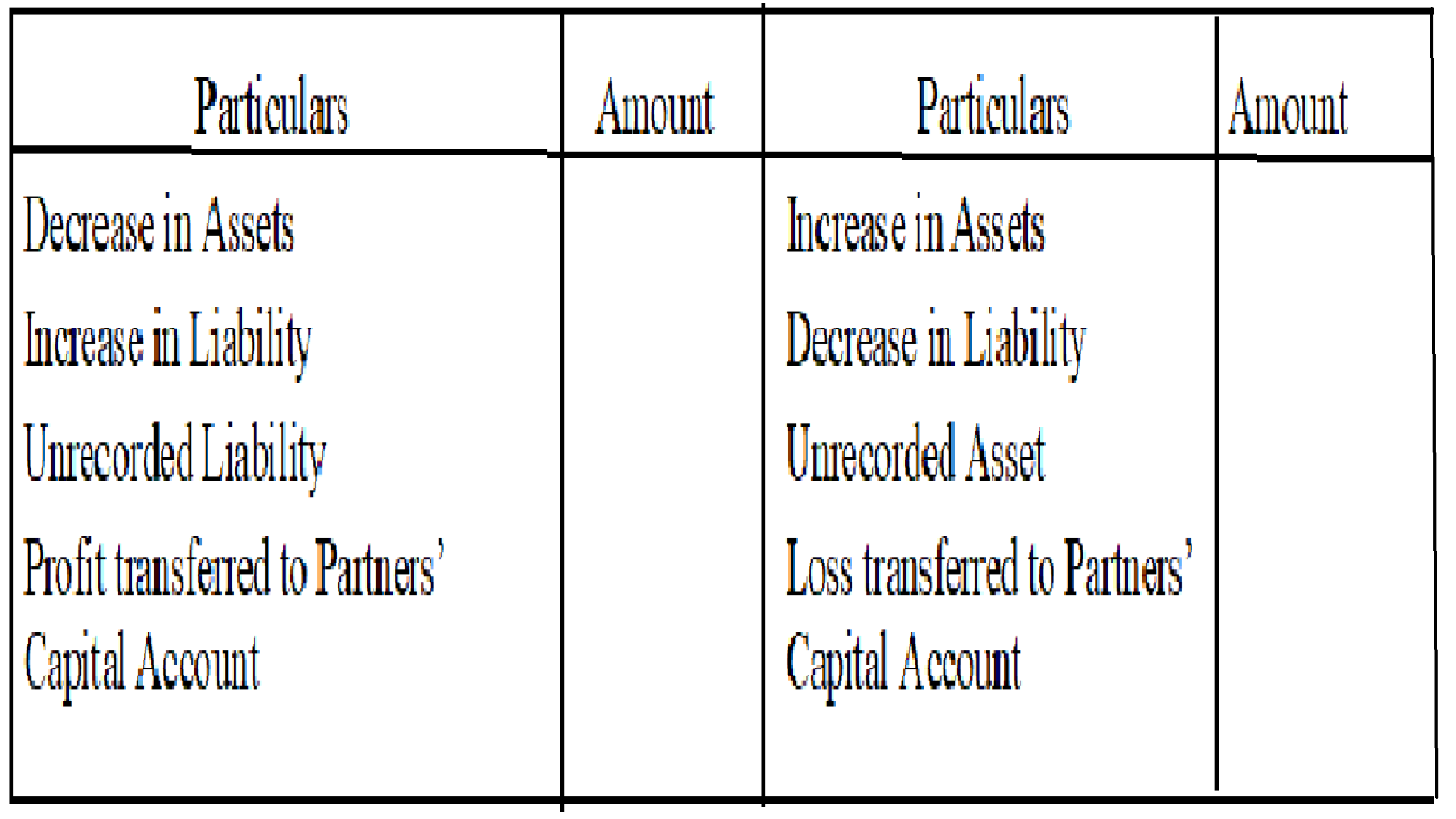
The increase or decrease in the value of assets and liabilities is transferred to the Realisation Account and the gain or loss thereof is transferred to the old partner’s capital account.
- A decrease in Assets and an Increase in Liabilities is debited since it is a loss for the firm and all the losses are debited.
- An increase in Assets and a Decrease in Liabilities is credited since it is gained for the firm and all the profits are credited.
Format of Revaluation Account will be:
Format of Realization Account will be:
The difference between Realisation and Revaluation Account is:
| Revaluation Account | Realization Account |
| Prepared to record changes in assets and liabilities | Prepared to record sale of assets and payment of liabilities |
| Prepared at the time of dissolution of the partnership | Prepared at the time of dissolution of partnership firm |
| Assets and liabilities still exist in the books only their values change | Assets and liabilities do not exist in the books of the firm |
| This account contains only those assets and liabilities that are to be revalued. | This account contains all the assets and liabilities of the firm. |
| A revaluation Account can be prepared any number of times during the lifetime of the firm. | The realization Account is only made once during the dissolution of the firm. |
| The gain or loss during revaluation is transferred to the old partner’s capital accounts. | The gain or loss during realization is transferred to the capital account of all the partners. |
See less


Before we jump in the concept of valuation of Goodwill, let us first understand the meaning of term “Goodwill”. Goodwill is an Intangible asset of the business. As the definition of Intangible asset, Goodwill cannot be seen or felt. In simple words it is business’s worth or its reputation earned oveRead more
Before we jump in the concept of valuation of Goodwill, let us first understand the meaning of term “Goodwill”.
Goodwill is an Intangible asset of the business. As the definition of Intangible asset, Goodwill cannot be seen or felt. In simple words it is business’s worth or its reputation earned over a period of time.
Calculation of value of the goodwill in monetary terms is done at the time of merger or acquisition of the business. Goodwill is often applied to businesses which are earning large number of profits, have crucial corporate links and large customer/client base.
Self-earned goodwill is never shown in monetary terms in business’s own balance sheet while goodwill which is purchased is shown in the asset side of the balance sheet of the buyer business.
Following are the methods under which goodwill can be valued:
Goodwill = Average Profit x No. of Years Purchase
Goodwill = Weighted Average Profit x No. of Years Purchase
Where,
Weighted Average Profit = Sum of Profits multiplied by weights / Sum of Weights
Formula for the same would be as follows:
Goodwill = Super Profits x (100/Normal Rate of Return)
Formula for the same would be as follows:
Goodwill = Super Profit x Discounting Factor
Formula for the same would be as follows:
a. Average Profit Capitalization Method –
Goodwill = [Average Profit / Normal Rate of Return x 100] – Capital Employed
b. Super Profit Capitalization Method –
Goodwill = Super Profits x (100/ Normal Rate of Return)
See less