Land in the balance sheet The land is an asset and hence it is shown on the asset side of the balance sheet. On the asset side of the balance sheet, the land is stated under the heading long-term assets. Balance Sheet (for the year…) Explanation The land is a fixed asset and is supposed not to be caRead more
Land in the balance sheet
The land is an asset and hence it is shown on the asset side of the balance sheet.
On the asset side of the balance sheet, the land is stated under the heading long-term assets.
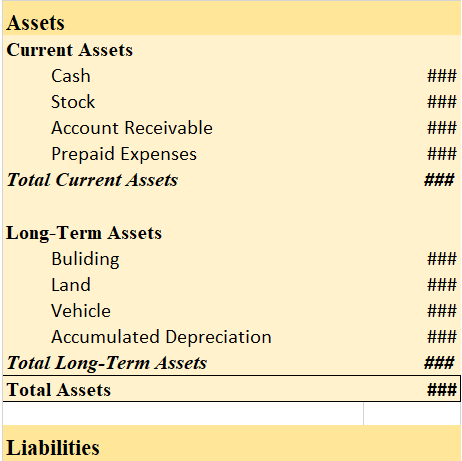
Balance Sheet (for the year…)
Explanation
The land is a fixed asset and is supposed not to be cashed, consumed, last, sold, or written off within one accounting year and is purchased for long-term use. The fixed assets are also called non-current assets and the reason behind it is that current assets are easily converted into cash within one year and they are not.
- The sole purpose of buying fixed assets like the land is that they are planned to be used for the long term in order to generate income.
- Examples of fixed assets – Land, buildings, furniture, plants & equipment, etc.
- Also called non-current assets and capital assets.
Why is it shown on the asset side?
The land is an asset, although it is not depreciable it is still considered to be an asset because just like other assets the business spends its own money to acquire it, and it gives them a long-term benefit while reselling it.
Therefore, the land is shown on the asset side under the fixed asset heading.
See less

The land is a fixed asset and is treated as a long-term asset account. Explanation The land is a fixed asset which is also referred to as a long-term asset. The fixed assets are those assets that are not expected to be cashed, consumed, last, sold, or written off within one accounting year and areRead more
The land is a fixed asset and is treated as a long-term asset account.
Explanation
The land is a fixed asset which is also referred to as a long-term asset.
The fixed assets are those assets that are not expected to be cashed, consumed, last, sold, or written off within one accounting year and are purchased for long-term use. The fixed assets are also called non-current assets and the reason behind it is that current assets are easily converted into cash within one year and they are not.
Fixed assets are planned by the company to be used for the long term in order to generate income.
Example- Land, building, furniture, plants & equipment, etc.
Why is land an asset?
Although the land is not depreciated, it is still considered to be an asset because just like other assets the business spends its own money to acquire it.
It can also be used by the business for different operations and it doesn’t create any liability for the business. Instead, reselling the land after a few years can help the company earn a huge margin of profit.
Land in the balance sheet
On the asset side of the balance sheet, the land is stated under the heading long-term assets.
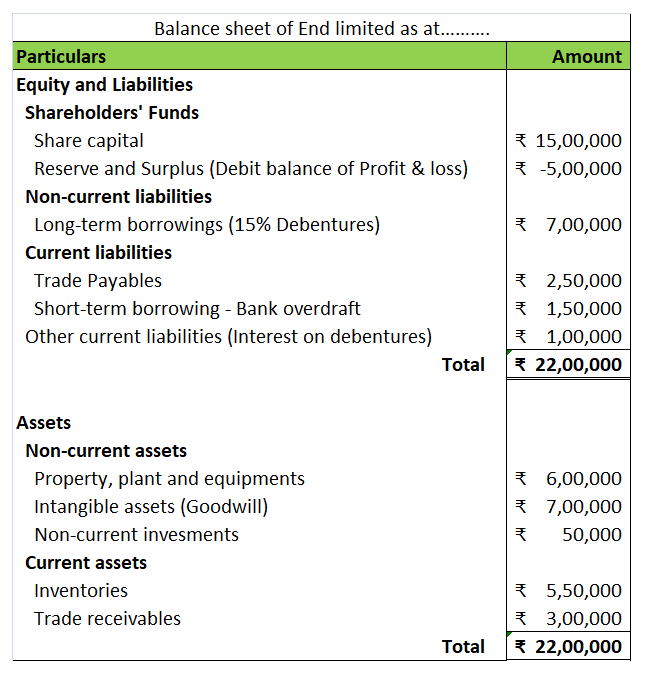
Balance Sheet (for the year…)
Therefore, the land is a fixed asset and is treated as a long-term asset account.
See less