Goods and services tax (GST) is an indirect tax that was introduced in place of other indirect taxes like value-added tax, service tax, purchase tax, etc. It was introduced to ensure that only one tax would be applicable all over India. Reverse Charge is a mechanism where the liability to pay tax onRead more
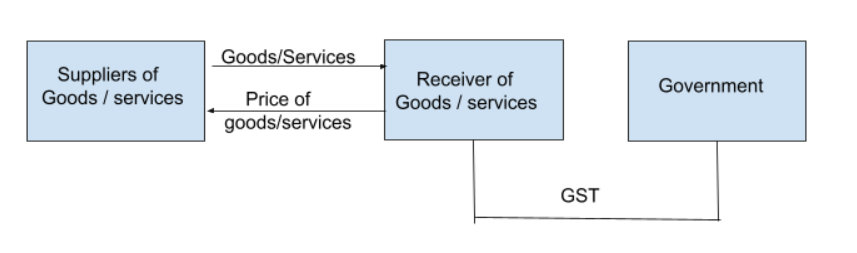
Goods and services tax (GST) is an indirect tax that was introduced in place of other indirect taxes like value-added tax, service tax, purchase tax, etc. It was introduced to ensure that only one tax would be applicable all over India. Reverse Charge is a mechanism where the liability to pay tax on goods and services lies on the recipient instead of the supplier.
APPLICABILITY
Reverse charge is applicable when:
- It is specified by the CBIC for the supply of certain goods and services.
- Goods are supplied by an unregistered dealer to a registered dealer.
- There is a supply of services through an E-commerce operator.
TIME OF SUPPLY
As per reverse charge in the case of goods, the time of supply is the earliest of the three:
- Date of receipt of goods
- Date of payment
- The date is immediately after 30 days from the date of issue of invoice from the supplier.
For example, If goods were received by the supplier on 15th June, and the date of the invoice was on 3rd July but the date of entry in the books of the receiver was 25th June, then the time of supply of goods would be on 15th June.
As per reverse charge in the case of services, the time of supply is the earliest of the two:
- Date of payment.
- Date immediately after 60 days from the date of issue of invoice by the supplier.
For example, if the date of payment of services provided was on 16th July, and the date of issue of the invoice was on 15th May ( 60 days from 15th May is 14th July), then the time of supply of services would be 14th July.
See less
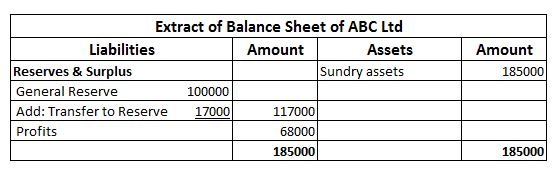
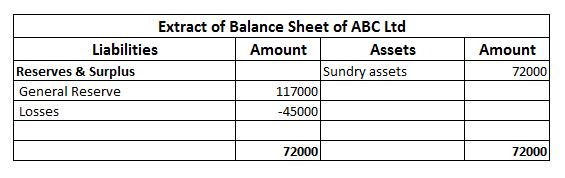
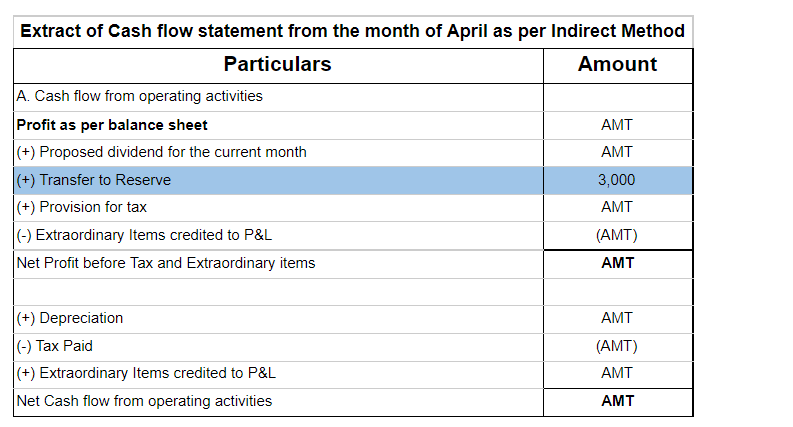


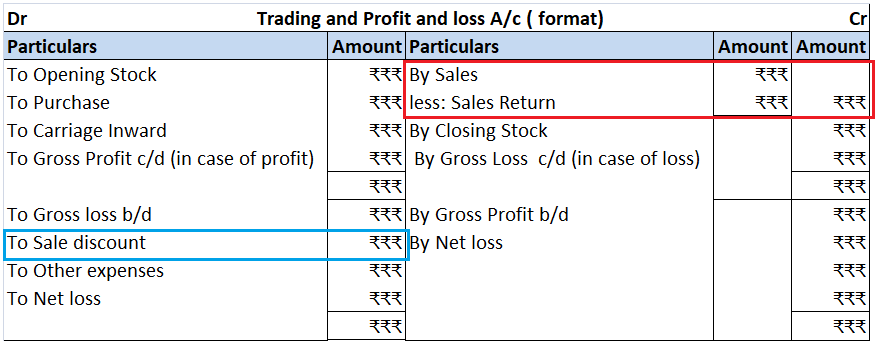
When a firm grants an extra amount of reward to its employees based on their performance, it is termed a bonus. An accrued bonus is contingent on performance. Bonus accruals are recorded in the books so that inaccuracies can be avoided in the financial statements. Such bonuses may be given as a singRead more
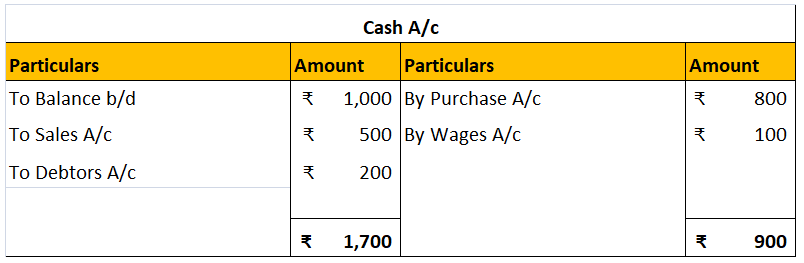
When a firm grants an extra amount of reward to its employees based on their performance, it is termed a bonus. An accrued bonus is contingent on performance. Bonus accruals are recorded in the books so that inaccuracies can be avoided in the financial statements.
Such bonuses may be given as a single flare amount or as a percentage of their salaries. These bonuses can be given quarterly or annually or in any manner in which the firm decides.
If the bonus is accrued to its employees at 5% of their salary of Rs 30,000, then the accrual bonus can be shown in the journal as follows:
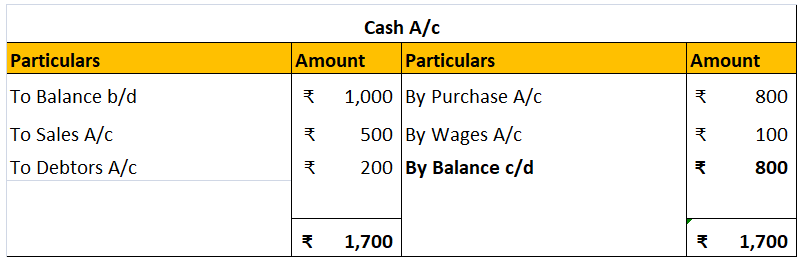
When it is time to pay such bonus amounts to its employees, then they can be journalised as:
In this case, the accrued bonus liability is eliminated and hence debited because according to the rule of accounting, “ Decrease in liability is debited” whereas cash account is credited since “the decrease in the asset is credited.”:
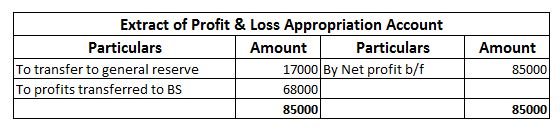
Failing to accrue these bonuses will lead to an overstatement of revenues in the financial statements and hence result in inaccurate data. If employees do not meet the required performance targets, then a bonus will not be given and hence the entries will be reversed.
See less